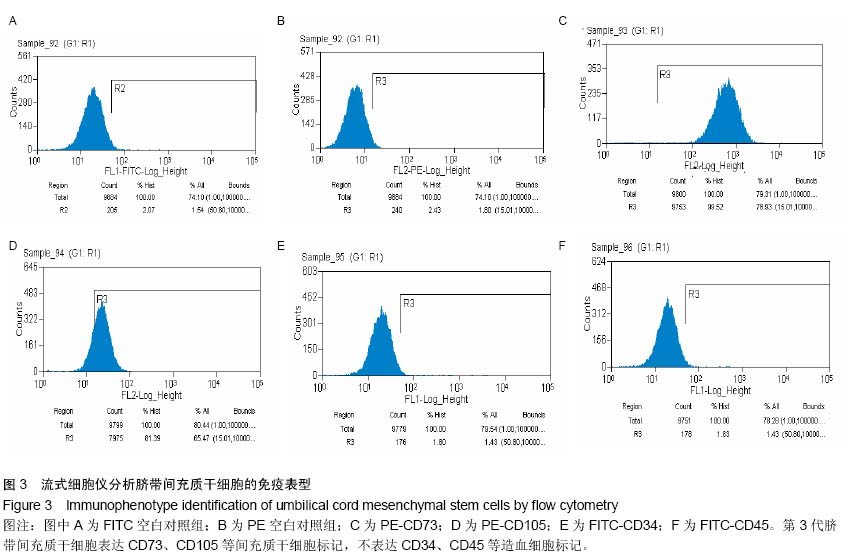
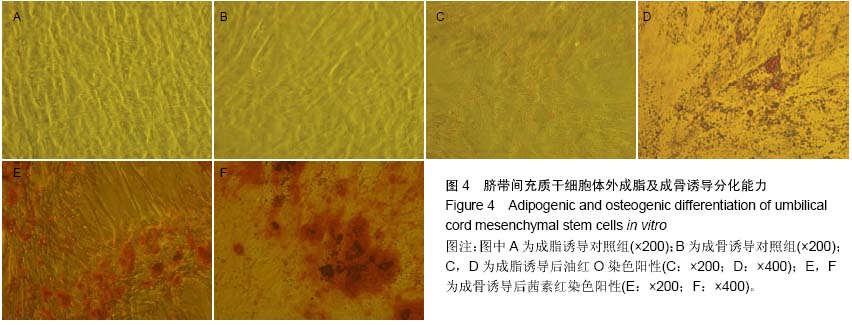
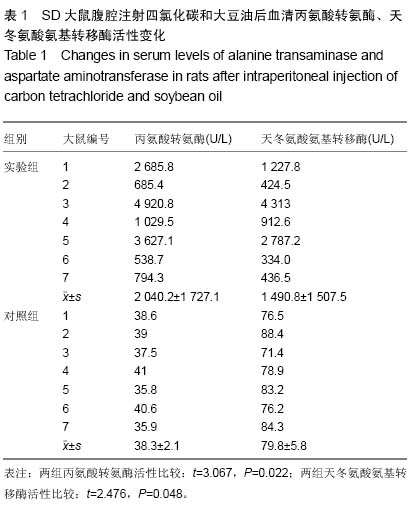
| [1] Tanabe S, Sato Y, Suzuki T, et al. Gene expression profiling of human mesenchymal stem cells for identification of novel markers in early- and late-stage cell culture. J Biochem. 2008; 144(3):399-408.
[2] Zeddou M, Briquet A, Relic B, et al. The umbilical cord matrix is a better source of mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) than the umbilical cord blood. Cell Biol Int. 2010;34(7):693-701.
[3] Kretlow JD, Jin YQ, Liu W, et al. Donor age and cell passage affects differentiation potential of murine bone marrow-derived stem cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2008;9:60.
[4] Zhang X, Hirai M, Cantero S, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood: reevaluation of critical factors for successful isolation and high ability to proliferate and differentiate to chondrocytes as compared to mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(4):1206-1218.
[5] Montanucci P, Basta G, Pescara T, et al. New simple and rapid method for purification of mesenchymal stem cells from the human umbilical cord Wharton jelly. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(21-22):2651-2661.
[6] Tsagias N, Koliakos I, Karagiannis V, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells using the total length of umbilical cord for transplantation purposes. Transfus Med. 2011;21(4): 253-261.
[7] Shi M, Zhang Z, Xu R,et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell transfusion is safe and improves liver function in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2012;1(10):725-731.
[8] Tsai PC, Fu TW, Chen YM, et al. The therapeutic potential of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton's jelly in the treatment of rat liver fibrosis. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15(5):484-495.
[9] Kita K, Gauglitz GG, Phan TT, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from the sub-amniotic human umbilical cord lining membrane. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(4):491-502.
[10] Sarugaser R, Lickorish D, Baksh D, et al. Human umbilical cord perivascular (HUCPV) cells: a source of mesenchymal progenitors. Stem Cells. 2005;23(2):220-229.
[11] Mitchell KE, Weiss ML, Mitchell BM, et al. Matrix cells from Wharton's jelly form neurons and glia. Stem Cells. 2003;21(1): 50-60.
[12] Fan CG, Zhang QJ, Zhou JR.Therapeutic potentials of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(1):195-207.
[13] Capelli C, Gotti E, Morigi M, et al. Minimally manipulated whole human umbilical cord is a rich source of clinical-grade human mesenchymal stromal cells expanded in human platelet lysate. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(7):786-801.
[14] Lee KD, Kuo TK, Whang-Peng J,et al. In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1275-1284.
[15] Schwartz RE, Reyes M, Koodie L, et al. Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells. J Clin Invest. 2002;109(10):1291-1302.
[16] 任红英,赵钦军,刘拥军,等. 脐带间充质干细胞体外诱导分化为肝细胞样细胞的研究[J]. 山东医药, 2008,48(30):24-26.
[17] Rao SB, Young RA, Mehendale HM. Hepatic polyamines and related enzymes following chlordecone-potentiated carbon tetrachloride toxicity in rats. J Biochem Toxicol. 1989;4(1): 55-63.
[18] Yuan S, Jiang T, Sun L, et al. The role of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of acute liver failure. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:251846.
[19] Salomone F, Barbagallo I, Puzzo L, et al. Efficacy of adipose tissue-mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in rats with acetaminophen liver injury. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(3): 1037-1044.
[20] Hong J, Jin H, Han J, et al. Infusion of human umbilical cord?derived mesenchymal stem cells effectively relieves liver cirrhosis in DEN?induced rats. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(4): 1103-1111.
[21] Sukhanov DS, Vinogradova TI, Zabolotnykh NV, et al. Comparative study of hepatoprotective action of remaxol, reamberin and ademethionine in liver injury induced by antituberculosis drugs (experimental study). Antibiot Khimioter. 2011;56(1-2):13-17.
[22] Zhang S, Chen L, Liu T, et al. Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells efficiently rescue acute liver failure through paracrine effects rather than hepatic differentiation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(13-14):1352-1364.
[23] Zhang Z, Lin H, Shi M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve liver function and ascites in decompensated liver cirrhosis patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27 Suppl 2:112-120.
[24] Bishi DK, Mathapati S, Cherian KM, et al. In vitro hepatic trans-differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells using sera from congestive/ischemic liver during cardiac failure. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92397.
[25] Aw MM, Mitry RR, Hughes RD, et al. Serum hepatocyte growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in children with acute liver failure. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007;44(2):224-227.
[26] Michalopoulos GK. Liver regeneration. J Cell Physiol. 2007; 213(2):286-300. |