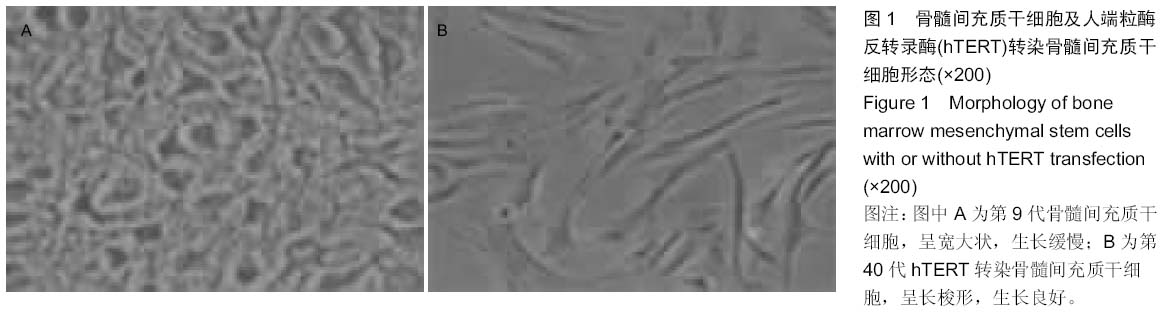
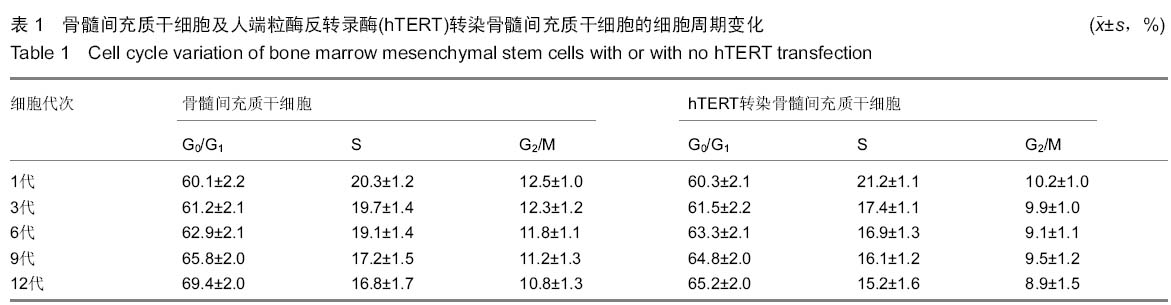
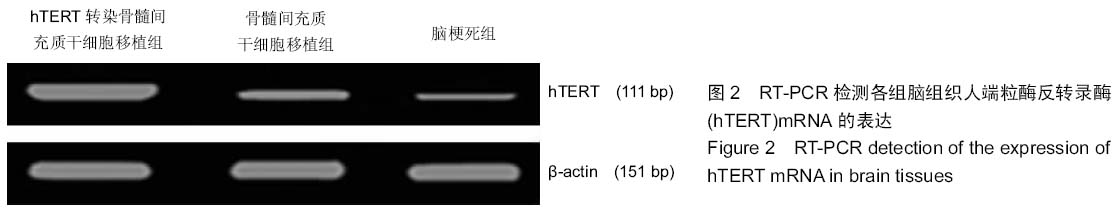
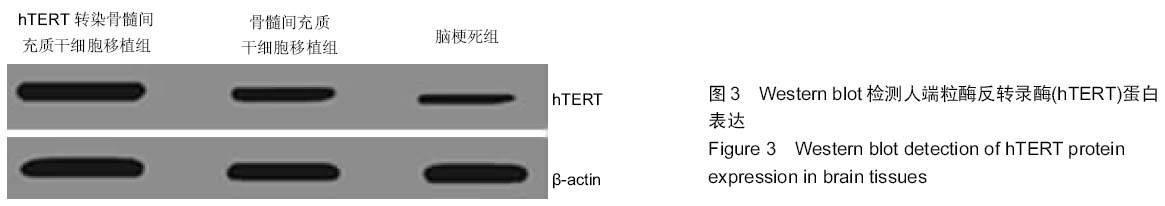
|
[1] 王小红,郑美霞.438例脑梗死患者自身免疫性抗体检测的结果分析[J].放射免疫学杂志,2013,26(1):118-119.
[2] Peng Y, Zhang QM, You H, et al. Growth-associated protein 43 and neural cell adhesion molecule expression follow-ing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2010; 5(13):975-980.
[3] 解启瑞.急性脑梗死溶栓和非溶栓治疗效果对比[J].吉林医学, 2013,34(4):651-652.
[4] Jensen JK, Hallén J, Lund T, et al. Troponin I degradation in serum of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2011;71(1):74-80.
[5] Rafferty M, Walters MR, Dawson J. Anti-platelet therapy and aspirin resistance - clinically and chemically relevant. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(36):4578-4586.
[6] 郑朋.脑梗死患者的饮食现状生活态度及行为方式调查分析[J].山西医药杂志,2010,39(4):311-312.
[7] Jin R, Yang G, Li G. Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: role of inflammatory cells. J Leukoc Biol. 2010;87(5): 779-789.
[8] 崔立玲,黄国志,王康玲,等.重复经颅磁刺激联合高压氧治疗脑梗死患者的初步研究[J].中华物理医学杂志,2013,35(3):193-196.
[9] Hayase M, Kitada M, Wakao S, et al. Committed neural progenitor cells derived from genetically modified bone marrow stromal cells ameliorate deficits in a rat model of stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(8):1409-1420.
[10] 刘桂芳.急性脑梗死的治疗进展[J].中国民康医学,2014, 26(4): 90-92.
[11] Li J, Zhu H, Liu Y, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation protects against cerebral ischemic injury and upregulates interleukin-10 expression in Macacafascicularis. Brain Res. 2010;1334:65-72.
[12] 张洪连,吴晓牧.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死及存在问题[J].中华脑血管病杂志:电子版,2010,4(4):300-307.
[13] van Velthoven CT, Kavelaars A, van Bel F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell treatment after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury improves behavioral outcome and induces neuronal and oligodendrocyte regeneration. Brain Behav Immun. 2010;24(3):387-393.
[14] 帕丽哈•巴依道列提,兴红. 脑梗死患者危险因素的临床分析[J].中国实用医药,2010,5(8):127-128.
[15] 赵小妹,刘永刚.骨髓间充质干细胞与上清液治疗大鼠脑梗死的疗效[J].新乡医学院学报,2012,29(8):571-574.
[16] 王光,王代第,杨方印,等.脑梗死患者的危险因素分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2009,12(9):42-43.
[17] Tsujita K, Shimomura H, Kawano H, et al. Effects of edaravone on reperfusion injury in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2004;94(4):481-484.
[18] 邬英全,邬巍,张力,等.急性脑梗死的一级及二级的预防[J].中国实用内科杂志,2009,29(11):980-981.
[19] 曹宏旺.急性脑梗死治疗及早期康复新进展[J].包头医学,2014, 38(1):3-5.
[20] Wang Y, Tu W, Lou Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells regulate the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells through Notch signaling. Cell Biol Int. 2009;33(11):1173-1179.
[21] 柳太云,熊符,林军,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞移植促进脑梗死大鼠神经细胞再生和神经功能恢复[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012, 16(1):70-75.
[22] Edaravone Acute Infarction Study Group. Effect of a novel free radical scavenger, edaravone (MCI-186), on acute brain infarction. Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study at multicenters. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003;15(3):222-229.
[23] Goto H, Fujisawa H, Oka F, et al. Neurotoxic effects of exogenous recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator on the normal rat brain. J Neurotrauma. 2007;24(4):745-752.
[24] Ansara AJ, Nisly SA, Arif SA, et al. Aspirin dosing for the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke: an indication-specific review of the literature. Ann Pharmacother. 2010;44(5):851-862.
[25] Zhang N, Komine-Kobayashi M, Tanaka R, et al. Edaravone reduces early accumulation of oxidative products and sequential inflammatory responses after transient focal ischemia in mice brain. Stroke. 2005;36(10):2220-2225.
[26] Yagi K, Kitazato KT, Uno M, et al. Edaravone, a free radical scavenger, inhibits MMP-9-related brain hemorrhage in rats treated with tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke. 2009;40(2): 626-631.
[27] Terao Y, Ohta H, Oda A, et al. Macrophage inflammatory protein-3alpha plays a key role in the inflammatory cascade in rat focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Res. 2009;64(1):75-82.
Abdallah BM, Haack-Sørensen M, Burns JS, et al. Maintenance of differentiation potential of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells immortalized by human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene despite [corrected] extensive proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;326(3):527-538. |