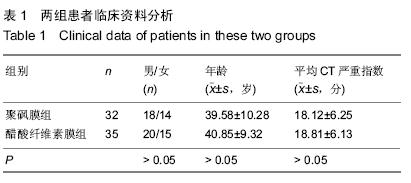
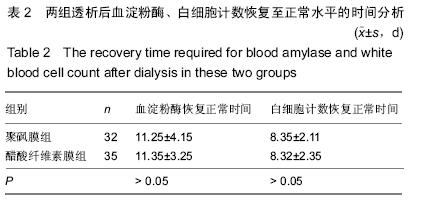
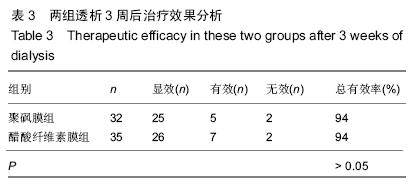
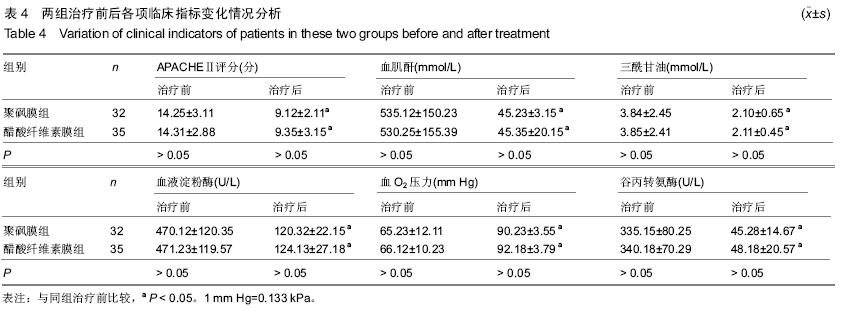
| [1] 陈波,周青山,张静静,等.重症胰腺炎中血液透析膜的应用价值[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(28):20-22,33. [2] 刘斌斌,胡才宝.持续性肾脏替代治疗滤器、管路凝血的主要原因分析及干预策略[J].护士进修杂志,2014,29(8):729-731. [3] 陈英全,谭双,陈国伟,等.血液灌流联合血液透析对急性重症胰腺炎患者抑制性T细胞的影响[J].中国全科医学, 2012, 15 (18) : 2098-2100. [4] 贾春红.血液灌流联合血液透析治疗重症急性胰腺炎9例疗效观察[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2008,15(6):349-349. [5] 杨军,杨太明,刘燕,等.血液灌流联合血液透析治疗重症急性胰腺炎的临床应用[J].中国危重病急救医学,2010,22(4):248-249. [6] 栾春艳,刘志刚,董涛,等.早期血液灌流联合血液透析滤过治疗重症急性胰腺炎疗效及对血液内环境的影响[J].中国全科医学, 2012,15(23):2712-2714. [7] Kitamura H,Nomura K,Arai M,et al.Impairment of changes in the diameter of the pancreatic portion of the superior mesenteric vein: an ultrasonographic sign of chronic pancreatitis or fibrosis. J Ultrasound Med. 2009;28 (9):1229-1234. [8] 涂学珍.血液灌流联合血液透析治疗重症急性胰腺炎护理研究[J].大家健康(下旬版),2013,29(24):297-298. [9] 王玉琴.血液灌流联合血液透析滤过治疗高脂血症性重症急性胰腺炎8例[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2009,16(5):268. [10] 谢伟东.高脂血症性胰腺炎采用床旁持续血液滤过联合低分子肝素治疗的疗效观察[J].中外医学研究,2013,11(19):195-196. [11] 盛丹虹,吴思军,齐玲,等.血液灌流联合血液透析对重症胰腺炎内环境的影响[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2013,34(20):3008-3010. [12] 刘朝阳,马胜银,尹飞,等.维持性血液透析患者并发急性胰腺炎6例临床分析[J].医药前沿,2013,35(19):209-209. [13] 邹洪,胡建,胡睿东,等.联合应用血液灌流与血液透析对重症急性胰腺炎患者抑制性T细胞的影响及疗效[J].中国普通外科杂志, 2014,23(3):301-304. [14] Okita Y,Okahisa T,Sogabe M,et al.Low-volume continuous hemodiafiltration with nafamostat mesilate increases trypsin clearance without decreasing plasma trypsin concentration in severe acute pancreatitis.ASAIO J.2007;53(2):207-212. [15] 郑朝旭,谭敏,陈国泰,等.维持性腹膜透析和血液透析患者的急性胰腺炎(附9例报告)[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2002, 9 (1): 36-37. [16] 宋林,姜再英,向廷秀,等.十二指肠乳头切开术联合血液透析在重症胰腺炎治疗中的护理体会[J].现代医药卫生, 2004, 20 (15): 1457-1459. [17] 郁国强,曾军红,禤江华,等.血浆置换联合血液透析滤过治愈重症急性胰腺炎1例[J].内科,2009,4(2):248-249. [18] 梁馨苓,史伟,梁永正,等.短时高容量血液滤过与间歇性血液透析治疗重症胰腺炎的疗效比较[J].中国血液净化, 2003, 2 (7): 366-368. [19] 黄克刚.血液灌流联合血液透析治疗急性重症胰腺炎43例临床疗效观察[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(9):124-125. [20] 冯德辉.血液透析膜材料在重症胰腺炎领域的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(29):5417-5420. [21] Bachmann K,Tomkoetter L,Kutup A,et al.Is the whipple procedure harmful for long-term outcome in treatment of chronic pancreatitis? 15-years follow-up comparing the outcome after pylorus-preserving pancreatoduodenectomy and frey procedure in chronic pancreatitis. AnnSurg. 2013; 258(5):815-821. [22] Holmes BJ,Hruban RH,Wolfgang CL,et al.Fine needle aspirate of autoimmune pancreatitis (lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis): Cytomorphologic characteristics and clinical correlates.Acta Cytologica.2012;56(3):228-232. [23] 喻超,孙诚谊,江建新,等.组合型血液净化联合早期肠内营养治疗急性高脂血症性胰腺炎[J].贵阳医学院学报, 2012, 37 (3): 228 -230. [24] Bruno MJ,van Westerloo-DJ,van Dorp-WT,et al.Acute pancreatitis in peritoneal dialysis and haemodialysis: risk, clinical course, outcome, and possible aetiology. Gut. 2000; 46(3):385-389. [25] 杨宏.浅谈急性胰腺炎的治疗方法及临床疗效[J].求医问药(下半月刊),2013,11(6):92-92,93. [26] 高烽,董勤,崔杰,等.CVVHDF联合乌司他丁治疗慢性肾脏病并发急性胰腺炎疗效观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2012, 21 (1): 27-29. [27] 程斌,龚园其,詹亚琨,等.短时连续性静-静脉血液透析滤过对重症急性胰腺炎并急性肺损伤的治疗研究[J].中国全科医学, 2010, 13(24):2664-2666. [28] 朱长举,王万鹏,刘保池,等.血液透析滤过联合血浆置换治疗妊娠并重度高脂血症性胰腺炎效果观察[J].郑州大学学报:医学版, 2007,42(2):276-278. [29] 李勇.血液透析滤过联合血浆置换治疗妊娠并重度高脂血症性胰腺炎的临床疗效观察[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(36):116-117. [30] Hu WY,Fua L.Simultaneous characterization of pancreatic stellate cells and other pancreatic components within three-dimensional tissue environment during chronic pancreatitis.J Biomed Optics.2013;18(5):056002-1-056002-8. [31] 黄智.观察血液透析滤过联合血浆置换治疗妊娠并重度高脂血症性胰腺炎的效果[J].吉林医学,2013,34(30):6255-6256. [32] 杨晓娟,李丽霞,王淑贤,等.血液灌流与血液透析滤过联用治疗重症急性胰腺炎合并急性肾功能衰竭[J].中国危重病急救医学, 2007,19(8):476. [33] 马国英,刘福胜.血液灌流联合血液透析/血液透析滤过治疗急性重症胰腺炎的临床应用[C].//中华医院管理学会血液净化中心管理分会2008年学术年会论文集,2008:181-182. [34] 李永胜,高红宇,于丹,等.持续性与间歇性血液净化治疗重症急性胰腺炎合并急性肾衰竭的疗效比较[J].内科急危重症杂志, 2010, 16(3):139-142. [35] 吴灏,孙婧,苏红,等.连续性肾脏替代疗法治疗重症急性胰腺炎合并急性肾损伤患者的临床分析[J].内科急危重症杂志, 2011, 17 (2):84-87. [36] 毛杰,李梅,王俭勤,等.连续静-静脉血液透析滤过在重症急性胰腺炎治疗中的内环境稳态维持作用[J].兰州大学学报:医学版, 2011,37(3):49-53,57. [37] 吴灵敏.血液透析联合血液灌流治疗重症胰腺炎25例临床分析[J].航空航天医学杂志,2010,21(12):2279. [38] Layer P,Dellinger EP,Forsmark CE,et al.Determinant-based classification of acute pancreatitis severity.Zeitschrift fur Gastroenterologie.2013;51(6):544-550. [39] 谢红浪,季大玺.应用CVVH治疗重症急性胰腺炎[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2000,9(5):510-512. [40] 郁国强,曾军红,禤江华,等.血浆置换联合血液透析滤过治疗重症急性胰腺炎临床疗效分析[J].临床荟萃, 2011, 26(9): 760 -762, 765. |
.jpg)