残根残冠是口腔科常见的临床疾病,传统的方法是将残根残冠拔除,再行修复治疗。由于拔除患牙存在一定的风险,并且越来越多的患者要求在保留患牙的基础上行牙体修复治疗
[19],因此在临床上如何妥善处理残根残冠就显得非常重要。近几年来根管治疗有了很大的发展,使得越来越多的残根残冠得以保留,但治疗过程中器械分离的意外也在逐渐增加。Wu等
[20]通过对前后牙距根尖不同距离横断面的研究得出,若将根管长径大于或等于短径2倍以上的根管定义为扁根管,大部分残根残冠的根管类型都属于扁根管。由于扁根管的结构特殊、形态复杂,临床上大部分器械分离的病例都发生在扁根管内
[21]。因此,若器械分离发生在这一类根管内,为了取出分离的器械常常要过度切削根管,这样做的结果会使根管的抗力与固位下降,甚至造成牙体侧穿。
Nevares等[22]通过研究发现若器械分离在根管内,可从分离器械旁建立通路到达根尖进行根管充填来实现完善的根管治疗。由于扁根管结构的特殊性,扁根管根管的横截面是不规则的圆形[23],器械在根管内分离后与根管部分内壁紧密嵌合,存在一定间隙,大部分患牙可从分离器械旁建直通路到达根尖,实现旁路根管的预备,但扁根管形态具有复杂性,存在很多不规则间隙,常规的冷测压技术很难实现根管的有效充填。热牙胶技术是利用牙胶在加热软化时能够顺应管壁的复杂形态,进入管腔的不规则间隙,达到较理想的三维根管充填效果[24],在充填过程中热牙胶能有效将分离器械紧密包裹、固定[25],而且与管壁有良好的密合性,能有效减少微渗漏的发生。
由于扁根管的结构特殊,特别是为了获得从分离器械旁到达根尖的通路,往往会在根管的某些部位进行不规则的预备,这样就使得复杂的扁根管形态变得更加复杂与不规则。由于旁路充填后扁根管形态的复杂性与不规则性,桩核对于牙体应力变化的特殊性,至今尚未找到一种合理的桩核修复系统适用于扁根管旁路充填后的牙体修复。
根折是桩核修复中最严重的并发症之一,特别是在形态结构较为复杂的扁根管内,桩核修复体如果选择不当,牙根折断的风险就会显著增加[26]。Raygot等[27]的研究中倾向于选择更坚硬不易折断的桩核系统,这样即使桩的直径较小也能够达到所需强度,牙体组织可得到更多的保留,牙根抗折力更强。而近年来的大量研究认为,如果桩的弹性模量高出牙本质的弹性模量很多,当桩核修复体承受较大咬合力时,应力集中在桩的末端,根尖区的牙体首先发生折裂;当桩的弹性模量与牙本质相接近时,因牙根内的应力分布比较均匀,受力时应力较分散,根尖区牙体发生折裂的可能性会相应降低[28-30]。
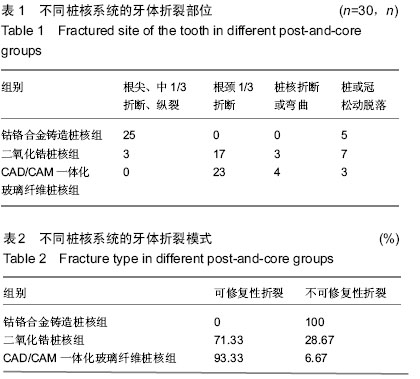
目前认为桩的弹性模量不超过牙本质弹性模量值2倍时的根折发生概率较小[31],本实验结果也证实了这一点。本实验中弹性模量最高的钴铬合金桩修复后牙根的抗折力最高,但牙根折裂全部发生在根尖及根中1/3,为不可修复性破坏,完全无法进行再次修复。二氧化锆桩弹性模量接近钴铬合金,但脆性相对较大[32],承受较大咬合力时桩会出现折断,牙根反而受到保护,本实验中其修复后的抗折力低于钴铬合金铸造桩核组,但高于CAD/CAM一体化玻璃纤维桩组,出现了3例桩的折断,牙根折裂多发生在牙根颈部,多为可修复性破坏,但二氧化锆桩发生折裂后在临床上往往预后较差,分析原因为二氧化锆桩几乎无法用钻针拆除[33],同时由于经旁路治疗后扁根管的牙体结构较为复杂[34],难以将折断后的二氧化锆桩核彻底去除,所以二氧化锆桩折断后患牙很难能够再次修复。而弹性模量最接近牙本质的CAD/CAM一体化纤维桩,虽然修复后牙根抗折力相对较小,但折裂全部发生在牙根颈部,综合以上实验结果显示,CAD/CAM一体化玻璃纤维桩修复后不易发生根中和根尖区的折裂,在相同的牙体条件下比钴铬合金桩和二氧化锆桩更加有利于保护牙根,与一些学者研究的结果相一致[35-37],所以在临床上对于牙体较为薄弱的根管,特别是经旁路治疗后存在薄弱区域的扁根管进行牙体修复时,应该倾向于选择纤维桩修复。
此外,实验中钴铬合金铸造桩组出现了5例桩脱落,分析原因可能与金属桩的黏结剂选择及扁根管的复杂形态难以让钴铬桩获得良好的机械固位力有关。CAD/CAM一体化玻璃纤维桩组中还出现3例桩脱落,分析原因可能是由于扁根管结构较为复杂特殊,CAD/CAM一体化玻璃纤维桩在切削制作过程中难以完全顺应扁根管复杂的形态,同时纤维桩的弹性模量虽然与牙体组织接近[38],但在承受功能性负荷时,纤维桩的潜在弯曲易使粘接剂受到拉伸和剪切力,使粘接剂边缘封闭丧失[39],因而发生脱落。二氧化锆桩核组有7例桩脱落,分析原因可能与二氧化锆桩核表面的瓷处理及黏结剂的选择有关。
实验中发现,二氧化锆桩核组全部发生断裂,没有桩核出现弯曲变形,这一结果提示二氧化锆桩的弹性限度较小,脆性较大,在承受力时易于折断,在临床使用时应该注意避免过大的侧向咬合力。也因二氧化锆桩核存在这一特性,二氧化锆桩桩核没有出现弯曲形变的发生,所以发生微渗漏的可能性比较小。由于桩核材料抗折强度在修复中的重要性,因此如何提高桩核的抗折能力就显得十分重要,一些实验结果表明桩的直径越大抗折强度越高,修复牙抗折力越大[40-42]。所以针对结构较为复杂的扁根管,应该考虑在不影响牙根抗折力的前提下,尽量增加桩的直径以提高桩核的抗折能力。
综上所述,临床上扁根管内器械分离行旁路热牙胶充填进行合理桩核修复时,应综合考虑患牙的特点与临床需求,选择适合的桩核修复系统。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
.jpg)