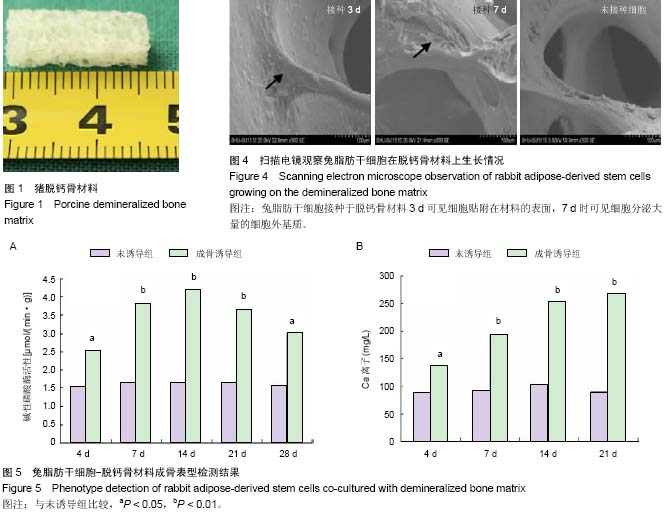
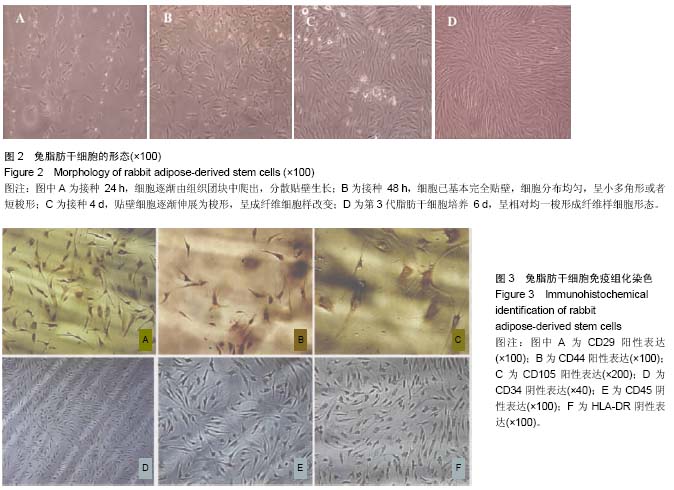
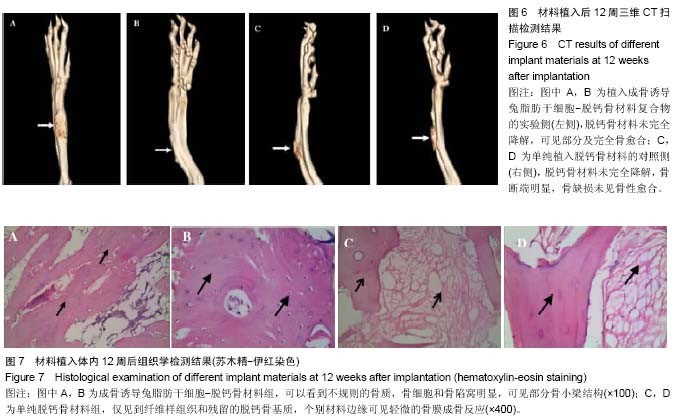
| [1] 王伟,卜志勇,李安军.基因增强的组织工程骨修复骨缺损的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(11):2509-2511.
[2] 黄成龙,肖金刚. 脂肪干细胞成骨分化及与复合支架结合:在修复骨质疏松症骨缺损中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(41):6696-6702.
[3] 郭艳萍,陶常波,张爱君,等.成人脂肪间充质干细胞的定向成骨诱导[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(19):2987-2992.
[4] 曹娜,裴路,张微.脂肪干细胞和生物支架应用于牙槽骨修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(1):137-142.
[5] 宁兆荣,郭延伟,李松,等.脂肪干细胞复合载淫羊藿苷支架材料对兔下颌骨缺损的修复[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2013,29(5):611-615.
[6] 熊竹友,方小魁,徐静.同种异体脂肪干细胞复合脱钙骨修复大鼠尺骨缺损[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2013,9(5):245-250.
[7] 刘刚,汪明星,闫长明,等.脂肪干细胞复合明胶海绵修复兔桡骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(34):6083-6088.
[8] Chen Q, Yang Z, Sun S, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells modified genetically in vivo promote reconstruction of bone defects. Cytotherapy. 2010;12(6):831-840.
[9] Kim HJ, Park SS, Oh SY, et al. Effect of acellular dermal matrix as a delivery carrier of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2012;100(6):1645-1653.
[10] Han DS, Chang HK, Park JH, et al. Consideration of bone regeneration effect of stem cells: comparison between adipose-derived stem cells and demineralized bone matrix. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(1):189-195.
[11] 房殿吉,郭延伟,李松,等.脂肪干细胞复合载杜仲醇提取物支架材料修复兔下颌骨缺损的实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2013, 31(1):65-69.
[12] 姜全春,赵秀兰.脂肪干细胞与Bio-oss支架构建组织工程骨治疗种植体周围骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(6): 1111-1115.
[13] 赵铭,李博.骨形态生发蛋白2基因修饰脂肪干细胞对去卵巢骨质疏松性大鼠骨缺损的修复作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012, 18(8):706-708.
[14] Liao YH, Chang YH, Sung LY, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells and calvarial defect repair using baculovirus-mediated co-expression of BMP-2 and miR-148b. Biomaterials. 2014;35(18):4901-4910.
[15] Ma J, Both SK, Ji W, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells as monocultures or cocultures with human umbilical vein endothelial cells: performance in vitro and in rat cranial defects. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014; 102(4):1026-1036.
[16] Liu G, Zhang Y, Liu B, et al. Bone regeneration in a canine cranial model using allogeneic adipose derived stem cells and coral scaffold. Biomaterials. 2013;34(11):2655-2664.
[17] 董凯,柳忠豪.脂肪源性干细胞在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2012,17(3):129-133.
[18] 李晓宇,姚金凤,刘政华.成骨诱导脂肪基质细胞在骨组织工程体内成骨中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(27): 4985-4990.
[19] 郝伟,姜明,王新,等.Ⅰ型胶原凝胶包埋脂肪干细胞复合PLGA-β- TCP支架修复兔自体桡骨缺损[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011, 28(9):1547-1549.
[20] 余美春,陶晖,杨会营,等.骨缺损对脂肪源干细胞骨形态发生蛋白信号通路相关分子的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(9): 856- 860.
[21] Lin CY, Lin KJ, Li KC, et al. Immune responses during healing of massive segmental femoral bone defects mediated by hybrid baculovirus-engineered ASCs. Biomaterials. 2012; 33(30):7422-7434.
[22] Niemeyer P, Fechner K, Milz S, et al. Comparison of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue for bone regeneration in a critical size defect of the sheep tibia and the influence of platelet-rich plasma. Biomaterials. 2010;31(13):3572-3579.
[23] Schubert T, Lafont S, Beaurin G, et al. Critical size bone defect reconstruction by an autologous 3D osteogenic-like tissue derived from differentiated adipose MSCs. Biomaterials. 2013;34(18):4428-4438.
[24] 鞠刚,徐卫袁,张亚.多孔丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石复合脂肪间充质干细胞修复兔关节软骨及软骨下骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(29):5327-5333.
[25] 李冬松,李叔强,蔡波,等.血管内皮生长因子基因修饰脂肪干细胞对糖尿病骨质疏松性骨缺损的修复作用[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2011,28(2):193.
[26] 许胜,周文娟.脂肪基质干细胞在骨缺损中的应用现状及研究新进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2010,15(4):204-207.
[27] Han D, Li J. Repair of bone defect by using vascular bundle implantation combined with Runx II gene-transfected adipose-derived stem cells and a biodegradable matrix. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;352(3):561-571.
[28] Daei-Farshbaf N, Ardeshirylajimi A, Seyedjafari E, et al. Bioceramic-collagen scaffolds loaded with human adipose-tissue derived stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Mol Biol Rep. 2014;41(2):741-749.
[29] Sándor GK, Tuovinen VJ, Wolff J, et al. Adipose stem cell tissue-engineered construct used to treat large anterior mandibular defect: a case report and review of the clinical application of good manufacturing practice-level adipose stem cells for bone regeneration. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(5):938-950.
[30] 施咏毅,王根林,杨惠林.多孔型丝素蛋白/羟基磷灰石复合脂肪间充质干细胞修复兔股骨骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(8):1341-1344.
[31] 崔磊,王琛.脂肪干细胞在骨组织工程中的应用进展[J].解剖学杂志,2009,32(5):579-582.
[32] Zanetti AS, McCandless GT, Chan JY, et al. In vitro human adipose-derived stromal/stem cells osteogenesis in akermanite:poly-ε-caprolactone scaffolds. J Biomater Appl. 2014;28(7):998-1007.
[33] Bigham-Sadegh A, Mirshokraei P, Karimi I, et al. Effects of adipose tissue stem cell concurrent with greater omentum on experimental long-bone healing in dog. Connect Tissue Res. 2012;53(4):334-342.
[34] Choi K, Kang BJ, Kim H, et al. Low-level laser therapy promotes the osteogenic potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded on an acellular dermal matrix. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(6): 919-928.
[35] 张钦,马真胜,刘建,等.成骨诱导自体脂肪源性干细胞用于修复兔颅骨缺损[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2009,8(2):104-107.
[36] Rhee SC, Ji YH, Gharibjanian NA, et al. In vivo evaluation of mixtures of uncultured freshly isolated adipose-derived stem cells and demineralized bone matrix for bone regeneration in a rat critically sized calvarial defect model. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(2):233-242.
[37] Han DS, Chang HK, Kim KR, et al. Consideration of bone regeneration effect of stem cells: comparison of bone regeneration between bone marrow stem cells and ad ipose-derived stem cells. J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(1): 196-201.
[38] 马舟涌,李放,雷伟,等.兔自体脂肪干细胞成骨诱导后经皮注射修复骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(12): 2245-2249.
[39] 刘云松,周永胜,谭建国.脂肪组织是骨、软骨、软组织缺损组织工程再建的理想干细胞来源[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2007,13(3): 217-224.
[40] 杨在亮,张波,周继红. rhBMP-2和rhVEGF转染ADSCs后体外表达及诱导骨缺损成骨修复的实验研究[J].创伤外科杂志,2007, 9(4):296-300. |