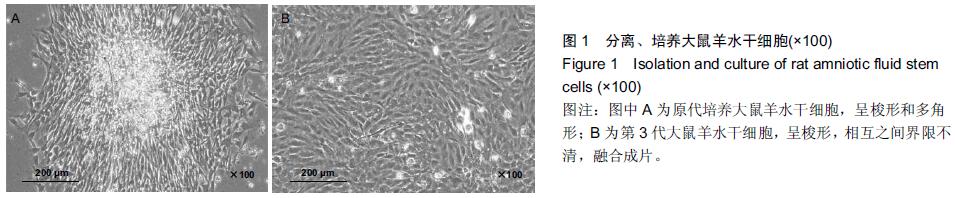
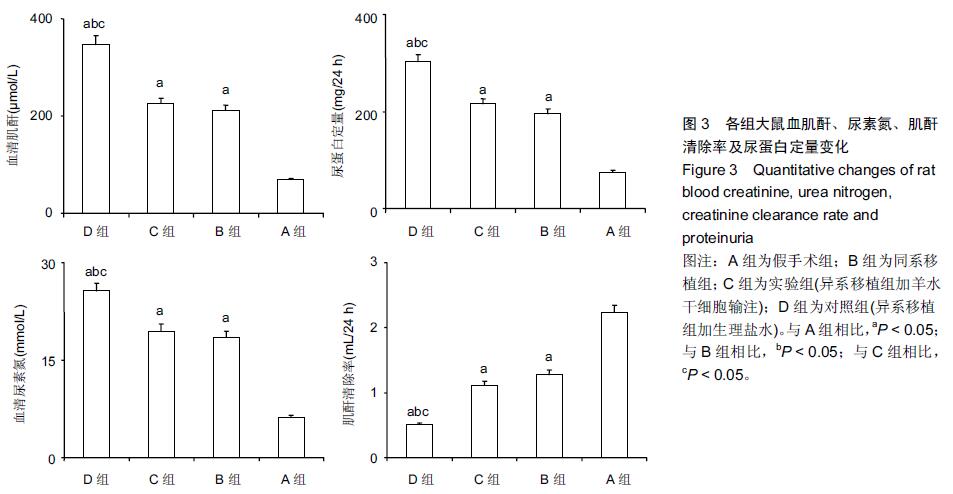
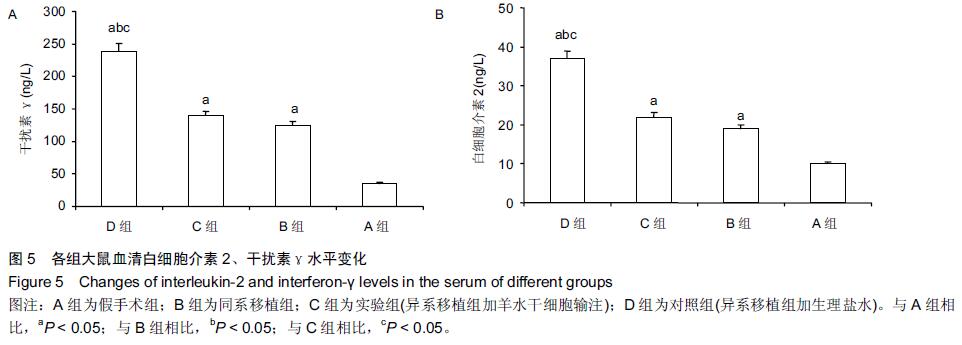
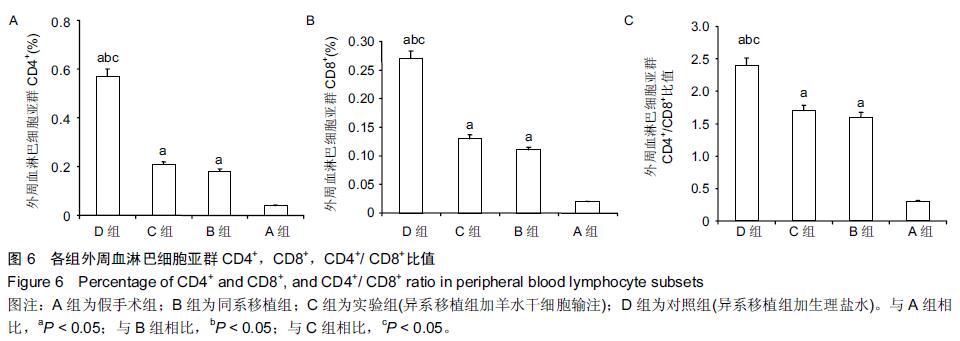
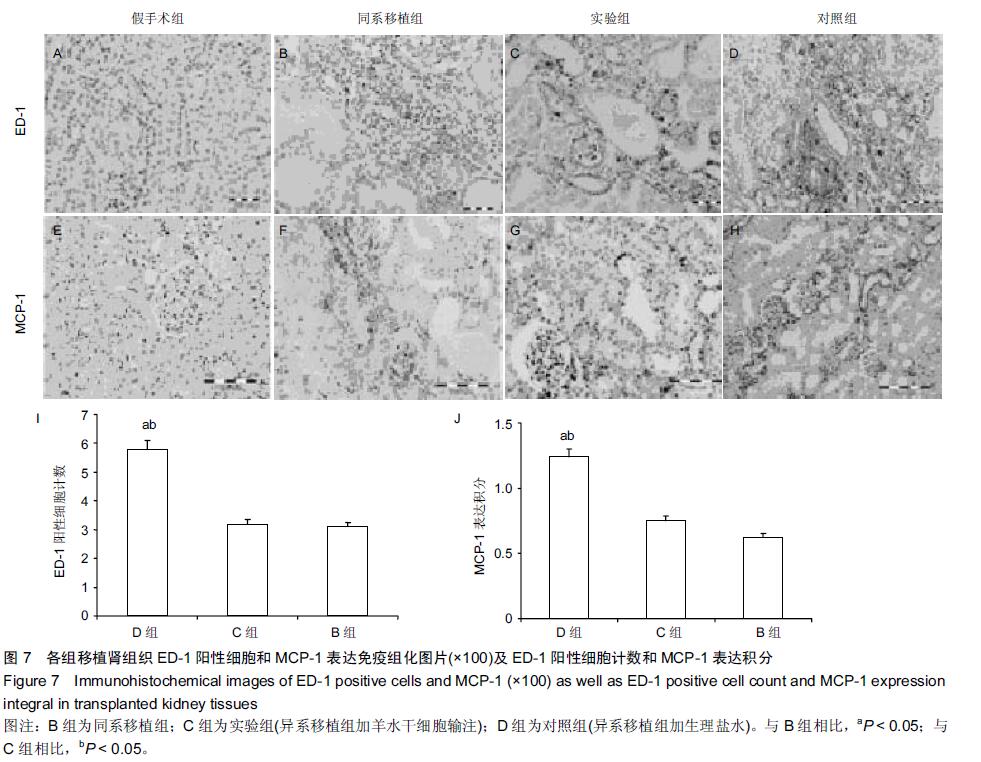
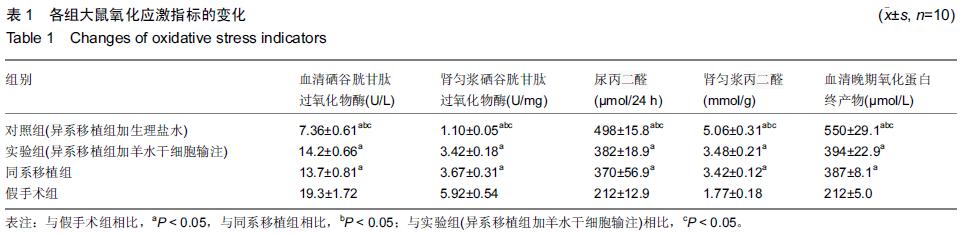
[2] Le Blanc K, Tammik L, Sundberg B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit and stimulate mixed lymphocyte cultures and mitogenic responses independently of the major histocompatibility complex. Scand J Immunol. 2003;57(1): 11-20.
[3] González MA, Gonzalez-Rey E, Rico L, et al. Treatment of experimental arthritis by inducing immune tolerance with human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(4):1006-1019.
[4] González MA, Gonzalez-Rey E, Rico L, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental colitis by inhibiting inflammatory and autoimmune responses. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(3):978-989.
[5] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005; 105(4):1815-1822.
[6] 赵霞,贺韦东,马秀明,等.骨髓间充质干细胞体外对T淋巴细胞分泌IL-2、IL-4功能的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2008,24(2):126- 130.
[7] Okusa MD.The inflammatory cascade in acute ischemic renal failure. Nephron. 2002;90(2):133-138.
[8] Ho JH, Tseng TC, Ma WH, et al. Multiple intravenous transplantations of mesenchymal stem cells effectively restore long-term blood glucose homeostasis by hepatic engraftment and β-cell differentiation in streptozocin- induced diabetic mice. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(5):997-1009.
[9] De Coppi P, Bartsch G Jr, Siddiqui MM, et al. Isolation of amniotic stem cell lines with potential for therapy. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(1):100-106.
[10] Degenhardt TP, Grass L, Reddy S, et al. Technical note. The serum concentration of the advanced glycation end-product N epsilon-(carboxymethyl)lysine is increased in uremia.Kidney Int. 1997;52(4):1064-1067.
[11] Sebeková K, Blazícek P, Syrová D, et al. Circulating advanced glycation end product levels in rats rapidly increase with acute renal failure. Kidney Int Suppl. 2001;78:S58-62.
[12] He C, Sabol J, Mitsuhashi T, et al. Dietary glycotoxins: inhibition of reactive products by aminoguanidine facilitates renal clearance and reduces tissue sequestration. Diabetes. 1999;48(6):1308-1315.
[13] Faist V, Erbersdobler HF. Metabolic transit and in vivo effects of melanoidins and precursor compounds deriving from the Maillard reaction. Ann Nutr Metab. 2001;45(1):1-12.
[14] Flohé L, Günzler WA. Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:114-121.
[15] Racusen LC, Solez K, Colvin RB, et al. The Banff 97 working classification of renal allograft pathology. Kidney Int. 1999; 55(2):713-723.
[16] Nagano H, Nadeau KC, Takada M, et al. Sequential cellular and molecular kinetics in acutely rejecting renal allografts in rats. Transplantation. 1997;63(8):1101-1108.
[17] Li B, Hartono C, Ding R, et al. Noninvasive diagnosis of renal-allograft rejection by measurement of messenger RNA for perforin and granzyme B in urine. N Engl J Med. 2001;344 (13):947-954.
[18] De Martino M, Zonta S, Rampino T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells infusion prevents acute cellular rejection in rat kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2010;42(4):1331-1335.
[19] Li Volti G, Sorrenti V, Murabito P, et al. Pharmacological induction of heme oxygenase-1 inhibits iNOS and oxidative stress in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplant Proc. 2007;39(10):2986-2991.
[20] 梁东彦,岳中瑾,包军胜,等.黄嘌呤氧化脱氢酶在大鼠肾移植急性排斥反应中的作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2008,25(3):349-350.
[21] Xiaoguang N, Zhong L, Hailong C, et al. The relation between apoptosis of acinar cells and nitric oxide during acute rejection of pancreas transplantation in rats. Transpl Immunol. 2003;11(1):15-21.
[22] Magnasco A, Corselli M, Bertelli R, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells protective effect in adriamycin model of nephropathy. Cell Transplant. 2008;17(10-11):1157-1167.