中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (14): 2086-2091.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.14.016
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
自体外周血干细胞局部注射联合腔内介入治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变
顾 露1,张姝梅1,于 翔1,杨 毅2
- 四川省医学科学院•四川省人民医院,1介入中心,2内分泌科,四川省成都市 610072
Autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation combined with percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for diabetic lower extremity vascular disease
Gu Lu1, Zhang Shu-mei1, Yu Xiang1, Yang Yi2
- 1Intervention Center, 2Department of Endocrinology, Medical Science Academy of Sichuan & People’s Hospital of Sichuan, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
外周血干细胞:正常情况下,存在于外周血的干/祖细胞的含量占单个核细胞的0.01%-0.1%,相当于骨髓的1%-10%,动员后外周血单个核细胞中CD34+细胞数及粒细胞巨噬细胞集落生成单位均明显高于骨髓。迄今已发现多聚阴离子化合物(如硫酸葡聚糖)、糖皮质激素、细菌内毒素、抗肿瘤药物、四氢叶酸以及造血生长因子等均能有效地动员骨髓和其他部位的造血干/祖细胞进入外周血。
踝肱指数:是血管外科最常用、最简单的一种检查方法,通过测量踝部胫后动脉或胫前动脉以及肱动脉的收缩压,可得到踝部动脉压与肱动脉压之间的比值。正常人休息时踝肱指数的范围为0.9-1.3。
背景:研究表明外周血干细胞具有高度分化潜能,可分化成血管内皮细胞,促进血管再生,改善侧支循环,从而达到治疗肢体缺血的目的。
目的:观察糖尿病下肢血管病变患者腔内治疗结合自体外周血干细胞移植的临床效果。
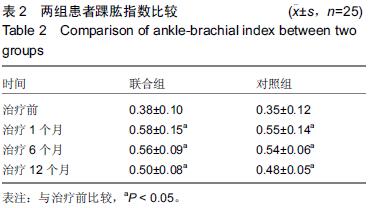
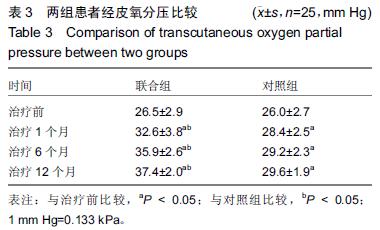
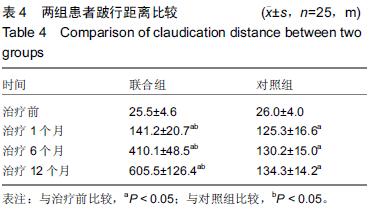
方法:收集2011年3月至2014年12月住院治疗的糖尿病下肢血管病变患者50例,其中25例采取腔内治疗和自体外周血干细胞移植(联合组),另外25例只采取腔内治疗(对照组)。所有患者于治疗后1,6,12个月随访,记录患肢疼痛、冷感等主观评分,测定踝肱指数、经皮氧分压、跛行距离等客观指标。
结果与结论:①两组患者治疗后踝肱指数均明显增加,尤其是治疗后1个月时增加显著,治疗后6,12个月有所下降,但与治疗前比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。治疗后1,6,12个月时两组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②两组患者治疗后经皮氧分压、跛行距离也明显增加,治疗后1,6,12个月与治疗前比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),治疗后1,6,12个月时联合组经皮氧分压、跛行距离高于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③治疗后12个月内患肢痛感和冷感均有不同程度改善,联合组改善更明显;④外周血干细胞采集过程中出现低钙血症3例,移植后出现发热2例,局部渗血3例,对症治疗后好转;⑤结果表明,糖尿病下肢血管病变患者行腔内治疗结合自体外周血干细胞移植加速患肢侧支循环的建立,从而减轻患肢缺血症状,因此能取得比单独采取腔内治疗更好的临床效果。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-3537-6537(顾露)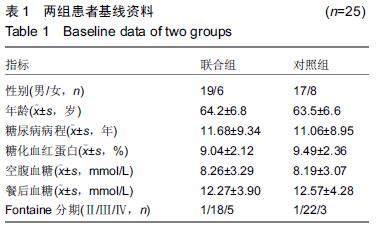
.jpg)