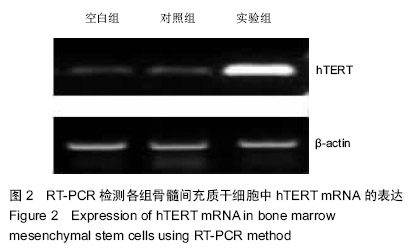
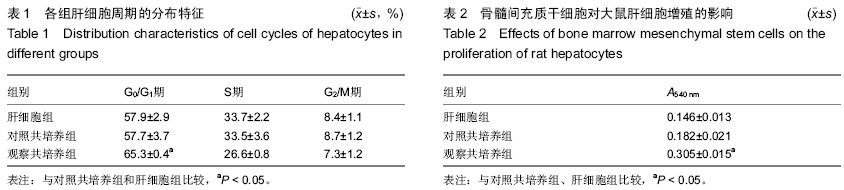
| [1] 张业伟,牛坚,赵何伟,等.干细胞表面标志物CD90及端粒酶逆转录酶在原发性肝癌中的表达及临床意义[J].中华肝胆外科杂志, 2012,18(1):37-39.
[2] Thenappan A, Li Y, Kitisin K, et al. Role of transforming growth factor beta signaling and expansion of progenitor cells in regenerating liver. Hepatology. 2010;51(4):1373-1382.
[3] 张莉萍,康格非.原代肝细胞培养的研究现状[J].国外医学:临床生物化学与检验学分册,2004,25(3):193-196.
[4] Liang X, So YH, Cui J, et al. The low-dose ionizing radiation stimulates cell proliferation via activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway in rat cultured mesenchymal stem cells. J Radiat Res. 2011;52(3):380-386.
[5] Kisseleva T, Gigante E, Brenner DA. Recent advances in liver stem cell therapy. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2010;26(4):395- 402.
[6] 刘京龙,邓志华,郭素雅,等. Ad-hTERTp-单纯疱疹病毒胸苷激酶/丙氧鸟苷系统联合奥沙利铂对人类肝癌细胞的影响[J].肿瘤研究与临床,2011,23(8):526-531.
[7] Crop MJ, Baan CC, Korevaar SS, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce explosive T-cell proliferation. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(12):1843-1853.
[8] 何吉文,李华,向国安,等.肿瘤靶向性细胞穿膜肽介导小分子干扰RNA对肝癌细胞的抑制作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(10): 2040-2043.
[9] Shi Y, Xia YY, Wang L, et al. Neural cell adhesion molecule modulates mesenchymal stromal cell migration via activation of MAPK/ERK signaling. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318(17): 2257-2267.
[10] Matuskova M, Hlubinova K, Pastorakova A, et al. HSV-tk expressing mesenchymal stem cells exert bystander effect on human glioblastoma cells. ancer Lett. 2010;290(1):58-67.
[11] 周佳美,向慧玲,朱争艳,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基对大鼠肝癌细胞系CBRH,7919增殖能力的影响[J].天津医科大学学报,2011,17(4):455-458.
[12] Lim YS. Acute liver failure in Korea: etiology, prognosis and treatment. Korean J Hepatol. 2010;16(1):5-18.
[13] 邵志红,王培军,李铭华,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞移植对Walker-256肝癌生长影响的实验研究[J].中华医学杂志,2009, 89(7):491-496.
[14] Gilchrist ES, Plevris JN. Bone marrow-derived stem cells in liver repair: 10 years down the line. Liver Transpl. 2010;16(2): 118-129.
[15] Aquino JB, Bolontrade MF, García MG, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutic tools and gene carriers in liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gene Ther. 2010; 17(6):692-708.
[16] Bergfeld SA, DeClerck YA. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010;29(2):249-261.
[17] Park SA, Ryu CH, Kim SM, et al. CXCR4-transfected human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells exhibit enhanced migratory capacity toward gliomas. Int J Oncol. 2011; 38(1):97-103..
[18] Li GC, Ye QH, Xue YH, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit metastasis of a hepatocellular carcinoma model using the MHCC97-H cell line. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(12):2546- 2553.
[19] 林沪,陈黎明,王福生,等.间充质干细胞在肝脏的分化机制研究进展[J].实用肝脏病杂志,2010,13(3):238-240.
[20] Røsland GV, Svendsen A, Torsvik A, et al. Long-term cultures of bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells frequently undergo spontaneous malignant transformation. Cancer Res. 2009;69(13):5331-5339.
[21] Hasebe Y, Hasegawa S, Hashimoto N, et al. Analysis of cell characterization using cell surface markers in the dermis. J Dermatol Sci. 2011;62(2):98-106.
[22] 顾劲扬,施晓雷,张悦,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞维持猪肝细胞形态与功能的实验研究[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2010,16(2):130-133.
[23] Klopp AH, Gupta A, Spaeth E, et al. Concise review: Dissecting a discrepancy in the literature: do mesenchymal stem cells support or suppress tumor growth. Stem Cells. 2011;29(1):11-19.
[24] 沈中,徐小梅,孟琴,等.原代肝细胞体外培养用于利福平和异烟肼肝毒性的研究[J].中国药科大学学报,2005,36(3):250-253.
[25] Zou C, Luo Q, Qin J, et al. Osteopontin promotes mesenchymal stem cell migration and lessens cell stiffness via integrin β1, FAK, and ERK pathways. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;65(3):455-462.
[26] Abdel aziz MT, El Asmar MF, Atta HM, et al. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in suppression of hepatocarcinorigenesis in rats: possible role of Wnt signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2011;30:49.
[27] Ho IA, Chan KY, Ng WH, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 1 is necessary for the migration of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells toward human glioma. Stem Cells. 2009;27(6):1366-1375.
[28] Han Z, Jing Y, Zhang S, et al. The role of immunosuppression of mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair and tumor growth. Cell Biosci. 2012;2(1):8.
[29] 王雪峰,梅佳玮,廖传文,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与小鼠肝癌肝移植术后复发关系的实验观察[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(6): 455-458.
[30] Gao P, Ding Q, Wu Z, et al. Therapeutic potential of human mesenchymal stem cells producing IL-12 in a mouse xenograft model of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2010; 290(2):157-166.
|