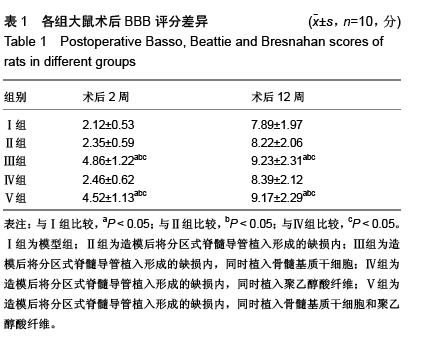
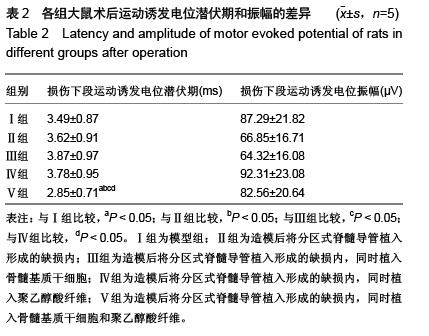
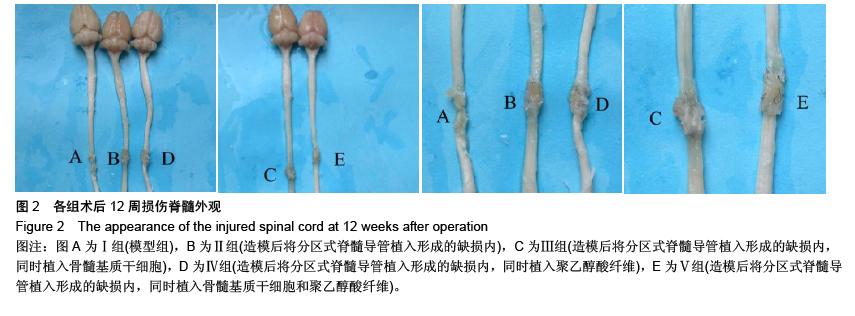
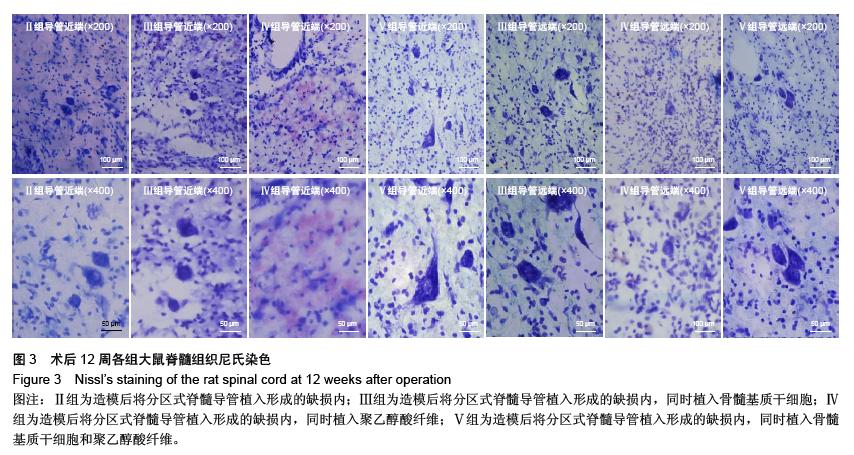
| [1] 王雪松,陈雪,李奕,等.分区式脊髓导管联合骨髓基质干细胞修复脊髓横断损伤[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(7):1403,1405.
[2] Liu KJ, Xu J, Yang CY, et al. Analysis of olfactory ensheathing glia transplantation-induced repair of spinal cord injury by electrophysiological, behavioral, and histochemical methods in rats.J Mol Neurosci. 2010;41(1):25-29.
[3] 段朝霞,张洁元,陈魁君,等.细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2012,36(12):57-59.
[4] 蒲渝,郭庆山,王爱民,等.改性胶原支架构建组织工程化神经复合物修复大鼠脊髓损伤[J].中华创伤杂志,2013,29(1):67-72.
[5] Haga KK, McClymont KL, Clarke S, et al. The effect of tight glycaemic control, during and after cardiac surgery, on patient mortality and morbidity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;6:3.
[6] Banskota B, Bijukachhe B, Kazi S, et al. Neuroarthropathy of the hip following spinal cord injury. Indian J Orthop. 2011; 45(1): 87-90.
[7] Rodríguez-Salceda I, Escortell-Mayor E, Rico-Blázquez M, et al. EDUCORE project: a clinical trial, randomised by clusters, to assess the effect of a visual learning method on blood pressure control in the primary healthcare setting. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:449.
[8] Faresjö T, Faresjö A. To match or not to match in epidemiological studies--same outcome but less power. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2010;7(1):325-332.
[9] 喻皇飞,方宁,陈代雄,等.人羊膜问充质干细胞移植对大鼠脊髓损伤神经功能恢复的影响[J].中华神经外科杂志,2012,28(4): 412-415.
[10] 吴月奎,王尚武,孙起军,等.脐血源神经干细胞移植治疗大鼠脊髓损伤及其差异基因表达[J].中华神经医学杂志,2014,13(8): 772-777.
[11] 吴立生,吴仕峰,高万里,等.嗅鞘细胞和骨髓基质干细胞联合培养修复大鼠脊髓损伤[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(7): 1217, 1220.
[12] Choi JS, Leem JW, Lee KH, et al. Effects of human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation combined with polymer on functional recovery following spinal cord hemisection in rats. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;16(6): 405-411.
[13] 赵建罡,马立学,张伟东,等.不同靶点注射骨髓基质干细胞对大鼠脊髓损伤修复的影响[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,16(5):581,585.
[14] 陈少强,吴碧莲,贾小力,等.骨髓基质干细胞旁分泌作用促进大鼠损伤脊髓的血管新生[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2015,17(3): 257-262.
[15] Hawryluk GW, Mothe A, Wang J, et al. An in vivo characterization of trophic factor production following neural precursor cell or bone marrow stromal cell transplantation for spinal cord injury. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(12):2222-2238.
[16] 陈伟,羊明智.实验性脊髓损伤动物模型的制备及研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(6):520-523.
[17] 杨国宏,张春军,赵富生,等.自体骨髓基质干细胞移植联合EPO治疗脊髓损伤的研究[J].中国医学创新,2014,11(32):1-3.
[18] 徐小林,管雅琳,张雪青,等.两种方式移植骨髓基质干细胞治疗大鼠脊髓损伤的电生理研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(12): 1076-1081.
[19] De Laporte L, des Rieux A, Tuinstra HM, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and fibroblast growth factor 2 delivery from spinal cord bridges to enhance angiogenesis following injury. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011;98(3):372-382.
[20] 陈少强,林建华.骨髓基质于细胞在损伤脊髓内向少突胶质细胞定向分化的分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(9):795-799.
[21] 郭晓鹤,步星耀,闫兆月,等.自体骨髓基质干细胞动员联合神经生长因子及综合康复治疗脊髓损伤[J].中华神经医学杂志,2013, 12(8):833-837.
[22] 王晶,李超,王业杨,等.骨髓基质干细胞生物学特性及其移植修复脊髓损伤进展[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志:电子版,2013,3(2): 99-102.
[23] Ayatollahi M, Salmani MK, Geramizadeh B, et al. Conditions to improve expansion of human mesenchymal stem cells based on rat samples. World J Stem Cells. 2012;4(1):1-8.
[24] 阮智,黄慧,孙建华,等.异体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脊髓损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(36): 6729- 6732.
[25] Kang ES, Ha KY, Kim YH. Fate of transplanted bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells following spinal cord injury in rats by transplantation routes. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27(6):586-593.
[26] Ruff CA, Wilcox JT, Fehlings MG. Cell-based transplantation strategies to promote plasticity following spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2012;235(1):78-90.
[27] 刘钦毅,程兆华,邵国喜,等.3.4聚乳酸-聚三亚甲基碳酸酯/GDNF导管对大鼠脊髓损伤区GAP-43蛋白表达的影响[J].中国实验诊断学,2014,18(8):1219-1221.
[28] 张秋娟.自体骨髓基质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤[J].河北医药, 2014,36(10):1527-1528.
[29] van den Brand R, Heutschi J, Barraud Q, et al. Restoring voluntary control of locomotion after paralyzing spinal cord injury. Science. 2012;336(6085):1182-1185.
[30] 杨阳,陈雪,李奕,等.不同浓度BMSCs联合壳聚糖导管对大鼠全横断脊髓损伤修复作用的比较[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2011, 30(6):931-937.
|
.jpg)
.jpg)