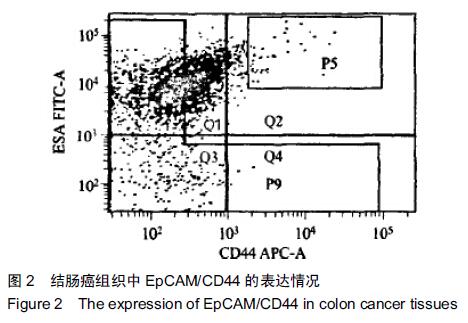
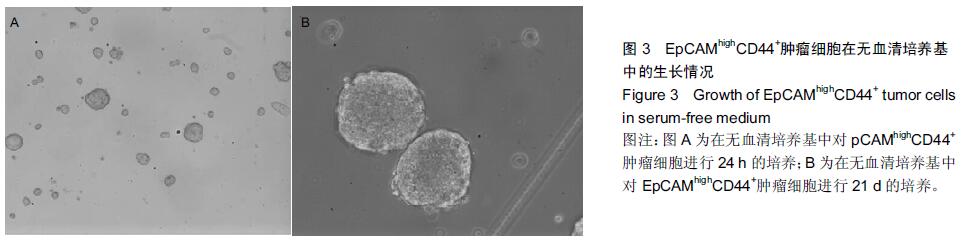
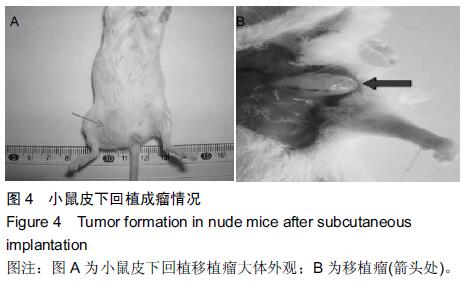
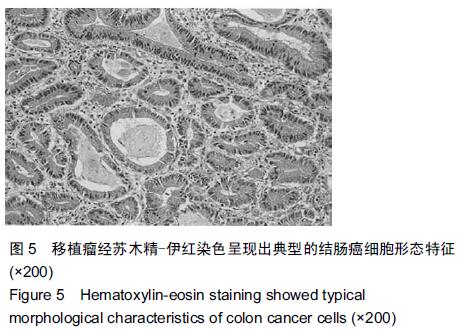
| [1] 翟荣林,张小明,王继亮,等.O6-甲基鸟嘌呤DNA甲基转移酶在结肠癌干细胞中的表达及其与结肠癌5-氟尿嘧啶获得性耐药的关系[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(2):248-250.
[2] Liu Y,Han ZP,Zhang SS, et al.Effects of inflammatory factors on mesenchymal stem cells and their role in the promotion of tumor angiogenesis in colon cancer. J Biol Chem. 2011;286 (28): 25007-25015.
[3] 邓艳红.塞来昔布下调干性标记物CD133表达靶向治疗结直肠癌干细胞的研究;EGFR在结直肠癌原发灶和淋巴结转移灶表达的对比研究[D].中山大学,2008.
[4] 饶军,杨景,吴峰,等.神经轴突导向分子Semaphorin 3F调节结肠癌细胞干细胞干性的研究[C].//第十届全国肿瘤转移学术大会论文集, 2013.
[5] Amsterdam A, Shezen E, Raanan C, et al. Two initiation sites of early detection of colon cancer revealed by localization of pERK1/2 in the nuclei or in aggregates at the perinuclear region of the tumor cells. Acta Histochem. 2013;115(6):569-576.
[6] Bourguignon LY,Peyrollier K,Xia WL, et al.Hyaluronan-CD44 interaction activates stem cell marker Nanog, Stat-3-mediated MDR1 gene expression, and ankyrin-regulated multidrug efflux in breast and ovarian tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283(25):17635-17651.
[7] Lin L, Fuchs J, Li,C, et al. STAT3 signaling pathway is necessary for cell survival and tumorsphere forming capacity in ALDH +/CD133 + stem cell-like human colon cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;416(3/4):246-251.
[8] Amsterdam A, Raanan C, Schreiber L, et al. Use of multiple biomarkers for the localization and characterization of colon cancer stem cells by indirect immunocytochemistry. Int J Oncol. 2012;41(1):285-291.
[9] Kobayashi S, Yamada-Okabe H, Suzuki M, et al.LGR5-positive colon cancer stem cells interconvert with drug-resistant LGR5-negative cells and are capable of tumor reconstitution.Stem Cells. 2012;30(12):2631-2644.
[10] Lin JT, Wang JY, Chen MK, et al. Colon cancer mesenchymal stem cells modulate the tumorigenicity of colon cancer through interleukin 6. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(14):2216-2229.
[11] Santos IS, Ponte BM, Boonme P, et al. Nanoencapsulation of polyphenols for protective effect against colon-rectal cancer. (Special Issue: Pearl (30th) Anniversary Edition: Nanotechnology and regenerative medicine). Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(5):514-523.
[12] 陈克力,梁后杰,江恒,等.人HCT116结肠癌细胞系中CD133+结肠癌干细胞分离及鉴定[J].第三军医大学学报,2009,31(4): 330-333.
[13] 朱其勇,吴可,黄海宁,等.T3期大肠癌患者新辅助化疗与手术前后外周血T细胞亚群变化的研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2013, (12): 2261-2264.
[14] 王居峰,刘莺,刘文静,等.RNA干扰Nucleostemin基因对人结肠癌细胞株HT-29细胞增殖及细胞周期的影响[J].华中师范大学学报(自然科学版),2010,44(3):463-467.
[15] Thirabunyanon M, Hongwittayakorn P. Potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria of human origin induce antiproliferation of colon cancer cells via synergic actions in adhesion to cancer cells and short-chain fatty acid bioproduction. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2013;169(2):511-525.
[16] 沈雄飞. 腹腔镜辅助结直肠癌手术并发症相关风险因素分析[D].重庆医科大学,2011.
[17] 张金龙,王海娟,刘健,等.结肠癌组织中MTA1的表达水平及定位与患者预后的相关性研究[J].癌症进展,2012,10(3):216-220.
[18] 孙昭,薛春玲,高鹤丽,等.脂肪间充质干细胞分泌的Exosome促进结肠癌细胞系上皮间质转化[J].癌症进展,2015,13(3):312-316.
[19] 王瑞海.肿瘤干细胞的分离培养及生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27):5087-5090.
[20] 时伟红,刘京津,王我惟,等.信号通路β-连环蛋白在人结肠癌cc1227细胞及其肿瘤球细胞中的表达[C].//2011年第9届中国北方实验动物科技年会论文集,2011:69-71.
[21] 夏维,田锐,秦仁义,等.干细胞相关基因Oct-4在人肿瘤细胞系中的表达及其意义[J].胰腺病学,2007,7(6):360-362.
[22] 李宁,张力,陈小兵,等.干细胞标志物Oct-4Sox-2表达与结肠癌术后复发转移的关系[J].中国肿瘤临床,2012,39(9):574-577.
[23] 陈方军,刘玉兰,张育军,等.结肠癌干细胞生物学特性研究进展[J].第二军医大学学报,2014,35(11):1262-1266.
[24] 方仕,龙健婷,张冰,等.结肠癌干细胞样细胞的体外培养、鉴定及n-3多不饱和脂肪酸对结肠癌干细胞样细胞的抗增殖作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2014,30(12):2135-2141.
[25] Apostolou P, Toloudi M, Ioannou E, et al. Study of the interaction among Notch pathway receptors, correlation with stemness, as well as their interaction with CD44, dipeptidyl peptidase-IV, hepatocyte growth factor receptor and the SETMAR transferase, in colon cancer stem cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2013;33(6):353-358.
[26] Benoit YD, Witherspoon MS, Laursen KB, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of polycomb repressive complex-2 activity induces apoptosis in human colon cancer stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(10):1463-1470.
[27] 邓艳红,黄美近,汪建平,等.5氟尿嘧啶上调干细胞标记物CD133在结肠癌细胞中的表达[J].中国病理生理杂志,2009,25(11): 2187-2191.
[28] 韩军平,刘斌,林艳丽,等.结直肠癌及人结肠癌细胞系SW620中CD44+/Ki-67-癌细胞的表达及意义[J].临床与实验病理学杂志, 2012,28(6):608-612.
[29] 艾亮,刘美,陈宓,等.结肠腺癌中结肠癌干细胞的分离、鉴定[J].世界科技研究与发展,2011,33(1):141-147,96.
[30] 陈全莉,程慧敏,李琳琳,等.三氧化二砷对人结肠癌SW620细胞OCT4和FOXO3a因子表达影响的研究[J].医学研究生学报, 2013,26(7):695-699.
[31] Massey AR, Reddivari L,Vanamala J, et al. The Dermal Layer of Sweet Sorghum {Sorghum bicolor) Stalk, a Byproduct of Biofuel Production and Source of Unique 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins, Has More Antiproliferative and Proapoptotic Activity than the Pith in p53 Variants of HCT116 and Colon Cancer Stem Cells. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. [Epub ahead of print]
[32] 李逸仙,孙保存,刘志勇,等.血管内皮诱导培养基促进结肠癌细胞向血管内皮细胞方向分化的研究[J].中国肿瘤临床,2014,41(10): 620-623.
[33] Amsterdam A, Shezen E, Raanan C, et al. Two initiation sites of early detection of colon cancer, revealed by localization of pERK1/2 in the nuclei or in aggregates at the perinuclear region of tumor cells. Int J Oncol. 2012;40(3):782-788.
[34] De Boeck A, Hendrix A, Maynard D, et al. Differential secretome analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts and bone marrow-derived precursors to identify microenvironmental regulators of colon cancer progression. Proteomics. 2013; 13(2):379-388.
[35] D'Anselmi F, Cucina A, Biava PM, et al. Zebrafish Stem Cell Differentiation Stage Factors Suppress Bcl-xL Release and Enhance 5-Fu-Mediated Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2011;12(2):261-267.
[36] Shinagawa K, Kitadai Y, Tanaka M, et al. Stroma-directed imatinib therapy impairs the tumor-promoting effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in an orthotopic transplantation model of colon cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013; 132(4):813-823.
[37] 张庆玲,汪志勋,丁彦青,等.CD133/1及Klf4蛋白免疫荧光共定位分析鉴定结直肠癌肿瘤干细胞[J].广东医学,2012,33(15): 2262-2264.
[38] 冯燕君,夏璐,李晓露,等.HT29和HCT116结肠癌细胞无血清培养形成肿瘤干细胞球特性的差异性研究[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2011,20(10):892-896.
[39] 杜敏,葛海燕,徐彬,等.外源性Muc1、Survivin和Nanog基因启动子在结肠癌干细胞中的表达活性[J].第二军医大学学报,2012, 33(10):1082-1085.
[40] 陈克力,江恒,陈建芳,等.人结肠癌HCT116细胞系肿瘤干细胞特性研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2009,34(11):1292-1296.
|