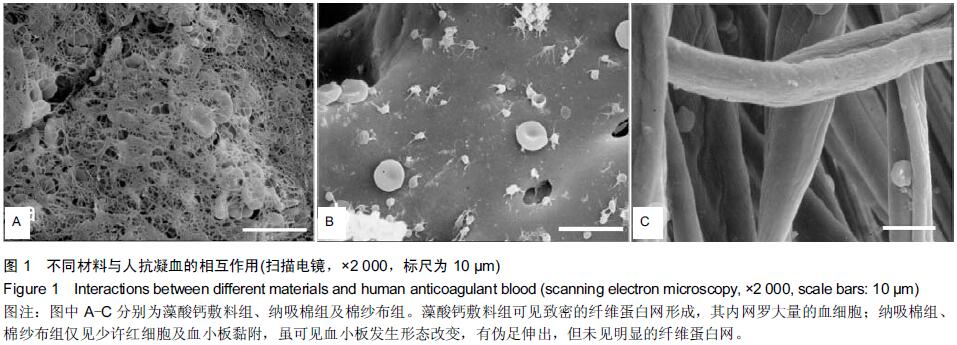
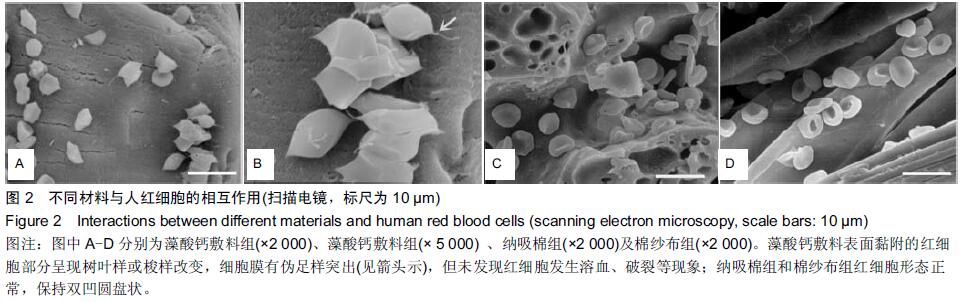
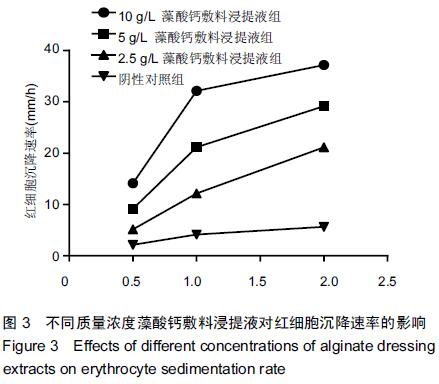
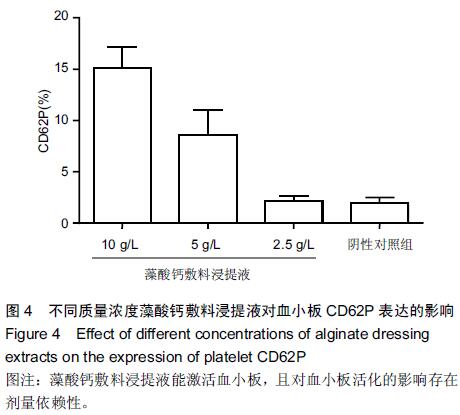
[1] Kauvar DS,Lefering R,Wade CE.Impact of hemorrhage on trauma outcome: an overview of epidemiology, clinical presentations, and therapeutic considerations.J Trauma. 2006;60(6 Suppl):S3-11.
[2] Cripps MW,Kutcher ME,Daley A,et al.Cause and timing of death in massively transfused trauma patients.J Trauma Acute Care Surg.2013;75(202):S255-S262.
[3] Alam HB,Burris D,DaCorta JA,et al.Hemorrhage control in the battlefield: role of new hemostatic agents.Mil Med. 2005; 170(1):63-69.
[4] 陈孝平,汪建平.外科学[M].8版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2013: 166-170.
[5] 柯林楠,冯晓明,王春仁.医用敷料研究的现状与进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(3):521-524.
[6] Jansdown AB,Payne MJ.An evaluation of the local reaction and biodegradation of calcium sodium alginate (Kaltostat) following subcutaneous implantation in the rat.J R Coll Surg Edinb.1994;39(5):284-288.
[7] Suzuki Y,Nishimura Y,Tanihara M,et al.Evaluation of a novel alginate gel dressing:cytotoxicity to fibroblasts in vitro and foreign-body reaction in pig skin in vivo.J Biomed Mater Res.1998;39(2):317-322.
[8] Tonnesen HH,Karlsen J.Alginate in drug delivery systems. Drug Dev Ind Pharn.2002;28(6):62l-630.
[9] Oliver LC,Blaine G. Haemostasis with absorbable alginates in neurosurgical practice. Br J Surg.1950; 37(147):307-310.
[10] Sirimanna KS.Calcium alginate fibre(Kahostat 2)for nasal packing after trimming of trubinates:a pilot study.J Laryngol Otol.1989;103(11):1067-1068.
[11] Groves AR,Lawrence JC.Alginate dressing as a donor site haemostat.Ann R coll Surg Engl.1986;68(1):27-28.
[12] Kim JT,Kim YH,Kim SW.Customized negative pressure wound therapy for intractable auricular defects using alginate dressings and feeding tubes.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014;67(11):e284-286.
[13] McBride CA,Kimble RM,Stockton K.Three donor site dressings in pediatric split-thickness skin grafts: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16(1): 557.
[14] Qin Y.The gel swelling properties of alginate fibers and their application in wound management.Polym Adv Technol. 2008; 19(1):6-14.
[15] 骆强,孙玉山.医用海藻纤维的研究[J].非织造布,2011,19(1): 30-32.
[16] Thomas S. Alginate dressings in surgery and wound management--Part 1. J Wound Care. 2000;9(2):56-60.
[17] 徐文荣,王建中.临床血液学检验[M].5版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2012:291-300.
[18] Smith CJ,Vournakis JN,Demcheva M,et al.Differential effect of materials for surface hemostasis on red blood cell morphology.Microsc Res Tech.2008;71(10):721-729.
[19] Mi chiels JJ,Berneman Z,Gadisseur A,et al. Aspirin-responsive, migraine-like transient cerebral and ocular ischemic attacks and erythromelalgia in JAK2-positive essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera.Acta Haematol.2015;133(1):56-63.
[20] Valeri CR,Cassidy G,Linda E,et al.Anemia-induced increase in the bleeding time: implications for treatment of nonsurgical blood loss.Transfusion.2001;41(8):977.
[21] Walker B,Towhid ST,Schmid E.Dynamic adhesion of eryptotic erythrocytes to immobilized platelets via platelet phosphatidylserine receptors.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014; 306(3):C291-297.
[22] Wang W,Diacovo TG,Chen J,et al.Simulation of platelet, thrombus and erythrocyte hydrodynamic interactions in a 3D arteriole with in vivo comparison.PLoS One. 2013;8(10): e76949.
[23] Wang L,Olivecrona G,Götberg M,et al.ADP acting on P2Y13 receptors is a negative feedback pathway for ATP release from human red blood cells.Circ Res. 2005;96(2):189-196.
[24] Goldsmith HL,Bell DN,Spain S,et al.Effect of red blood cells and their aggregates on platelets and white cells in flowing blood.Biorheology.1999;36(5-6):461-468.
[25] Gladwin MT,Crawford JH,Patel RP.The biochemistry of nitric oxide, nitrite, and hemoglobin: role in blood flow regulation. Free Radic Biol Med.2004;36(6):707-717.
[26] Smith CJ,Vournakis JN,Demcheva M,et al.Differential effect of materials for surface hemostasis on red blood cell Morphology. Microsc Res Tech.2008;71(10):721-729.
[27] Gu R,Sun W,Zhou H,et al.The performance of a fly-larva shell-derived chitosan sponge as an absorbable surgical hemostatic agent.Biomaterials.2010;31(6):1270-1277.
[28] Lewis DA,Nyska A,Potti A,et al.Hemostatic activation in a chemically induced rat model of severe hemolysis and thrombosis.Thromb Res.2006;118(6):747-753.
[29] Vahidkhah K,Diamond SL,Bagchi P.Platelet dynamics in three-dimensional simulation of whole blood.Biophys J. 2014;106(11):2529-2540.
[30] Jordan A,David T,Homer-Vanniasinkam S,et al.The effects of margination and red cell augmented platelet diffusivity on platelet adhesion in complex flow. Biorheology. 2004;41(5): 641-653.
[31] Zhao L,You G,Liao F,et al.Sodium alginate as viscosity modifier may induce aggregation of red blood cells.Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2010;38(5):267-276.
[32] Hori K,Miyasawa K,Ito K.Hemagglutinins in marine algae.Bull Jap Soc Soi Fish. 1981;47(6):793-798.
[33] Wu CC,Ko FN,Huang TF,et al.Mechanisms-regulated platelet spreading after initial platelet contact withcollagen Biochem Biophys Res Commun.1996;220(2):388-393.
[34] 吴鸿.血小板活化过程中的钙离子信号[J].生理科学进展, 2012, 43(6):417-421.
[35] Qin Y,Gilding DK.Alginate fibres and wound dressings.Med Dev Technol. 1996;7(9):32-41.
[36] Sweeney IR,Miraftab M,Collyer G.Absorbent alginate fibres modified with hydrolysed chitosan for wound care dressings--II. Pilot scale development. Carbohydr Polym. 2014;102:920-827.
[37] 秦益民,朱长俊,冯德明,等.海藻酸钙医用敷料与普通棉纱布的性能比较[J].纺织学报,2007,28(3):45-48.