| [1] 樊明文.牙体牙髓病学[M].2版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2003:56. [2] 潘悦萍,夏文薇.声波充填术与分层充填术对树脂微渗漏的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2015,31(12):1203-1205. [3] 李荣亮.Z250复合树脂修复牙体楔状缺损的临床效果观察[J].中国实用医药,2013,8(26):37-38. [4] 林红.口腔材料学[M].2版.北京:北京大学医学出版社, 2013:141. [5] 甘建华.不同口腔修复材料生物相容性及3种材料充填恒磨牙邻面龋的临床验证[J].中国医学创新, 2013,10(33): 127. [6] 吕雨霏,郭笑,仪虹,等.SonicFill超声流体后牙树脂充填后的微渗漏研究[J].中国医刊,2015,65(10):60-62. [7] Gurtu A.Sonicfill: The Breakthrough in the Evolution of Direct Composite Delivery; dr vineet vinayak. Journal of Dental Sciences & Oral Rehabilitation, 2013:4-6. [8] Giachetti L.A new method for direct composite restoration of the posterior teeth.Dental Tribune Middle East & Africa Edition,2015:1-2. [9] Nicoleta Ilie.Effect of sonic-activated resin composites on the repair of aged substrates: an in vitro investigation.Clin Oral Invest.2014;18:1605-1612. [10] Manhart J,Ilie N.Bulk Fill Komposite Vorund Nachteile. Wissen Kompakt,2015:27-42. [11] Bucuta S,Llie N.Light transmittance and micro-mechanical proper-ties of bulk fill vs. conventional resin based composite.Clin Oral Investiq. 2014;18(8):1991-2000. [12] Garcia D,Yaman P,Dennison J,et al.Polymerization Shrinkage and Depth of Cure of Bulk Fill Flowable Composite Resins.Oper Dent. 2014;39(4): 441-448. [13] Tarle Z,Attin T,Marovic D,et al.Influence of irradiation time on subsurface degree of conversionand microhardness of high-viscosity bulk-fill resin composites.Clin Oral Investig.2015;19(4):831-840. [14] 崔庆超.不同盖髓材料对大鼠磨牙牙髓组织病理学改变的实验观察[D].河北医科大学,2014. [15] Esmeraldo MR,Carvalho MG,Carvalho RA,et al. Inflammatory effect of green propolis on dental pulp in rats.Braz Oral Res.2013;27(5):417-422. [16] 张淳.不同龋深状态下人成牙本质细胞的凋亡及凋亡蛋白Bcl-2,Bax的表达[D].河北医科大学,2013. [17] Smith AJ.Pulpal responses to caries and dental repair. Caries Res.2002; 36(4):223-232. [18] 陈少华.光固化复合树脂在牙体病治疗中的疗效观察[J].中国医学创新,2015,12(29):127-129. [19] 阮丹平,张丁华,吴春云,等.LED固化灯光照强度对光固化复合树脂聚合收缩的影响[J].口腔材料器械杂志, 2013, 22(1):28-32. [20] 于世凤.口腔组织病理学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2007: 30,57,61-62. [21] Bjorndal L,Darvann T.A light microscopic study of odontoblastic and non-odontoblastic cells involved intertiary dentinogenesis in well-defined cavitated carious lesions.Caries Res.1999;33(1):50-60. [22] Goldberg M,Smith AJ.Cells and extracellular matrices of dentin and pulp: a biological basis for repair and tissue engineering.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2004;15(1): 13-27. [23] Bjornal L,Kidd EA.The treatment of deep dentine caries lesions.Dent Update. 2005;32(7): 402-404, 407-410,413. [24] 雷丽珊.Filtek(TM)Z350纳米复合树脂生物相容性的实验研究[D].福建医科大学,2010. [25] 于清华,潘杏兰,许小鸿.大鼠实验性牙髓炎的组织病理学观察[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2006,56(6):471-473. [26] 童建斌,曾乐平,陈旦,等.明胶墨汁灌注展示大鼠视网膜血管的方法[J].第三军医大学学报, 2007,29(21):2031-2033. [27] 毕振宇.Wistar大鼠咬合创伤模型牙周与颞下颌关节毛细血管铸型研究[D].南方医科大学,2014. [28] 张淳.不同龋深状态下人成牙本质细胞的凋亡及凋亡蛋白Bcl-2,Bax的表达[D].河北医科大学,2013. [29] 张举之.口腔内科学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 1998:41-42. [30] 王燕.光固化复合树脂充填修复失败的相关因素及预防[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(24):783-784. [31] 左奇伟,万炜,周小兵,等.低分子右旋糖酐及明胶加墨汁灌注冠状窦的研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2009,18(13): 1467-1468. [32] Xue S,Gong H,Jiang T,et al.Indian-ink perfusion based method for reconstructing continuous vascular networks in whole mouse brain.PLoS One. 2014;9(1): e88067. [33] Isachenko V,Isachenko E,Sanchez R,et al. Cryopreservation of whole ovine ovaries with pedicles as a model for human: parameters of perfusion with simultaneous saturations by cryoprotectants.Clin Lab.2015;61(3-4):415-420. [34] Isachenko V,Rahimi G,Dattena M,et al.Whole ovine ovaries as a model for human: perfusion with cryoprotectants in vivo and in vitro.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:409019. [35] Isachenko V,Isachenko E,Peters D,et al.In vitro perfusion of whole bovine ovaries by freezing medium: effect of perfusion rate and elapsed time after extraction.Clin Lab.2013;59(9-10):1159-1166. [36] Alber MT,Brown MP,Merritt KA,et al.Vascular perfusion of the dorsal and palmar condyles of the equine third metacarpal bone.Equine Vet J. 014;46(3):370-374. [37] Li LY,Zhang LJ,Jia JY,et al.Does dynamic immobilization reduce chondrocyte apoptosis and disturbance to the femoral head perfusion?Int J Clin Exp Pathol.2013;6(2):212-223. [38] Pazzaglia UE,Congiu T,Marchese M,et al.Structural pattern and functional correlations of the long bone diaphyses intracortical vascular system: investigation carried out with China ink perfusion and multiplanar analysis in the rabbit femur.Microvasc Res. 2011;82(1): 58-65. [39] 宋玫侠,王丽,李上.改良墨汁明胶灌注法与胶原蛋白酶消化法在大鼠视网膜新生血管形态显示中的对比研究[J].眼科新进展,2015,36(2):129-131. |
.jpg)



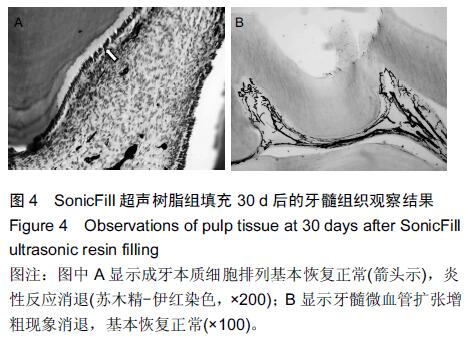
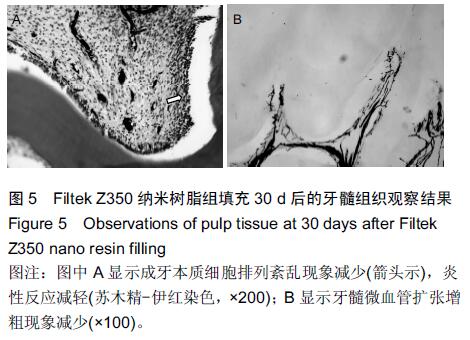
.jpg)