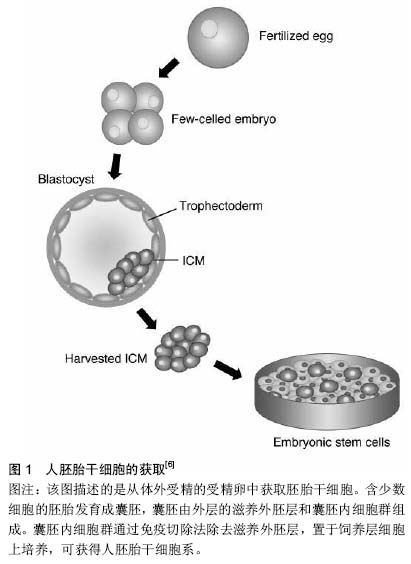
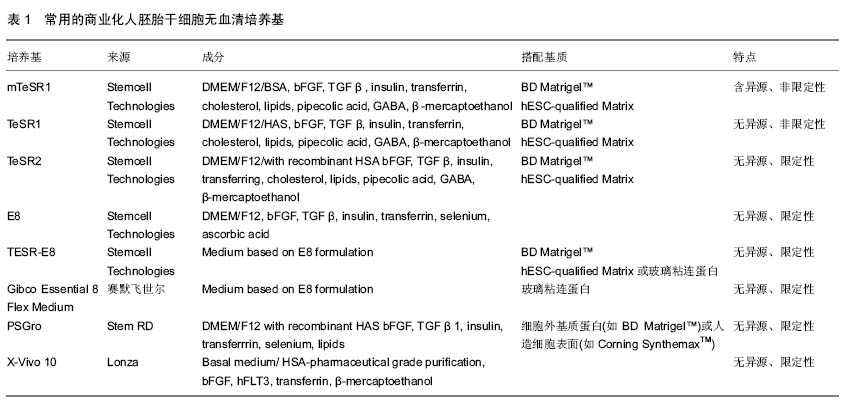
|
[1] Desai N, Rambhia P, Gishto A. Human embryonic stem cell cultivation: historical perspective and evolution of xeno-free culture systems Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015;13:9.
[2] DeRouen MC, McCormick JB, Owen-Smith J, et al. The race is on: human embryonic stem cell research goes global. Stem Cell Rev. 2012;8(4):1043-1047.
[3] Amit M. Sources and derivation of human embryonic stem cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;997:3-11.
[4] Stephenson E, Jacquet L, Miere C, et al. Derivation and propagation of human embryonic stem cell lines from frozen embryos in an animal product-free environment. Nat Protoc. 2012;7(7):1366-1381.
[5] 王芳,陈绍威.胚胎体外培养及胚胎干细胞系的建立[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(14): 2273-2277.
[6] Landry DW, Zucker HA. Embryonic death and the creation of human embryonic stem cells. J Clin Invest. 2004;114(9):1184-1186.
[7] Campbell JM, Lane M, Vassiliev I, et al. Use of insulin to increase epiblast cell number: towards a new approach for improving ESC isolation from human embryos. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:150901.
[8] Chen Y, Lai D. Pluripotent states of human embryonic stem cells. Cell Reprogram. 2015;17(1):1-6.
[9] Sundberg M, Bogetofte H, Lawson T, et al. Improved cell therapy protocols for Parkinson's disease based on differentiation efficiency and safety of hESC-, hiPSC-, and non-human primate iPSC-derived dopaminergic neurons. Stem Cells. 2013;31(8):1548-1562.
[10] Sundberg M, Andersson PH, Åkesson E, et al. Markers of pluripotency and differentiation in human neural precursor cells derived from embryonic stem cells and CNS tissue. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(2):177-191.
[11] Agulnick AD, Ambruzs DM, Moorman MA, et al. Insulin-Producing Endocrine Cells Differentiated In Vitro From Human Embryonic Stem Cells Function in Macroencapsulation Devices In Vivo. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(10):1214-1222.
[12] Pal R, Mamidi MK, Das AK, et al. Comparative analysis of cardiomyocyte differentiation from human embryonic stem cells under 3-D and 2-D culture conditions. J Biosci Bioeng. 2013;115(2):200-206.
[13] Alsanie WF, Niclis JC, Petratos S. Human embryonic stem cell-derived oligodendrocytes: protocols and perspectives. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(18):2459-2476.
[14] Miki T, Ring A, Gerlach J. Hepatic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells is promoted by three-dimensional dynamic perfusion culture conditions. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(5):557-568.
[15] Schwartz SD, Regillo CD, Lam BL, et al. Human embryonic stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium in patients with age-related macular degeneration and Stargardt's macular dystrophy: follow-up of two open-label phase 1/2 studies. Lancet. 2015;385(9967):509-516.
[16] Bose B, Katikireddy KR, Shenoy PS. Regenerative medicine for diabetes: differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into functional β-cells in vitro and their proposed journey to clinical translation. Vitam Horm. 2014;95:223- 248.
[17] Ambasudhan R, Dolatabadi N, Nutter A, et al. Potential for cell therapy in Parkinson's disease using genetically programmed human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitor cells. J Comp Neurol. 2014;522(12):2845-2856.
[18] Volz KS, Miljan E, Khoo A, et al. Development of pluripotent stem cells for vascular therapy. Vascul Pharmacol. 2012; 56(5-6):288-296.
[19] Rafii S, Kloss CC, Butler JM, et al. Human ESC-derived hemogenic endothelial cells undergo distinct waves of endothelial to hematopoietic transition. Blood. 2013;121(5): 770-780.
[20] Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18(4):399-404.
[21] Cobo F, Navarro JM, Herrera MI, et al. Electron microscopy reveals the presence of viruses in mouse embryonic fibroblasts but neither in human embryonic fibroblasts nor in human mesenchymal cells used for hESC maintenance: toward an implementation of microbiological quality assurance program in stem cell banks. Cloning Stem Cells. 2008;10(1):65-74.
[22] Huang Y, Gregori L, Anderson SA, et al. Development of dose-response models of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease infection in nonhuman primates for assessing the risk of transfusion- transmitted variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Virol. 2014; 88(23):13732-13736.
[23] Lee EJ, Kang HJ, Lee HN, et al. New culture system for human embryonic stem cells: autologous mesenchymal stem cell feeder without exogenous fibroblast growth factor 2. Differentiation. 2012;83(1):92-100.
[24] Park Y, Choi IY, Lee SJ, et al. Undifferentiated propagation of the human embryonic stem cell lines, H1 and HSF6, on human placenta-derived feeder cells without basic fibroblast growth factor supplementation. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(11): 1713-1722.
[25] Desai N, Ludgin J, Goldberg J, et al. Development of a xeno-free non-contact co-culture system for derivation and maintenance of embryonic stem cells using a novel human endometrial cell line. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30(5): 609-615.
[26] Ma X, Li H, Xin S, et al. Human amniotic fluid stem cells support undifferentiated propagation and pluripotency of human embryonic stem cell without b-FGF in a density dependent manner. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(8):4661-4673.
[27] Ávila-González D, Vega-Hernández E, Regalado-Hernández JC, et al. Human amniotic epithelial cells as feeder layer to derive and maintain human embryonic stem cells from poor-quality embryos. Stem Cell Res. 2015;15(2):322-324.
[28] 刘峰,徐永胜,俞海燕,等.人脐带间充质干细胞作为维持人胚胎干细胞生长饲养层细胞的研究[J].中国实验动物学报, 2011, 19(4): 271-276.
[29] Kaur J, Tilkins ML. Methods for culturing human embryonic stem cells on feeders. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;997:93-113.
[30] Fu X, Toh WS, Liu H, et al. Autologous feeder cells from embryoid body outgrowth support the long-term growth of human embryonic stem cells more effectively than those from direct differentiation. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(4): 719-733.
[31] Tsai ZY, Singh S, Yu SL, et al. A feeder-free culture using autogeneic conditioned medium for undifferentiated growth of human embryonic stem cells: comparative expression profiles of mRNAs, microRNAs and proteins among different feeders and conditioned media. BMC Cell Biol. 2010;11:76.
[32] Bigdeli N, Andersson M, Strehl R, et al. Adaptation of human embryonic stem cells to feeder-free and matrix-free culture conditions directly on plastic surfaces. J Biotechnol. 2008; 133(1):146-153.
[33] Abraham S, Sheridan SD, Laurent LC, et al. Propagation of human embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cells in an indirect co-culture system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;393(2):211-216.
[34] Hakala H, Rajala K, Ojala M, et al. Comparison of biomaterials and extracellular matrices as a culture platform for multiple, independently derived human embryonic stem cell lines. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(7):1775-1785.
[35] Montes R, Ligero G, Sanchez L, et al. Feeder-free maintenance of hESCs in mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned media: distinct requirements for TGF-beta and IGF-II. Cell Res. 2009;19(6):698-709.
[36] Priddle H, Allegrucci C, Burridge P, et al. Derivation and characterisation of the human embryonic stem cell lines, NOTT1 and NOTT2. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2010; 46(3-4):367-375.
[37] Meng G, Liu S, Li X, et al. Extracellular matrix isolated from foreskin fibroblasts supports long-term xeno-free human embryonic stem cell culture. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(4): 547-556.
[38] Fu X, Toh WS, Liu H, et al. Establishment of clinically compliant human embryonic stem cells in an autologous feeder-free system. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2011;17(9): 927-937.
[39] Wang Q, Mou X, Cao H, et al. A novel xeno-free and feeder-cell-free system for human pluripotent stem cell culture. Protein Cell. 2012;3(1):51-59.
[40] Zhu H, Yang J, Wei Y, et al. Development of a xeno-free substrate for human embryonic stem cell growth. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:621057.
[41] Khoo TS, Hamidah Hussin N, Then SM, et al. Autogenic feeder free system from differentiated mesenchymal progenitor cells, maintains pluripotency of the MEL-1 human embryonic stem cells. Differentiation. 2013;85(3):110-118.
[42] 陈厚良,陈宇.人胚胎干细胞培养体系的研究进展[J].安徽医科大学学报, 2014, 49(12):1834-1837.
[43] Rodin S, Antonsson L, Niaudet C, et al. Clonal culturing of human embryonic stem cells on laminin-521/E-cadherin matrix in defined and xeno-free environment. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3195.
[44] Melkoumian Z, Weber JL, Weber DM, et al. Synthetic peptide-acrylate surfaces for long-term self-renewal and cardiomyocyte differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(6):606-610.
[45] Jin S, Yao H, Weber JL, et al. A synthetic, xeno-free peptide surface for expansion and directed differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(11): e50880.
[46] Kawase E. Efficient Expansion of Dissociated Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Using a Synthetic Substrate. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1307:61-69.
[47] Wu S, Johansson J, Damdimopoulou P, et al. Spider silk for xeno-free long-term self-renewal and differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells. Biomaterials. 2014;35(30):8496-8502.
[48] Jang M, Lee ST, Kim JW, et al. A feeder-free, defined three-dimensional polyethylene glycol-based extracellular matrix niche for culture of human embryonic stem cells. Biomaterials. 2013;34(14):3571-3580.
[49] Lee ST, Yun JI, Jo YS, et al. Engineering integrin signaling for promoting embryonic stem cell self-renewal in a precisely defined niche. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6):1219-1226.
[50] Lee ST, Jang M, Lee G, et al. Development of three dimensional culture and expression of integrin heterodimers in human embryonic stem cells. Organogenesis. 2013;9(3): 143-148.
[51] Wang Y, Cheng L, Gerecht S. Efficient and scalable expansion of human pluripotent stem cells under clinically compliant settings: a view in 2013. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014; 42(7):1357-1372.
[52] Badenes SM, Fernandes TG, Rodrigues CA, et al. Scalable expansion of human-induced pluripotent stem cells in xeno-free microcarriers. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1283:23-29.
[53] Want AJ, Nienow AW, Hewitt CJ, et al. Large-scale expansion and exploitation of pluripotent stem cells for regenerative medicine purposes: beyond the T flask. Regen Med. 2012; 7(1):71-84.
[54] Oh SK, Chen AK, Mok Y, et al. Long-term microcarrier suspension cultures of human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2009;2(3):219-230.
[55] Marinho PA, Vareschini DT, Gomes IC, et al. Xeno-free production of human embryonic stem cells in stirred microcarrier systems using a novel animal/human- component-free medium. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013; 19(2):146-155.
[56] Steiner D, Khaner H, Cohen M, et al. Derivation, propagation and controlled differentiation of human embryonic stem cells in suspension. Nat Biotechnol. 2010;28(4):361-364.
[57] Freitas ER, Santos RL, Lima EC, et al. Feeder-free culture of human embryonic stem cell line BG01V/hOG using magnetic field-magnetic nanoparticles system. Biomed Pharmacother. 2013;67(1):17-21.
Chen X, Prowse AB, Jia Z, et al. Thermoresponsive worms for expansion and release of human embryonic stem cells. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(3):844-855. |