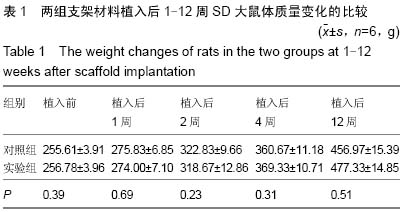
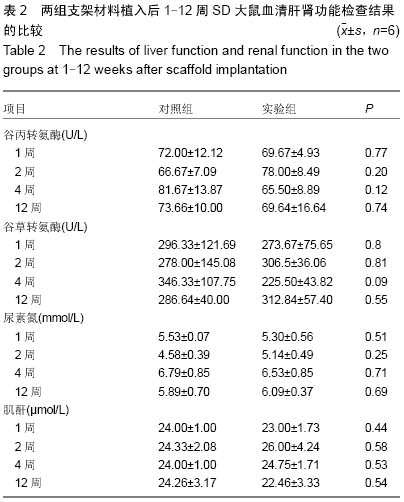
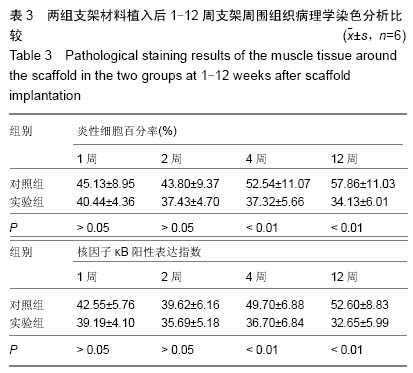
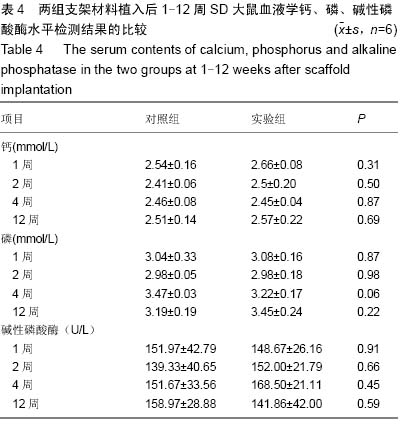
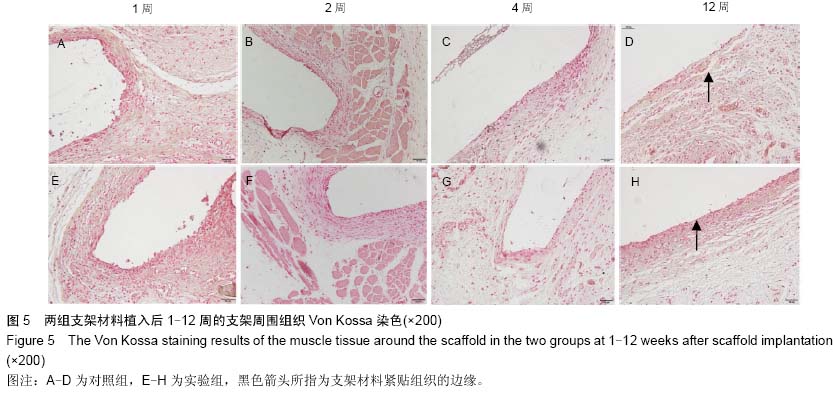
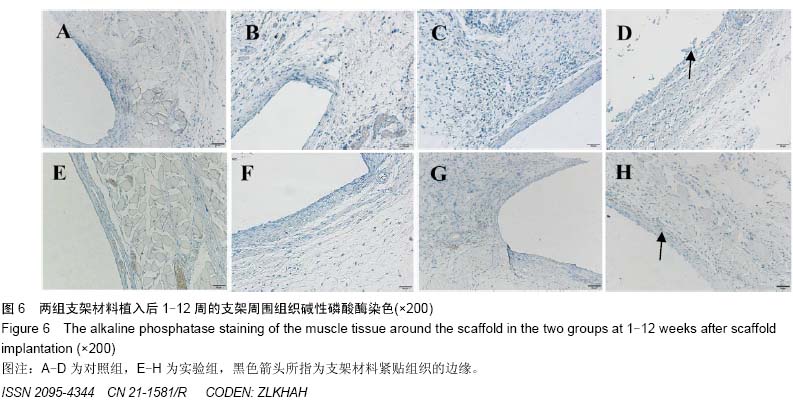
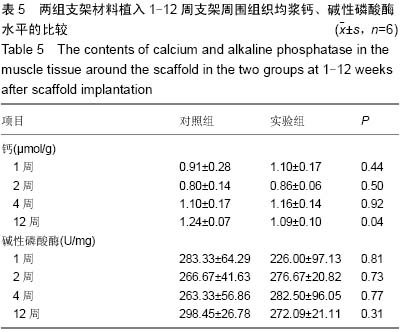
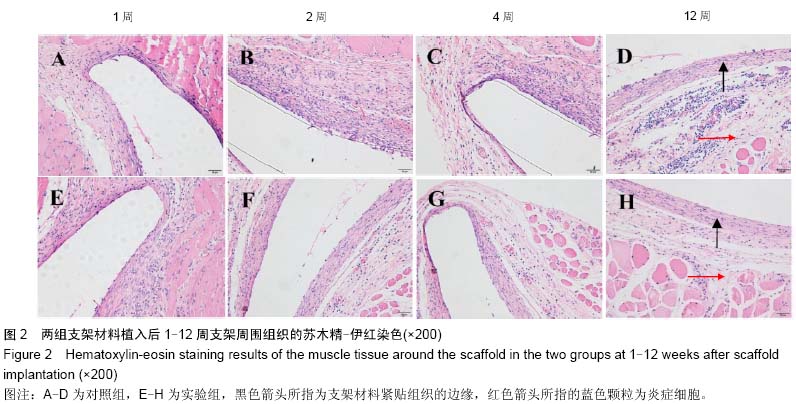
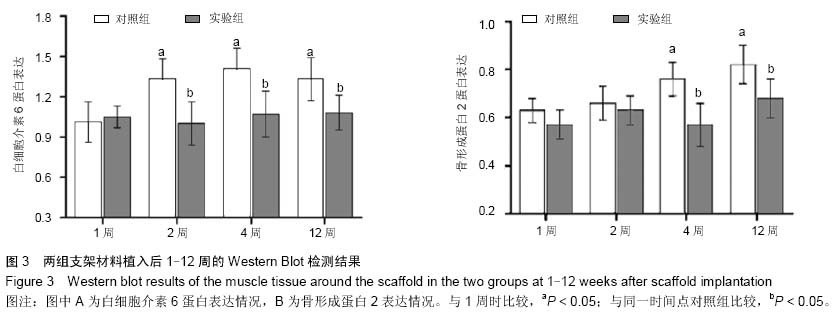
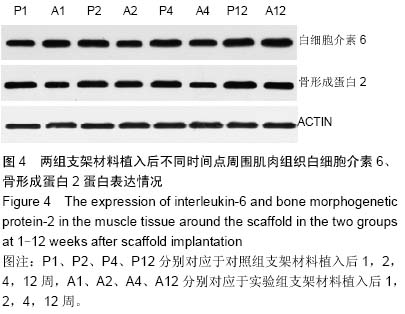
| [1] 肖越勇,.张金山,崔福斋,等.新型生物可降解高分子支架[J].中国医疗器械信息,2004,10(2):12-15.
[2] Serruys PW,Onuma Y,Dudek D,et al.Evaluation of the second generation of a bioresorbable everolimus-eluting vascular scaffold for the treatment of de novo coronary artery stenosis: 12-month clinical and imaging outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(15):1578-1588.
[3] Lincoff AM,Furst JG,Ellis SG,et al.Sustained local delievery of dexamethasone by a novel intravascular eluting stent to prevent restenosis in the porcine coronary injury model.J Amcoll Cardic. 1997;29(4):808-816.
[4] Chang EJ, Kim HH, Huh JE,et al.Low proliferation and high apoptosis of osteoblastic cells on hydrophobic surface are associated with defective Ras signaling. Exp Cell Res.2005; 303(1):197-206.
[5] Commandeur S,van Beusekom HM,van der Giessen WJ.Polymers, drug release, and drug-eluting stents.J Interv Cardiol.2006;19 (6):500-506.
[6] 卢钊,蒋学俊,冯高科,等.生物全降解药物支架植入小型猪冠状动脉:安全性及组织相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(34): 5429-5433.
[7] 贺素媛,李虎,任珊,等.新型生物全降解药物释放支架对小型实验猪冠状动脉内膜的影响[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2013,21(3): 178-183.
[8] 冯高科,蒋学俊,郑晓新,等.新型生物全降解药物支架对小型猪冠状动脉内皮修复的影响[J]. 武汉大学学报:医学版,2013,34(6): 822-826.
[9] 李虎,李晓艳,蒋学俊,等.新型生物全降解药物支架植入小型猪冠状动脉的安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2013,17(38): 6773- 6778.
[10] Zheng X,Wang Y,Lan Z,et al.Improved biocompatibility of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) orv and poly-L-lactic acid blended with nanoparticulate amorphous calcium phosphate in vascular stent applications.J Biomed Nanotechnol.2014; 10(6):900-910.
[11] Lan Z,Lyu Y,Xiao J,et al.Novel biodegradable drug-eluting stent composed of poly-L-lactic acid and amorphous calcium phosphate nanoparticles demonstrates improved structural and functional performance for coronary artery disease.J Biomed Nanotechnol.2014;10(7):1194-1204.
[12] Cushman M,Arnold AM,Psaty BM, et al.C-reactive protein and the 10-year incidence of coronary heart disease in older men and women: the cardiovascular health study. Circulation. 2005;112(1):25-31.
[13] Pepys MB,Hirschfield GM,Tennent GA,et al.Targeting C-reactive protein for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Nature. 2006; 440(7088):1217-1221.
[14] Mallavia B, Recio C,Oguiza A, et al.Peptide inhibitor of NF-kappaB translocation ameliorates experimental atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol.2013;182(5):1910-1921.
[15] Hirose K,Iwabuchi K,Shimada K,et al.Different responses to oxidized low-density lipoproteins in human polarized macrophages.Lipids Health Dis.2011;10:1.
[16] Ong AT,McFadden EP,Regar E,et al.Late angiographic stent thrombosis (LAST) events with drug-eluting stents. J Am Coll Cardiol.2005;45(12):2088-2092.
[17] 秦超师,冯高科,李晓艳,等.无定形磷酸钙应用在生物医学中的特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(39):6353-6357.
[18] 覃春美.骨形态发生蛋白2与血管钙化的相关性研究进展[J].山东医药,2014,54(26): 97-99.
[19] Shioi A,Katagi M, Okuno Y,et al.Induction of bone-type alkaline phosphatase in human vascular smooth muscle cells: roles of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and oncostatin M derived from macrophages.Circ Res.2002;91(1):9-16.
[20] Tintut Y, Patel J, Parhami F, et al.Tumor necrosis factor-alpha promotes in vitro calcification of vascular cells via the cAMP pathway.Circulation.2000;102(21):2636-2642.
[21] Tintut Y, Patel J, Territo M, et al.Monocyte/macrophage regulation of vascular calcification in vitro.Circulation. 2002; 105(5):650-655.
[22] Moe SM,Chen NX.Inflammation and vascular calcification. Blood Purif.2005;23 (1):64-71. |