中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (43): 6940-6945.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.43.010
• 细胞外基质材料 extracellular matrix materials • 上一篇 下一篇
脱细胞真皮基质修复猪胆管缺损:促进血管及胆管上皮再生
陈 刚,白建华,朱新锋,曹 俊,刘其雨,赵英鹏,李 立
- 昆明市第一人民医院肝胆外科,云南省昆明市 650011
Acellular dermal matrix for repair of porcine bile duct defects: to promote vascular and bile duct epithelial regeneration
Chen Gang, Bai Jian-hua, Zhu Xin-feng, Cao Jun, Liu Qi-yu, Zhao Ying-peng, Li Li
- Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the First People’s Hospital of Kunming, Kunming 650011, Yunnan Province, China
摘要:
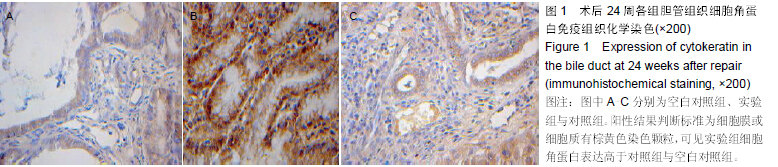
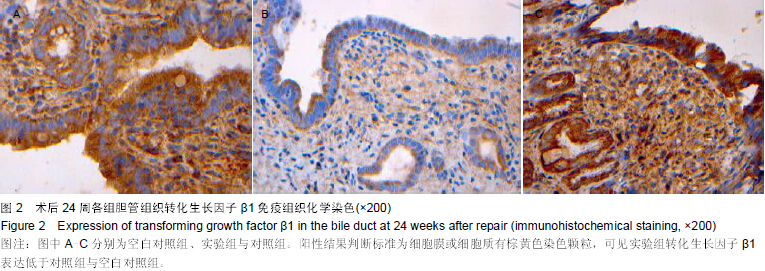
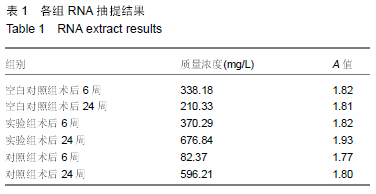
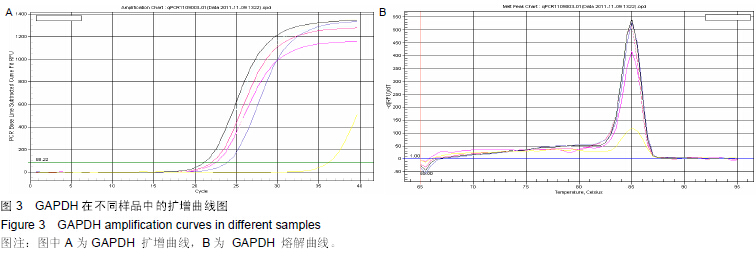
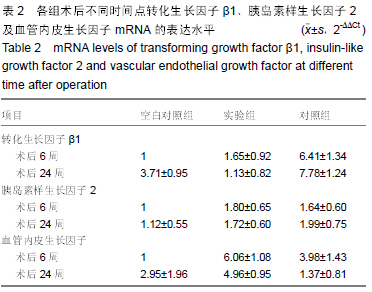
背景:脱细胞真皮基质是无细胞的天然组织支架,与人体软组织十分相近,易于塑形,无毒副作用,已被用于修补尿道与输尿管。 目的:观察脱细胞基质修补胆管损伤的效果。 方法:将30头滇南小耳猪随机均分为3组,空白对照组切断胆管后行端端吻合,实验组人为制作胆管缺损后以脱细胞真皮基质修补,对照组人为制作胆管缺损后以膨体聚四氟乙烯修补。修补后6,24周取胆管补片及其周围组织,进行免疫组织化学与RT-PCR检测。 结果与结论:免疫组织化学显示,实验组细胞角蛋白表达高于空白对照组与对照组,转化生长因子β1表达低于空白对照组与对照组。术后24周内RT-PCR检测显示,实验组总体转化生长因子β1基因表达低于空白对照组与对照组(P < 0.05),总体胰岛素样生长因子2基因表达高于空白对照组(P < 0.05),总体血管内皮生长因子基因表达高于空白对照组与对照组(P < 0.05)。表明脱细胞基质修复胆道损伤可促进血管及胆管上皮的再生,并且不增加瘢痕的形成。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程