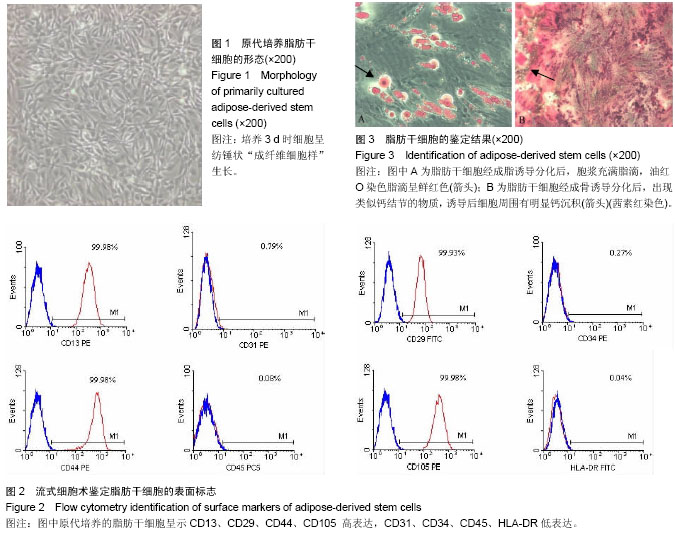
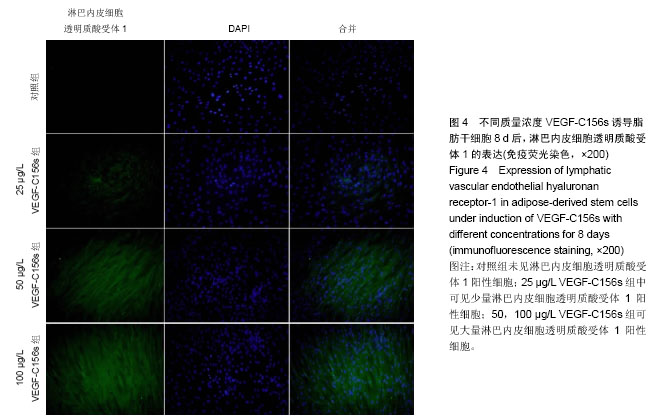
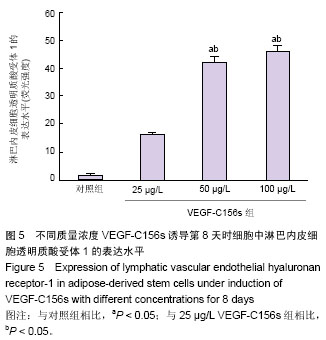
| [1] Thomas-MacLean R, Miedema B, Tatemichi SR. Breast cancer-related lymphedema: women's experiences with an underestimated condition. Can Fam Physician. 2005;51: 246-247.
[2] Holmes LB, Fields JP, Zabriskie JB. Hereditary late-onset lymphedema. Pediatrics. 1978;61(4):575-579.
[3] Wing PL. Can a comprehensive lymphedema management program decrease limb size and reduce the incidence of infection in a woman with postmastectomy lymphedema? Phys Ther. 2002;82(9):923; author reply 923-924.
[4] Mortimer PS. Therapy approaches for lymphedema. Angiology. 1997;48(1):87-91.
[5] 朱家恺,于国中,刘均墀,等.深淋巴管静脉吻合术治疗先天性四肢淋巴水肿的初步观察[J].中山医学院学报,1982,5(2):805.
[6] 刘均墀,朱家恺,于国中,等.淋巴管静脉吻合术治疗淋巴管疾病100例报告[J].中华显微外科杂志,1986,9(2):89-99.
[7] 汤海云,朱家恺,于国中,等.静脉移植重建淋巴通道的实验研究[J].中华外科杂志,1985,23:6-8.
[8] 程钢,朱家恺,于国中,等.肢体淋巴管结构及在淋巴水肿时的病理学研究[J].中华显微外科杂志,1989,12(2):84-86.
[9] 陈小虎,李付贵,杨羿,等.脂肪干细胞诱导分化成淋巴管内皮样细胞的初步研究[J].中华显微外科杂志,2013,36(1):40-45.
[10] Piller N, Carati C. The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema. Lymphology. 2009;42(3):146-147.
[11] Dai Tt, Jiang Zh, Li Sl, et al. Reconstruction of lymph vessel by lymphatic endothelial cells combined with polyglycolic acid scaffolds: a pilot study. J Biotechnol. 2010;150(1):182-189.
[12] McLafferty E, Hendry C, Farley A. The lymphatic system. Nurs Stand. 2012-2013;27(15-17):37-42.
[13] Wei L, Liu Y, Chen G, et al. Differentiation of lymphatic endothelial cells from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with VEGFs. Lymphology. 2012;45(4):177-187.
[14] Joukov V, Kumar V, Sorsa T, et al. A recombinant mutant vascular endothelial growth factor-C that has lost vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 binding, activation, and vascular permeability activities. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(12): 6599-6602.
[15] Kohlberger P, Gantert M, Volk-Orlowska T, et al. Immunohistochemical detection of lymph node metastases in node-negative breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2001; 21(1B):697-699.
[16] Mouta Carreira C, Nasser SM, di Tomaso E, et al. LYVE-1 is not restricted to the lymph vessels: expression in normal liver blood sinusoids and down-regulation in human liver cancer and cirrhosis. Cancer Res. 2001;61(22):8079-8084.
[17] Trojan L, Michel MS, Rensch F, et al. Lymph and blood vessel architecture in benign and malignant prostatic tissue: lack of lymphangiogenesis in prostate carcinoma assessed with novel lymphatic marker lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor (LYVE-1). J Urol. 2004;172(1):103-107.
[18] Hong YK, Harvey N, Noh YH, et al. Prox1 is a master control gene in the program specifying lymphatic endothelial cell fate. Dev Dyn. 2002;225(3):351-357.
[19] Hong YK, Foreman K, Shin JW, et al. Lymphatic reprogramming of blood vascular endothelium by Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Nat Genet. 2004;36(7): 683-685.
[20] Conklin BS, Richter ER, Kreutziger KL, et al. Development and evaluation of a novel decellularized vascular xenograft. Med Eng Phys. 2002;24(3):173-183.
|