• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
脐带源间充质干细胞移植治疗肝纤维化及肝硬化的相关机制
孙慧聪,张国尊,郭金波,冯 燕,郑力搏,张晓岚
- 河北医科大学第二医院东院消化科,河北省石家庄市 050000
Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell tansplantation for liver fibrosis and cirrhosis
Sun Hui-cong, Zhang Guo-zun, Guo Jin-bo, Feng Yan, Zheng Li-bo, Zhang Xiao-lan
- Department of Gastroenterology, the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
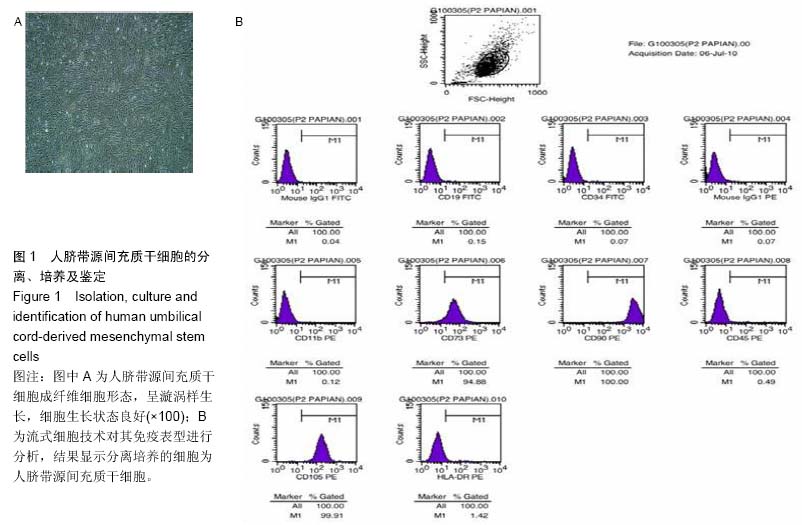
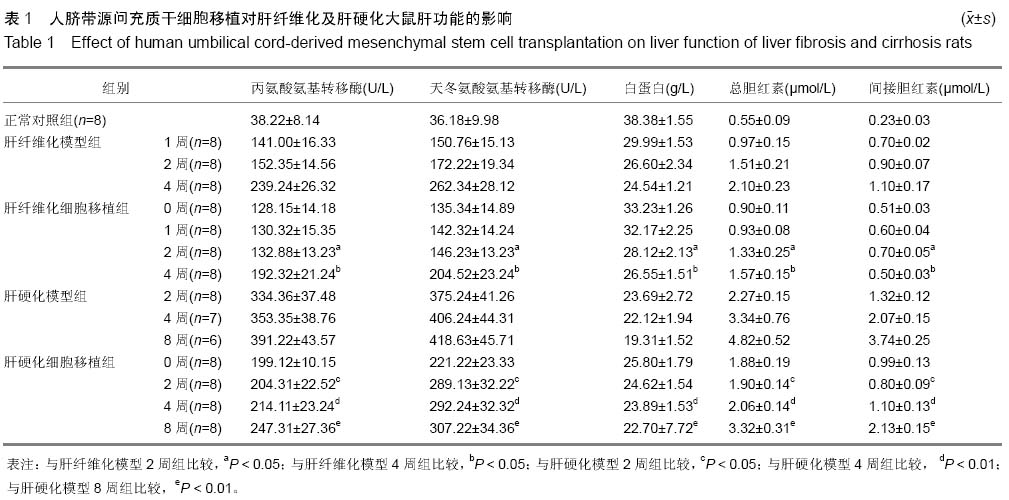
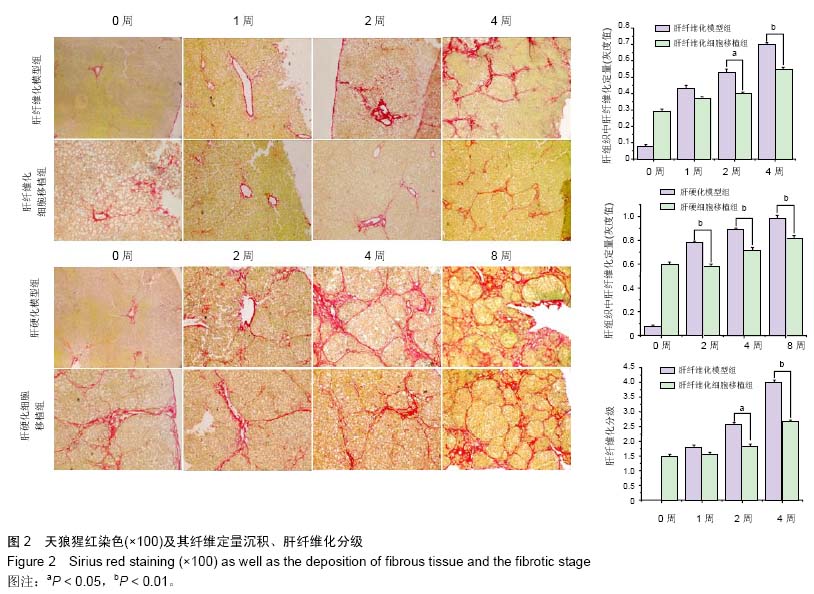
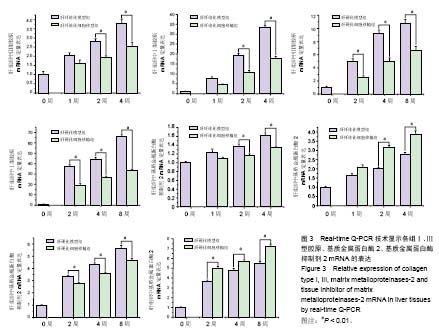
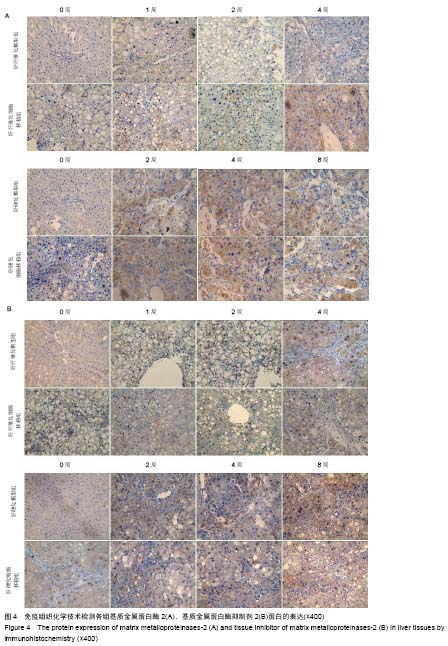
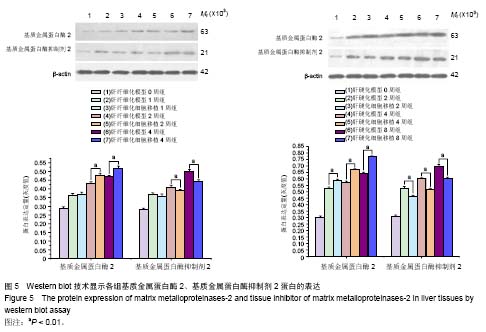
背景:肝硬化是多种原因引起的肝脏慢性病变,目前尚没有有效的治疗方法,很多研究表明,间充质干细胞对肝纤维化及肝硬化有一定的治疗作用。 目的:研究人脐带源间充质干细胞移植对大鼠肝纤维化及肝硬化的治疗作用及其作用机制。 方法:应用CCl4诱导制备肝纤维化及肝硬化模型,造模后经尾静脉注射人脐带间充质干细胞。细胞移植后采用Beckman Coulter analyzer检测人脐带源间充质干细胞移植对大鼠肝功能的影响;采用天狼猩红染色检测肝组织病理改变;应用免疫组织化学染色、Western blot和real-time Q-PCR方法检测Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原、基质金属蛋白酶2、基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2蛋白与mRNA在大鼠肝组织中的表达。 结果与结论:人脐带源间充质干细胞移植可以改善肝纤维化及肝硬化大鼠的肝功能。人脐带源间充质干细胞移植后,除肝纤维化细胞移植1周组与对应模型组相比差异无显著性意义外,其余各细胞移植组肝脏组织中基质金属蛋白酶2 mRNA及蛋白表达水平明显升高,而Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原、基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2表达水平明显降低。人脐带源间充质干细胞通过上调基质金属蛋白酶2表达,下调基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂2表达,对肝纤维化及肝硬化起到治疗作用;在致病因素持续存在的情况下,人脐带源间充质干细胞移植并不能逆转肝纤维化或者肝硬化,只能延缓肝纤维化或肝硬化的进程。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: