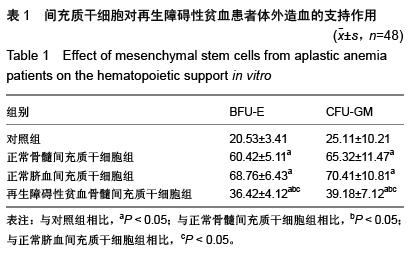
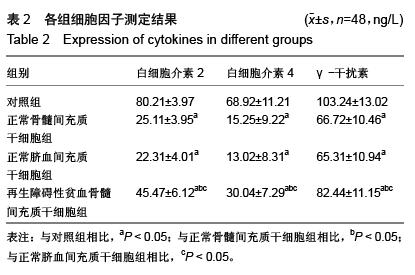
| [1] 刘海芸,刘婷婷.再生障碍性贫血发病机制研究进展[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2015,23(4): 1216-1220.[2] Zeng Y, Katsanis E.The complex pathophysiology of acquired aplastic anaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015;180(3): 361-370.[3] Young NS. Current concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of aplastic anemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2013;2013:76-81. [4] Fajardo-Orduña GR, Mayani H, Montesinos JJ. Hematopoietic Support Capacity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Biology and Clinical Potential. Arch Med Res. 2015 Oct 29. [Epub ahead of print][5] Sahraneshin Samani F, Ebrahimi M, Zandieh T, et al. In Vitro Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord Blood CD133(+)Cells into Insulin Producing Cells in Co-Culture with Rat Pancreatic Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell J. 2015;17(2):211-220.[6] Larijani B, Aghayan HR, Goodarzi P, et al. GMP-grade human fetal liver-derived mesenchymal stem cells for clinical transplantation. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1283:123-136.[7] Yin T, He S, Su C, et al. Genetically modified human placenta?derived mesenchymal stem cells with FGF?2 and PDGF?BB enhance neovascularization in a model of hindlimb ischemia. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(4):5093-5099.[8] 李启明,程天民,李宁,等.脐血间充质干细胞分离, 培养与鉴定[J].重庆医学,2005,34(6): 879-881.[9] Liao L, Zhao RC. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Immunomodulatory Properties. In: Stem Cells: Basics and Clinical Translation. Springer, 2015:67-83.[10] van den Berk LC, Jansen BJ, Snowden S, et al. Cord blood mesenchymal stem cells suppress DC-T Cell proliferation via prostaglandin B2. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(14):1582-1593.[11] Lee HJ, Ko JH, Ko AY, et al. Intravenous infusion of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells decreased CCR7(+) antigen presenting cells in mice with corneal allotransplantation. Curr Eye Res. 2014;39(8):780-789.[12] Plock JA, Schnider JT, Zhang W, et al. Adipose- and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prolong Graft Survival in Vascularized Composite Allotransplantation. Transplantation. 2015;99(9):1765-1773.[13] Wu Y, Cao Y, Li X, et al. Cotransplantation of haploidentical hematopoietic and umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for severe aplastic anemia: successful engraftment and mild GVHD. Stem Cell Res. 2014;12(1):132-138.[14] 张之南, 沈悌.血液病诊断及疗效标准[M].北京:科学出版社, 2007.[15] Qin X, Baumann I, Chen J, et al. Refractory cytopenia of children and acquired aplastic anemia: a clinical and pathological study of 130 cases. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2014;35(8):713-718.[16] Dolberg OJ, Levy Y. Idiopathic aplastic anemia: diagnosis and classification. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(4-5):569-573.[17] Qian D, Gong J, He Z, et al. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Repair Necrotic Pancreatic Tissue and Promote Angiogenesis by Secreting Cellular Growth Factors Involved in the SDF-1 α /CXCR4 Axis in Rats. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:306836.[18] Luan Y, Ding W, Ju ZY, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect against lung injury in a mouse model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(3):1945-1950.[19] Zhu F, Wang J, Qiu X, et al. Smoke inhalation injury repaired by a bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell paracrine mechanism: Angiogenesis involving the Notch signaling pathway. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;78(3):565-572.[20] 唐旭东,张姗姗,许勇钢, 等.T 细胞亚群在重型再生障碍性贫血治疗中的疗效预测价值[J].中医杂志,2013,54(20): 1755-1758.[21] 郭鹏,刘传方,赵雯.人脐带沃顿胶间充质干细胞对重型再生障碍性贫血调节性T细胞及Foxp3基因的影响[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2011,49(9): 71-76.[22] Wu Q, Zhang J, Shi J, et al. Increased bone marrow (BM) plasma level of soluble CD30 and correlations with BM plasma level of interferon (IFN)-γ, CD4/CD8 T-cell ratio and disease severity in aplastic anemia. PLoS One. 2014;9(11): e110787.[23] 蒋白丽,李建平,李文倩,等. CD8+T细胞及其分泌的细胞因子在再生障碍性贫血发病机制中的作用[J].中国实验血液学杂志, 2014, 22(2): 569-572.[24] 张婧瑶,许洪志,尹冬梅,等.再生障碍性贫血、骨髓增生异常综合征、急性髓系白血病患者CD8+T细胞亚群的变化及临床意义[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2013,21(1): 203-208.[25] Desalphine M, Bagga PK, Gupta PK, et al. To evaluate the role of bone marrow aspiration and bone marrow biopsy in pancytopenia. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014;8(11):FC11-15.[26] Desmond R, Townsley DM, Dunbar C, et al. Eltrombopag in aplastic anemia.Semin Hematol. 2015;52(1):31-37.[27] 向永胜,王龙.环孢素A对慢性再生障碍性贫血患者血清γ干扰素及一氧化氮、一氧化氮合酶的影响[J].中国动脉硬化杂志, 2011, 19(3):220-222. |
.jpg)

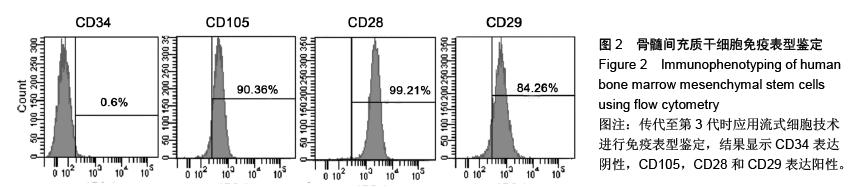
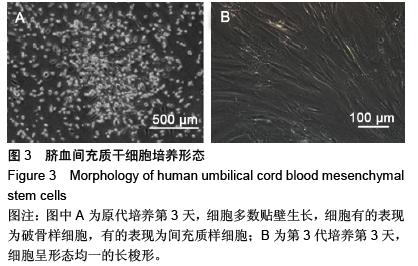
.jpg)