| [1] Burke AP, Virmani R. Pathophysiology of acute myocardial infarction. Med Clin North Am. 2007;91(4):553-572.
[2] Devlin RJ, Henry JA. Clinical review: Major consequences of illicit drug consumption. Crit. Care. 2008;12(1):202-202.
[3] Taghaddosi M, Dianati M, Fath Gharib Bidgoli J, et al. Delay and its Related Factors in Seeking Treatment in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. ARYA Atherosclerosis. 2010;6(1):35-41.
[4] Ellis SG, Tendera M, De Belder MA, et al. Facilitated PCI in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction. New Engl J Med. 2008;358(21):2205-2217.
[5] Lukenda J, Biocina-Lukenda D. Stent, endovascular prosthesis, net or strut? What would British dentist Charles Stent (1807-1885) have to say on all this? Lijec Vjesn. 2009; 131(1-2):30-33.
[6] Kim MS, Dean LS. In-stent restenosis. Cardiovasc Ther. 2011; 29(3):190-198.
[7] Holmes DR, Kereiakes DJ, Garg S, et al. Stent thrombosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(17):1357-1365.
[8] Mauri L, Hsieh W H, Massaro JM, et al. Stent Thrombosis in Randomized Clinical Trials of Drug-Eluting Stents. New Engl J Med. 2007;356(10):1020-1029.
[9] Palmerini T, Benedetto U, Biondi-Zoccai G, et al. Long-Term Safety of Drug-Eluting and Bare-Metal Stents: Evidence From a Comprehensive Network Meta-Analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;65(23):2496-2507.
[10] Amsterdam EA, Wenger NK, Brindis RG, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC Guideline for the Management of Patients With Non–ST-Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64(24):e139-e228.
[11] Mieres J, Fernandez-Pereira C, Risau G, et al. One-year outcome of patients with diabetes mellitus after percutaneous coronary intervention with three different revascularization strategies: results from the Diabetic Argentina Registry (DEAR). Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2012;13(5):265-271.
[12] Levine GN, Bates ER, Blankenship JC, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA/SCAI Guideline for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions. Circulation. 2011;124(23):e574-651.
[13] Cao J, Gao JX, Wei LP, et al. Preliminary experience of coronary stent implantation: clinical analysis of 20 cases. Zhongguo Yiyao Daokan. 2009;11(2):323-324.
[14] Shi CL, Li X, Liu PL, et al. Primary experience of coronary artery stent implantation in the treatment of coronary heart disease. Shiyong Xin Nao Xueguan Bing Zazhi. 2013;21(1):130-131.
[15] Liu PL, Zhang M, Miao L, et al. XTRM-FIT coronary coated stent combined with tirofiban in the treatment of elderly patients with acute coronary syndrome. Zhongguo Shiyong Yikan. 2012;39(7):91-93.
[16] Liu PL, Yuan L, Miao L, et al. Effect of percutaneous coronary intervention on B brain natriuretic peptide and ventricular remodeling in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Zhongguo Shiyong Yikan. 2011;38(1):79-80.
[17] Li X, Liu PL, Zhang M, et al. Clinical study of percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in elderly patients with coronary heart disease. Zhongguo Shiyong Yiyao. 2012;7(5):77-78.
[18] Oberhauser JP, Hossainy S, Rapoza RJ. Design principles and performance of bioresorbable polymeric vascular scaffolds. EuroIntervention. 2009;5 Suppl F(F15-22.
[19] Stone GW, Ellis SG, Cannon L, et al. Comparison of a polymer-based paclitaxel-eluting stent with a bare metal stent in patients with complex coronary artery disease: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2005;294(10):1215-1223.
[20] Menichelli M, Parma A, Pucci E, et al. Randomized Trial of Sirolimus-Eluting Stent Versus Bare-Metal Stent in Acute Myocardial Infarction (SESAMI). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 49(19):1924-1930.
[21] Violini R, Musto C, De Felice F, et al. Maintenance of long-term clinical benefit with sirolimus-eluting stents in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction 3-year results of the SESAMI (sirolimus-eluting stent versus bare-metal stent in acute myocardial infarction) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;55(8):810-814.
[22] Kaltoft A, Kelbæk H, Thuesen L, et al. Long-term outcome after drug-eluting versus bare-metal stent implantation in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: 3-year follow-up of the randomized DEDICATION (Drug Elution and Distal Protection in Acute Myocardial Infarction) Trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010;56(8):641-645.
[23] Wiebe J, Möllmann H, Most A, et al. Short-term outcome of patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) treated with an everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffold. Clin Res Cardiol. 2014;103(3):141-148.
[24] Diletti R, Karanasos A, Muramatsu T, et al. Everolimus-eluting bioresorbable vascular scaffolds for treatment of patients presenting with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: BVS STEMI first study. Eur Heart J. 2014;35(12):777-786. |
.jpg)
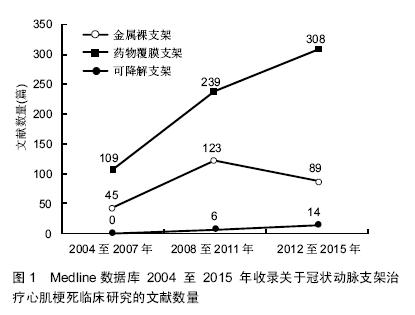
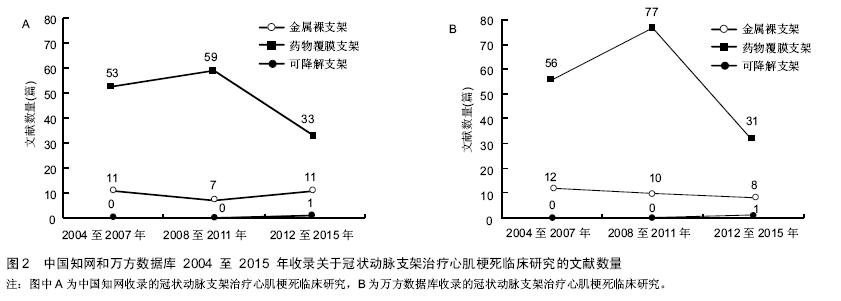
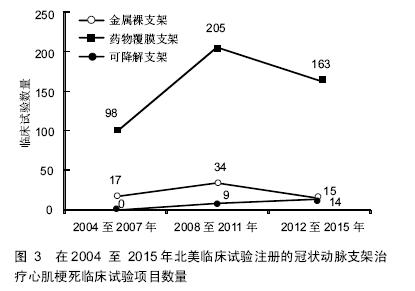
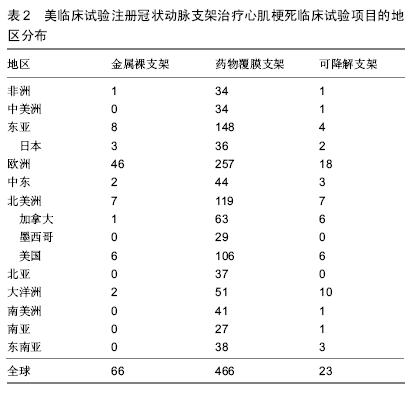
.jpg)
.jpg)