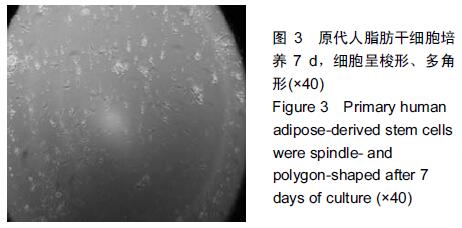
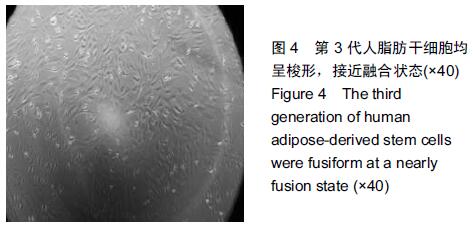
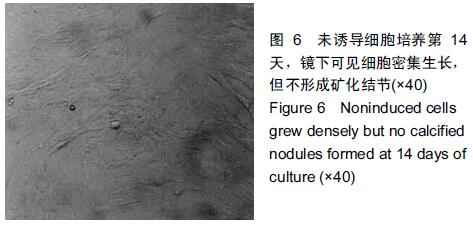
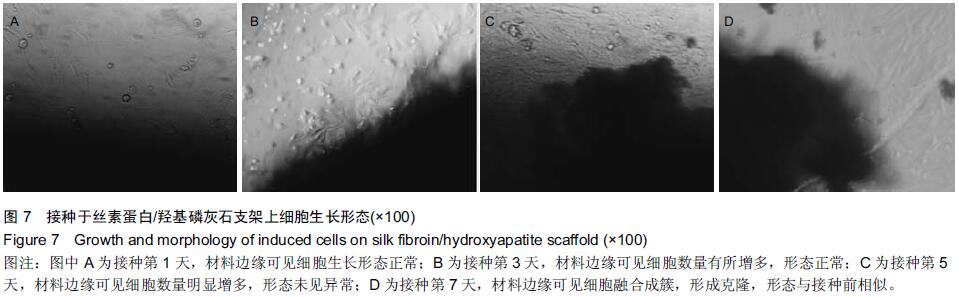
|
[1] 李小军,王文礼,刘海波.椎弓根钉系统固定结合经椎弓根自体骨移植治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折疗效分析[J].四川医学, 2012,33(9): 1597-1599.
[2] 林博文,黎伟凡,王华,等.异体骨移植在髋关节翻修术中应用的10年随访[J].中华关节外科杂志,2012,6(4):523-529.
[3] 郑华,何盛江,王群波.锁定钢板加同种异体骨移植治疗老年肱骨近端骨折[J].创伤外科杂志, 2012,14(2):130-132.
[4] 张大伟,田清业,刘光军,等.骨膜瓣复合异体骨移植修复大段骨缺损[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2012,8(1):26-31.
[5] 胡堃,刘斌. 骨移植材料发展趋势[J]. 生物骨科材料与临床研究, 2010,7(3):32-38.
[6] 王迎军,杜昶,赵娜如,等.仿生人工骨修复材料研究[J].华南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2012,40(10):51-58.
[7] 闵理,刘立岷,宋跃明,等.不同种类骨移植在青少年特发性脊柱侧凸后路矫形术中的中长期疗效评价[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2012, 5(5):382-388.
[8] Fraser JK, Wulur I, Alfonso Z, et al. Fat tissue: an underappreciated source of stem cells for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2006;24(4):150-154.
[9] Cirillo B, Morra M, Catapano G. Adhesion and function of rat liver cells adherent to silk fibroin/collagen blend films. Int J Artif Organs. 2004;27(1):60-68.
[10] 赵天源,孙红.骨组织工程支架材料及其血管化的研究进程[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(38): 6832-6838.
[11] Rodrigues CV, Serricella P, Linhares AB, et al. Characterization of a bovine collagen-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003;24(27):4987-4997.
[12] Hutmacher DW. Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials. 2000;21(24):2529-2543.
[13] Brittberg M, Nilsson A, Lindahl A, et al. Rabbit articular cartilage defects treated with autologous cultured chondrocytes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;(326):270-283.
[14] Itoh S, Kikuchi M, Takakuda K, et al. The biocompatibility and osteoconductive activity of a novel hydroxyapatite/collagen composite biomaterial, and its function as a carrier of rhBMP-2. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;54(3):445-453.
[15] 陈晓庆,杨惠林,干旻峰,等. 丝素蛋白对磷酸钙骨水泥抗压强度及注射性的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008, 12(45): 8985-8988.
[16] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.
[17] 覃杰,闫翠,陈极锋,等.碱性成纤维生长因子对脂肪干细胞分化为心肌细胞的影响[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2015,36(3): 346-351.
[18] 刘志,关键,段峰,等. 载辛伐他汀纳米羟基磷灰石支架材料对兔下颌骨缺损修复的影响[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志, 2013, 23(1): 14-17.
[19] Nerem RM, Sambanis A. Tissue engineering: from biology to biological substitutes. Tissue Eng. 1995;1(1):3-13.
[20] Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983;65(1-2):55-63.
[21] 朱文菁,金慰芳,张丽丽,等. MTT法分析培养成骨细胞的存活和增殖能力[J]. 上海医科大学学报, 1995, 22(4): 254-257.
[22] 胡江伟,王亮,马远征,等. Wnt3a 信号分子对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中端粒酶活性的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014, 20(1): 33-37. |