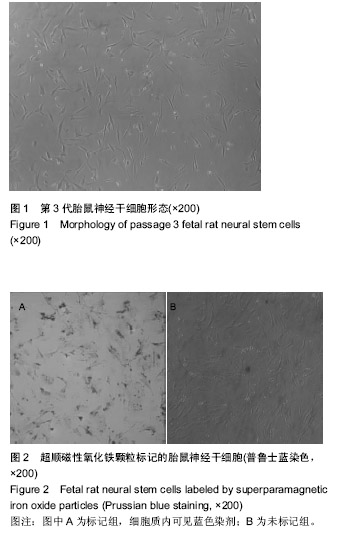
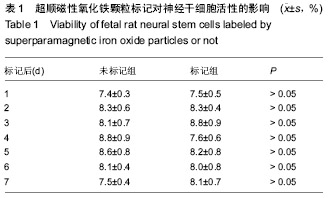
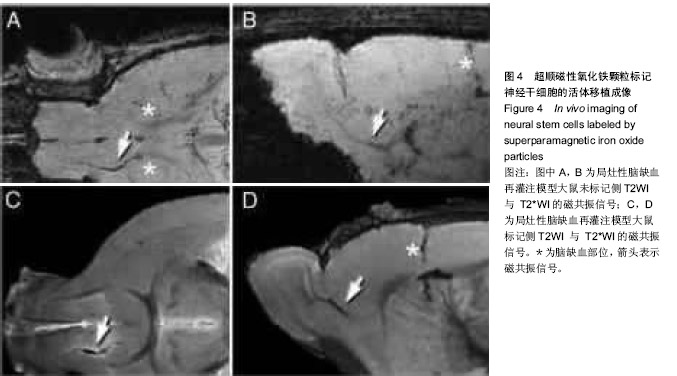
| [1] Tsuchiya K, Chen Q, Ushida A, et al. The effect of coculture of chondrocytes with mesenchymal stem cells on their cartilaginous phenotype in vitro. Mater Sci Eng C. 2012; 24(3): 391-396.
[2] Hill JM, Dick AJ, Raman VK, et al. Serial cardiac magnetic resonance imaging of injected mesenchymal stem cells. Circulation. 2003;108(8):1009-1014.
[3] Weissleder R. Molecular imaging: exploring the next frontier. Radiology. 1999;212(3):609-614.
[4] Katritsis DG, Sotiropoulou PA, Karvouni E, et al. Transcoronary transplantation of autologous mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitors into infarcted human myocardium. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2005;65(3):321-329.
[5] Baklanov DV, Demuinck ED, Thompson CA, et al. Novel double contrast MRI technique for intramyocardial detection of percutaneously transplanted autologous cells. Magn Reson Med. 2004;52(6):1438-1442.
[6] Schächinger V, Aicher A, Döbert N, et al. Pilot trial on determinants of progenitor cell recruitment to the infarcted human myocardium. Circulation. 2008;118(14):1425-1432.
[7] Sutton EJ, Henning TD, Pichler BJ, et al. Cell tracking with optical imaging. Eur Radiol. 2008;18(10):2021-2032.
[8] Lee SW, Padmanabhan P, Ray P, et al. Stem cell-mediated accelerated bone healing observed with in vivo molecular and small animal imaging technologies in a model of skeletal injury. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(3):295-302.
[9] Neri M, Maderna C, Cavazzin C, et al. Efficient in vitro labeling of human neural precursor cells with superparamagnetic iron oxide particles: relevance for in vivo cell tracking. Stem Cells. 2008;26(2):505-516.
[10] Santamaria-Martínez A, Barquinero J, Barbosa-Desongles A, et al. Identification of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in the reactive stroma of a prostate cancer xenograft by side population analysis. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(17):3004-3013.
[11] Frank JA, Miller BR, Arbab AS, et al. Clinically applicable labeling of mammalian and stem cells by combining superparamagnetic iron oxides and transfection agents. Radiology. 2003;228(2):480-487.
[12] Friedenstein AJ. Precursor cells of mechanocytes. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;47:327-359.
[13] Zhang RP,Zhang K,Li JD,et al.In vivo tracking of neuronal-like cells by magnetic resonance in rabbit models of spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(36): 3373-3381.
[14] Markus A, Patel TD, Snider WD. Neurotrophic factors and axonal growth. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2002;12(5):523-531.
[15] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[16] Campagnoli C, Roberts IA, Kumar S, et al. Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow. Blood. 2001;98(8): 2396-2402.
[17] Mahmood A, Lu D, Wang L, et al. Intracerebral transplantation of marrow stromal cells cultured with neurotrophic factors promotes functional recovery in adult rats subjected to traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2002;19(12):1609- 1617.
[18] Saito T, Kuang JQ, Lin CC, et al. Transcoronary implantation of bone marrow stromal cells ameliorates cardiac function after myocardial infarction. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003; 126(1):114-123.
[19] Coenegrachts K, Matos C, ter Beek L, et al. Focal liver lesion detection and characterization: comparison of non-contrast enhanced and SPIO-enhanced diffusion-weighted single-shot spin echo echo planar and turbo spin echo T2-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2009;72(3):432-439.
[20] Santoro L, Grazioli L, Filippone A, et al. Resovist enhanced MR imaging of the liver: does quantitative assessment help in focal lesion classification and characterization? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30(5):1012-1020.
[21] Liu ZH,Li SL,Liang ZB,et al.Targeting β-secretase with RNAi in neural stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease therapy.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(33): 3095-3106.
[22] Grazioli L, Bondioni MP, Romanini L, et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced liver MRI with SHU 555 A (RESOVIST): New protocol infusion to improve arterial phase evaluation--a prospective study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29(3):607-616.
[23] 谭延斌,武新英,张景峰,等.超顺磁性氧化铁对血管内皮细胞的生物学影响及其磁共振成像效应[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2010, 39(2):118-124.
[24] 谢辉,朱艳红,杨海,等.偶联乳铁蛋白的超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒对大鼠脑胶质瘤的成像研究[J].生物物理学报,2009(S1):309-311.
[25] 张勤惠,姜启玉,顾海鹰.超顺磁性氧化铁对肝脏MR成像效果的影响[J].中国医学影像技术,2010,26(10):1809-1813.
[26] Frank JA, Miller BR, Arbab AS, et al. Clinically applicable labeling of mammalian and stem cells by combining superparamagnetic iron oxides and transfection agents. Radiology. 2003;228(2):480-487.
[27] Bulte JW, Zhang S, van Gelderen P, et al. Neurotransplantation of magnetically labeled oligodendrocyte progenitors: magnetic resonance tracking of cell migration and myelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(26): 15256-15261.
[28] Arbab AS, Bashaw LA, Miller BR, et al. Characterization of biophysical and metabolic properties of cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and transfection agent for cellular MR imaging. Radiology. 2003;229(3):838- 846.
[29] Ishii K, Yoshida Y, Akechi Y, et a l. Hepatic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by tetracycline-regulated hepatocyte nuclear factor 3beta. Hepatology. 2008;48(2):597-606.
[30] 刘佳,赵江民,张蕾,等.超顺磁性氧化铁标记大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的研究[J].同济大学学报,2010,31(5):31-35.
[31] 陈舒怿,古宏晨,吴强,等.超顺磁性铁纳米颗粒标记对视网膜前体细胞体外培养的影响[J].国际眼科杂志,2008,8(5):913-915.
[32] 何庚戌,要彤,幺雯,等.超顺磁性氧化铁作为细胞标记试剂的可行性研究[J].华北国防医药,2009,21(2):9-11.
[33] 陈长青,王小宜,陈晨,等.SPIO标记脂肪干细胞移植治疗大鼠脑梗死的磁共振示踪成像研究[J].磁共振成像,2010,1(2):50-54.
[34] Sun JH, Zhang YL, Qian SP, et al. Assessment of biological characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide particles in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2012;5(2):317-320.
[35] Kim TH, Kim JK, Shim W, et al. Tracking of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells labeled with fluorescent magnetic nanoparticle in liver cirrhosis rat model with 3-T MRI. Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;28(7):1004-1013.
[36] 许杰华,李丹,于春鹏,等.SPIO标记下大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞生物学特性及多向分化潜能及体外MR成像[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2009,30(2):142-147.
[37] Chen YC, Hsiao JK, Liu HM, et al. The inhibitory effect of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle (Ferucarbotran) on osteogenic differentiation and its signaling mechanism in human mesenchymal stem cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;245(2):272-279.
[38] Kostura L, Kraitchman DL, Mackay AM, et al. Feridex labeling of mesenchymal stem cells inhibits chondrogenesis but not adipogenesis or osteogenesis. NMR Biomed. 2004;17(7): 513-517.
[39] Ju S, Teng G, Zhang Y, et al. In vitro labeling and MRI of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood. Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24(5):611-617. |