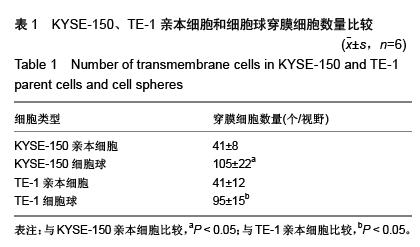
| [1] 朱孝中,刘德森,俞力超,等.人食管癌间充质干细胞对食管癌细胞株Eca-109侵袭性的影响[J].实用临床医药杂志,2012,16(22): 18-20.[2] 汪建林,孙志强,于静萍,等.食管癌细胞株中肿瘤干细胞样细胞培养分离及生物学鉴定[C].第八届中国肿瘤学术大会暨第十三届海峡两岸肿瘤学术会议论文集,2014:940.[3] 郑娇娇,吴清明,陈建华,等.P162对食管癌细胞株Eca109的放射增敏作用及其对p75NTR表达的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2013,29(1):103-107.[4] Kammori M, Izumiyama N, Nakamura K, et al. Telomere metabolism and diagnostic demonstration of telomere measurement in the human esophagus for distinguishing benign from malignant tissue by tissue quantitative fluorescence in situ hybridization. Oncology. 2006;71(5-6):430-436.[5] Chen B, Fang WK, Wu ZY, et al. The prognostic implications of microvascular density and lymphatic vessel density in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Comparative analysis between the traditional whole sections and the tissue microarray. Acta Histochem. 2014;116(4):646-653.[6] Yang Y, Wang L, Wang S, et al. Study of metabonomic profiles of human esophageal carcinoma by use of high-resolution magic-angle spinning 1H NMR spectroscopy and multivariate data analysis.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013;405(10):3381-3389.[7] Sun LL, Sun XX, Xu XE, et al. Overexpression of Jumonji AT-rich interactive domain 1B and PHD finger protein 2 is involved in the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Histochem. 2013;115(1):56-62.[8] 邹文萍,宋俊梅,李光明,等.氯化钴低氧诱导食管癌细胞VEGF与per2的节律性研究[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志,2015,22(4): 263-266, 271.[9] Chen J, Pan J, Zheng X, et al. Number and location of positive nodes, postoperative radiotherapy, and survival after esophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection for thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82(1):475-482.[10] Zhang J, Yang Y, Chen L, et al. Overexpression of pituitary tumor transforming gene (PTTG) is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Histochem. 2014;116(3): 435-439.[11] 孙志刚,黄盛东,张宝仁,等.应用p75NTR分选食管肿瘤干细胞并鉴定其生物学特性[J].第二军医大学学报,2009,30(5):481-486.[12] 赵生霞.食管癌Eca109单克隆细胞株的干细胞特性研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2013.[13] 余茜颖.miR-203调控食管癌干细胞自我更新及食管癌相关甚因ECRG1转录调控的研究[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院(中国医学科学院),2010.[14] 李林,田辉,岳韦名,等.人间充质干细胞对肿瘤细胞A549和Eca-109增殖、凋亡和侵袭影响的实验研究[C].山东省第十一次胸心血管外科学学术会议论文集,2011:458-472.[15] 苏鹏,刘洪峰,石磊芝,等.干细胞Nanog蛋白在食管癌组织中的表达及意义[J].山东医药,2013,53(33):26-27,29.[16] Kim MK, Cho KJ, Park SI, et al. Initial stage affects survival even after complete pathologic remission is achieved in locally advanced esophageal cancer: analysis of 70 patients with pathologic major response after preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75(1): 115-121.[17] Zhong X, Yu J, Zhang B, et al. Using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography to estimate the length of gross tumor in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;73(1): 136-141.[18] 黄盛东,刘晓红,袁扬,等.食管癌中p75NTR阳性细胞池的变化与顺铂耐药机制的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2007,24(12): 1560-1562.[19] 王洁莲,吴清明,李欢,等.环氧合酶抑制剂NS-398抑制食管癌干细胞增强放射敏感性的研究[J].中华消化杂志,2011,31(10): 697-698.[20] Nakajima TE, Yoshida H, Okamoto N, et al. Nucleostemin and TWIST as predictive markers for recurrence after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for esophageal carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2012; 103(2):233-238.[21] Yu X, Jiang X, Li H, et al. miR-203 inhibits the proliferation and self-renewal of esophageal cancer stem-like cells by suppressing stem renewal factor Bmi-1. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(6):576-585.[22] Gen Y, Yasui K, Nishikawa T, et al. SOX2 promotes tumor growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through the AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 2013;104(7):810-816.[23] Zinovyeva MV, Monastyrskaya GS, Kopantzev EP, et al. Identification of some human genes oppositely regulated during esophageal squamous cell carcinoma formation and human embryonic esophagus development. Dis Esophagus. 2010;23(3):260-270.[24] 刘志良,石磊芝,杜亚明,等.HIWI在食管癌细胞系Eca-109中的表达及意义[J].山东医药,2012,52(32):43-45,后插4.[25] 汪建林,孙志强,于静萍,等.食管癌细胞株中肿瘤干性细胞群的放射生物学特性[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2014,36(8):575-581.[26] 赵生霞,慕晓玲.食管癌干细胞分离方法研究现状[J].农垦医学, 2012,34(5):425-427.[27] 肖军兰,曾金林,湛曦,等.干细胞Nanog蛋白在食管癌组织中的表达及意义[J].中国医学创新,2014,11(36):41-42. [28] Wang Y, Fan H, Zhou B, et al. Fusion of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with esophageal carcinoma cells inhibits the tumorigenicity of esophageal carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(2):370-377.[29] Yang L, Ren Y, Yu X, et al. ALDH1A1 defines invasive cancer stem-like cells and predicts poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2014; 27(5): 775-783.[30] Fujiwara D, Kato K, Nohara S, et al. The usefulness of three-dimensional cell culture in induction of cancer stem cells from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;434(4):773-778.[31] Li H, Gao Q, Guo L, et al. The PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway regulates stem-like cells in primary esophageal carcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;11(11):950-958.[32] 何炜.干细胞因子OCT4、SOX2和HIWI在食管鳞癌中的表达及OCT4对食管癌生物学行为的影响[D]. 郑州:郑州大学,2009.[33] 周中卫,胡嘉波,施舜缤,等.人食管癌间充质干样细胞分离培养及生物学特性鉴定[J].基础医学与临床,2012,32(7):798-803.[34] 王勇,周兵,樊宏斌,等.人脐带间充质干细胞与食管癌细胞融合后的转录组比较[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2014,36(10):726-732.[35] Huang D, Gao Q, Guo L, et al. Isolation and identification of cancer stem-like cells in esophageal carcinoma cell lines. Stem Cells Dev. 2009;18(3):465-473.[36] Shahryari A, Rafiee MR, Fouani Y, et al. Two novel splice variants of SOX2OT, SOX2OT-S1, and SOX2OT-S2 are coupregulated with SOX2 and OCT4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Stem Cells. 2014;32(1):126-134.[37] Wang Q, He W, Lu C, et al. Oct3/4 and Sox2 are significantly associated with an unfavorable clinical outcome in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Anticancer Res. 2009; 29(4):1233-1241.[38] 马青.清热化痰活血方及其拆方对食管癌EC9706干细胞生物学性状和细胞周期蛋白的影响[D]. 上海:上海中医药大学,2014.[39] 高全立,李红霞,郭黎平,等.食管癌EC9706细胞中SP细胞与NSP细胞基因表达差异的研究[C].第一届国际肿瘤干细胞学术会议论文集,2007:81.[40] 赵生霞,黄燕燕,慕晓玲,等.食管癌Eca109单克隆细胞株的干细胞特性研究[J].石河子大学学报:自然科学版,2013,31(2):197- 201. |
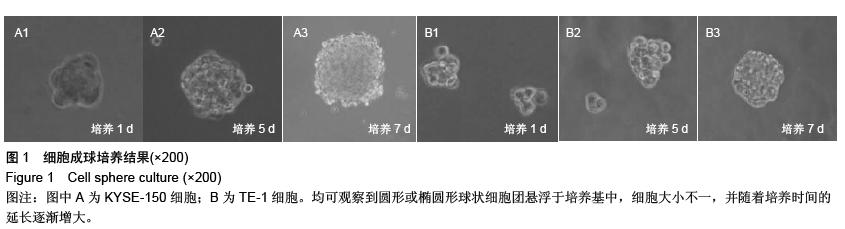
.jpg)
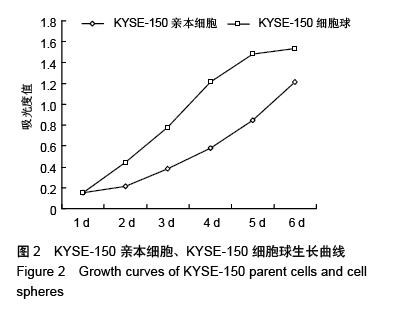
.jpg)