中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (28): 4445-4449.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.28.004
• 骨髓干细胞 bone marrow stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
适当质量浓度黄芪注射液可增强骨髓基质细胞的表面黏附性
王彩霞1,任明姬2,崔明玉2
- 1内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院麻醉科,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010030;
2内蒙古医科大学组织胚胎学教研室,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010059
Radix Astragali injection at appropriate concentrations enhances surface adhesion of bone marrow stromal cell
Wang Cai-xia1, Ren Ming-ji2, Cui Ming-yu2
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010030, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China;
2Department of Histology and Embryology, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010059, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
背景:研究发现很多益气补血类中药均是通过影响骨髓基质细胞分泌一些细胞因子来促进造血干细胞的分化增殖,或者促进骨髓基质细胞和造血干细胞的黏附而发挥作用。
目的:观察黄芪注射液对小鼠骨髓基质细胞表面细胞间黏附分子1、血管细胞间黏附分子1表达的影响。
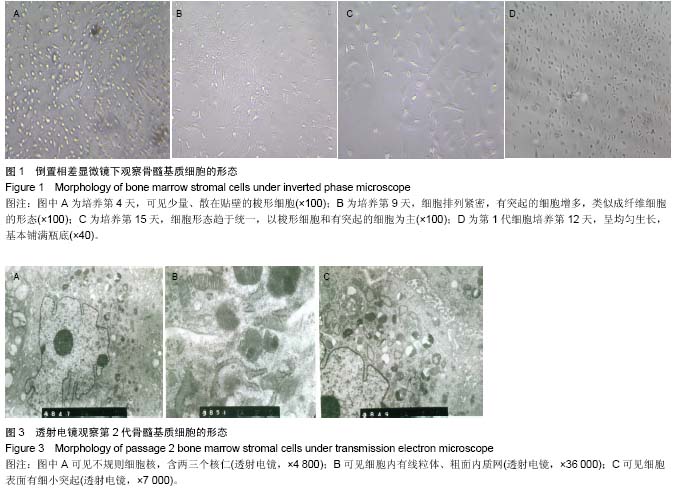
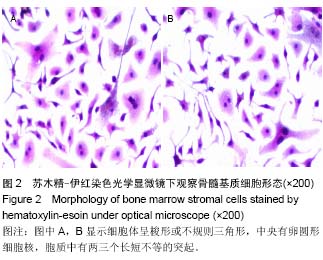
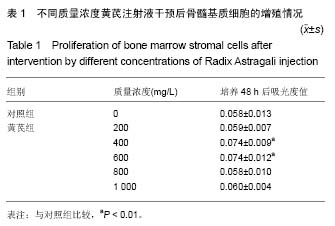
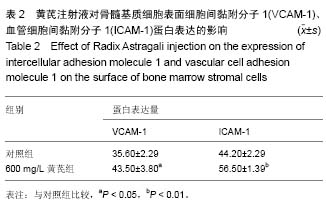
方法:采用全骨髓贴壁细胞分离筛选法培养小鼠骨髓基质细胞,倒置相差显微镜、苏木精-伊红染色光镜及透射电镜观察小鼠骨髓基质细胞的形态。MTT法检测黄芪注射液促进骨髓基质细胞增殖的最佳浓度。流式细胞术检测黄芪注射液干预后小鼠骨髓基质细胞表面细胞间黏附分子1、血管细胞间黏附分子1的表达。
结果与结论:倒置显微镜和光镜观察到骨髓基质细胞呈贴壁生长,细胞呈梭形或不规则形态,有突起;透射电镜观察到细胞内细胞器丰富,如粗面内质网、分泌小泡、线粒体等。黄芪注射液质量浓度为400和600 mg/L时可促进小鼠骨髓基质细胞增殖(P < 0.05),且两种剂量组间比较差异无显著性意义。600 mg/L黄芪注射液可增加小鼠骨髓基质细胞表面细胞间黏附分子1、血管细胞间黏附分子1蛋白表达。结果表明适当质量浓度黄芪注射液能够增强基质细胞的黏附性,对造血微环境有改善作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: