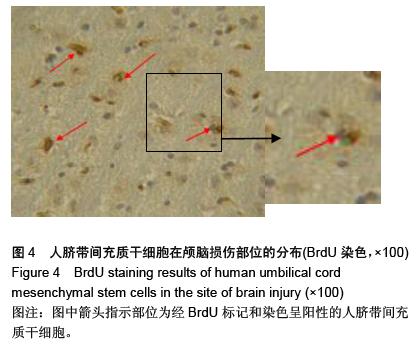
| [1] 张润,秦琨,法志强,等.Catwalk系统评估脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠脑损伤后运动功能的恢复情况[J].南方医科大学学报, 2012,32(4):449-455.
[2] 江伟,沈洁,史源,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的分离鉴定及其修复缺血缺氧脑损伤作用[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2011,37(2): 215-219,后插2.
[3] 袁源,但齐琴,刘佳,等.携带脑源性神经营养因子基因人脐带干细胞改善脑损伤大鼠神经功能的实验研究[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2011,20(2):115-118.
[4] 李长栋,荔志云,季玮,等.大黄素甲醚对脑损伤大鼠 bcl-2、bax 表达变化的影响[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2015,14(3): 200-203.
[5] 李静,杨波,刘献志,等.人脐带沃顿胶间充质干细胞移植对创伤性脑损伤大鼠脑损伤区微循环的影响[J].中华神经医学杂志,2013, 12(9):880-884.
[6] 阮光萍,姚翔,刘菊芬,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的作用:细胞移植、免疫调节及充当基因治疗靶细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(41):6714-6718.
[7] Heng BC, Phan TT, Liu H, et al. Can the therapeutic advantages of allogenic umbilical cord blood-derived stem cells and autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells be combined and synergized. ASAIO J. 2006;52(6):611-613.
[8] 袁源,但齐琴,刘佳,等.人脐带干细胞携带NGF基因脑内移植对脑损伤大鼠神经行为学的影响[J].中华行为医学与脑科学杂志, 2011,20(4):298-301.
[9] Wu KH, Tsai C, Wu HP, et al. Human application of ex vivo expanded umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: enhance hematopoiesis after cord blood transplantation. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(11):2041-2051.
[10] 李长栋,荔志云,白海,等.大黄素甲醚联合脐带间充质干细胞移植对创伤性脑损伤大鼠MMP-9和TIMP-1蛋白酶的影响[J].创伤外科杂志,2013,15(4):306-309.
[11] Roszek K, Bomastek K, Dro?d?al M, et al. Dramatic differences in activity of purines metabolizing ecto-enzymes between mesenchymal stem cells isolated from human umbilical cord blood and umbilical cord tissue. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;91(6):519-525.
[12] Weiwei Li,Min Li,Yantian Chen, et al.Various Seeding Methods for Tissue Development of Human Umbilical-cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in 3-Dimensional PET Matrix. Biotechnology and bioprocess engineering. 2014;19(1):108-117.
[13] Li WW, Li M, Chen YT, et al. Various seeding methods for tissue development of human umbilical-cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells in 3-dimensional PET matrix. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering. 2014;19(1): 108-117.
[14] 袁源.脐带间充质干细胞的生物学特性、向神经样细胞的分化及细胞移植治疗颅脑损伤的研究[D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2006.
[15] 李晓红,陈翀,涂悦,等.温敏脐带间充质干细胞联合亚低温对重型创伤性脑损伤大鼠认知功能的影响[J].中华创伤杂志,2014, 30(5):455-459.
[16] Hua J, Gong J, Meng H, et al. Comparison of different methods for the isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord matrix: proliferation and multilineage differentiation as compared to mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord blood and bone marrow. Cell Biol Int. 2014; 38(2):198-210.
[17] 梁璐,陈小军,吴昊,等.人脐带间充质干细胞在小鼠体内的迁移变化及宿主的免疫反应[J].郑州大学学报:医学版,2010,45(1): 33-36.
[18] 彭余江,李慧勇,何玺君,等.神经生长因子转染的人脐带间充质干细胞促进中枢神经系统损伤修复的实验研究[J].浙江医学,2015, 37(3):197-199,215.
[19] 张德双,王华,白小红,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗新生儿缺氧缺血性脑损伤的最新研究进展[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2013, 28(14):1112-1114.
[20] Hatlapatka T, Moretti P, Lavrentieva A, et al. Optimization of culture conditions for the expansion of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem or stromal cell-like cells using xeno-free culture conditions. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011; 17(4): 485-493.
[21] 张琴芬,屠文娟,李红新,等.人脐带间充质干细胞联用神经节苷酯GM1治疗新生大鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤[J].中国儿童保健杂志, 2014,22(8):819-821,825.
[22] Hollweck T, Marschmann M, Hartmann I, et al. Comparative analysis of adherence, viability, proliferation and morphology of umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded on different titanium-coated expanded polytetrafluoroethylene scaffolds. Biomed Mater. 2010;5(6): 065004.
[23] Lee HJ, Lee JK, Lee H, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve neuropathology and cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model through modulation of neuroinflammation. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33(3):588-602.
[24] 李长栋,孙建军,荔志云,等.DAPI标记脐带间充质干细胞在颅脑创伤模型大鼠脑内的迁徙和分布[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2013, 30(7):615-618.
[25] Yun SP, Lee SJ, Oh SY, et al. Reactive oxygen species induce MMP12-dependent degradation of collagen 5 and fibronectin to promote the motility of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2014;171(13):3283-3297.
[26] Cheng JL, Yang YJ, Li HL, et al. In vivo tracing of superparamagnetic iron oxide-labeled bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transplanted for traumatic brain injury by susceptibility weighted imaging in a rat model. Chin J Traumatol. 2010;13(3):173-177.
[27] Ziv-Polat O, Margel S, Shahar A.Application of iron oxide anoparticles in neuronal tissue engineering. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10 (2): 189-191
[28] 黄霞,潘兴华,庞荣清,等.脐带间充质干细胞培养中的染色标记及示踪技术[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(23):3751-3755.
[29] 汤华军,范光碧,郑宇杰,等. 脑出血后大鼠神经干细胞增殖及迁徙途径的实验研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2015,33(2): 189-192.
[30] Wang F, Zhang YC, Zhou H, et al. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo osteogenic differentiation of nano-hydroxyapatite/ chitosan/poly(lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(3):760-768.
[31] Liu S, Hou KD, Yuan M, et al. Characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells derived from Wharton's jelly of human umbilical cord and for fabrication of non-scaffold tissue-engineered cartilage. J Biosci Bioeng. 2014;117(2):229-235.
[32] 袁源,杨树源,张建宁.人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠创伤性脑损伤[J].中国工程组织研究与临床康复,2011,15(45):8424- 8428.
|
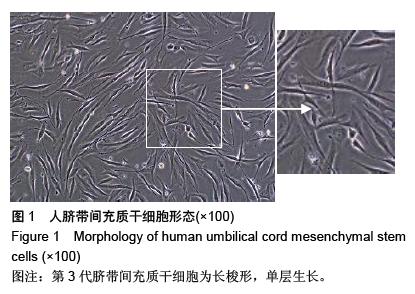
.jpg)
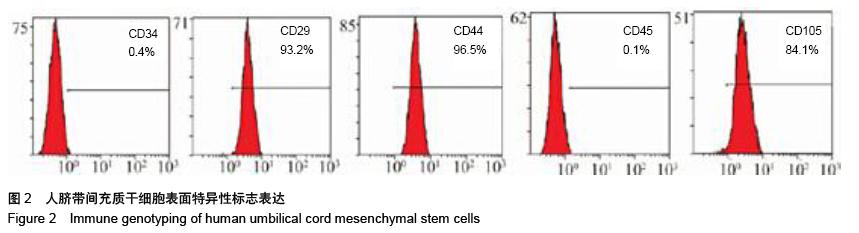
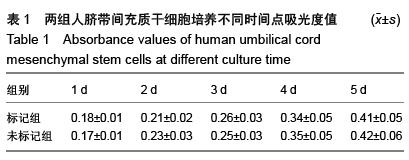
.jpg)