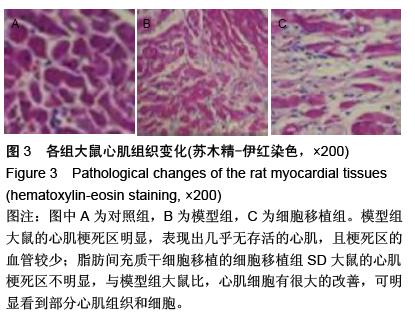
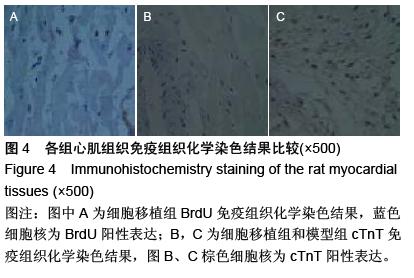
| [1] Groopman JE, Molina JM, Scadden DT. Hematopoietic growth factors. Biology snd clinical applications. N Engl J Med. 1989;321(5):1449.[2] 吴兆苏,赵冬.世纪之交的心血管流行病学和人群防治研究[J].中华心血管病杂志,1998,2(9):3-4. [3] 曹月娟,许静,付乃宽,等.干细胞治疗年龄相关性心肌梗死研究进展[J].天津医药,2010,38(7):635-637[4] 吴世凯,丁长才,柏芸,等.成体干细胞临床应用研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2010,10,(14):2763-2767.[5] 施志雄.骨髓干细胞移植治疗急性心肌梗死研究进展[J].医学信息:中间刊,2011,24(5):2015-2016.[6] 商保军,白炎亮.移植自体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗急性心肌梗死[J].中国实用医药,2010,5(15):120-121.[7] 周瑶,褚海涛,史记.干细胞治疗缺血性心脏病的临床价值[J].中医临床研究,2011,3(13):115-116.[8] 汤成春.心脏自身干细胞的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(19):3560-3564.[9] 晏凯利,陈苏,刘汉华.自体骨髓干细胞动员对急性心肌梗死患者心功能的影响[J].华中医学杂志,2008,32(5): 335-337.[10] 刘德峰,刘建平.骨髓间质干细胞移植与心肌再生[J].岭南心血管病杂志,2010,16(1):74-75.[11] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见.2006-09-30.[12] Olivetti G, Capasso JM, Meggs LG, et al. Cellular basis of chronic venrtiuclar remodeling after myoeardial inafrction in rast. Cire Res. 1991:68(11):856-869.[13] 陆东风,吴昊,黄璟,等.新生SD大鼠心脏干细胞的体外分离培养与鉴定[J].南方医科大学学报,2006(11):97-100.[14] Strauer BE, Brehm M, Zeus T, et al. Repair of infarcted myocardium by autologous intracoronary mononuclear bone marrow cell transplantation in humans. Circulation. 2002;106(15):1913-1918.[15] Makino S, Fukuda K, Miyoshi S, et al. Cardiomyocytes can be generated from marrow stromal cells in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1999;103(5):697-705.[16] KadivarM, Khatami S, Mortazavi Y, et al. In vitro cardiomyo genic potential of human umbilical vein derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;340(2):639-647.[17] Cheng F, Zou P, Yang H, et al. Induced differentiation of human cord blood mesenchymal stem progenitor cells into cardiomyocyte-like cells in vitro. Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.2003;23(2):154.[18] 罗凯,单根法,钟兹,等.脐血间充质干细胞肌源件诱导分化的研究[J].上海第二医科大学学报,2005,25(2):134-137.[19] Huang JL, Yang SX. Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord into cardiomyocytes. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuangkangfu. 2008;12(47):9367-9370.[20] 冯应君,汤天军.脐带血干细胞诱导分化为心肌样细胞电生理特性的实验研究[J].实用医学杂志,2007,23(5): 613-616.[21] Gang EJ, Jeong JA, Hong SH, et al. Skeletal myogenic differentiation 0f mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human umbilical cord blood. Stem Cells. 2004; 22(34): 617-624.[22] Siepe M, Akhyari P, Lichtenberg A, et al. Stem cells used for cardiovascular tissue engineering. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;34(2):242-254.[23] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem ceils. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(4):4279-4295.[24] Mizuno H, Zuk PA, Hu M, et al. Myogenic differentiation by human processed lipoaspirate cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1999;109(8):199-209.[25] Rangappa S, Fen C, Lee EH, et al. Transformation of adult mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the fatty tissue into cardiomyocytes. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003; 75(7):775-779.[26] Winter A. Breit S, Parsch D, et al. Cartilage-like gene expression in differentiated human stem cell spheroids: a comparison of bone marrow-derived and adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48(1):418-429.[27] Safford KM, Hicok KC, Safford SD, et al. Neurogenic differentiation of murine and human adipose-derived stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002; 294(31):371-379.[28] Ashjian PH, Elbarbary AS, Edmonds B, et al. In vitro differentiation of human processed lipoaspirate cells into early neural progenitors. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2003;111(21):1922-1931.[29] Guo H, Fang B, Zhao RC, et al. Hemangioblastic characteristics of fetal bone marrow-derived FlkI(+)CD31(-)CD34(-)cells. Exp Hematol. 2003; 31(31):650-658.[30] Bai X, Yan Y, Song YH. et al. Both cultured and freshly isolated adipose tissue-derived stem cells enhance cardiac function after acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 2010;31(2):489-501.[31] Shi Q, Rafii S, Wu MH, et al. Evidence for cicrulating bone morrow-derived endohtelial cells. Blood. 1998; 92(1):362-367.[32] Ferrari G, Cusella De Angelis G, et al. Muscle regeneration by bone Marrow-derived myogenic progenitors. Seinece. 1998;279(45):1528-1530.[33] Brazelotn TR, Rossi FM, Keshet Gl, et al. Blua for marrow to brain: expression of neuronal phenoytpes in dault mice. Seience. 2000;290(37):1775-1779.[34] Petersen BE, Bowen WC, Petrene KD, et al. Bone marrow as a poetntial source of hepatic oval cells. Science. 1999;284(11):1168-1170.[35] Christopher RR, Rodney RL, Bernt RA, et al. Turning brain into blood: a hematopoietic fate adopted by adult neural stem cells in vivo. Science. 1999;283(11): 534-537.[36] Buarwnald E, Bristow MR. Congestive heart failuer: fifty years of progerss. Cicrulation. 2000;102(32): IV14-IV23.[37] Beltrami AP, Urbanek K, Kajstura J, et al. Evidenee that human cardiac myoeytes divide after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(2):1750-1757.[38] Gronthos S, Franklin DM, Leddy HA, et al. Surface protein characterization of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. Cell Physiol. 2001; 189(9):54-63. |
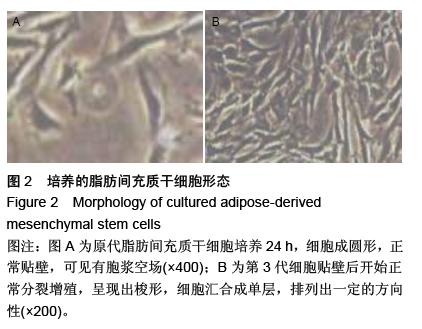
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)