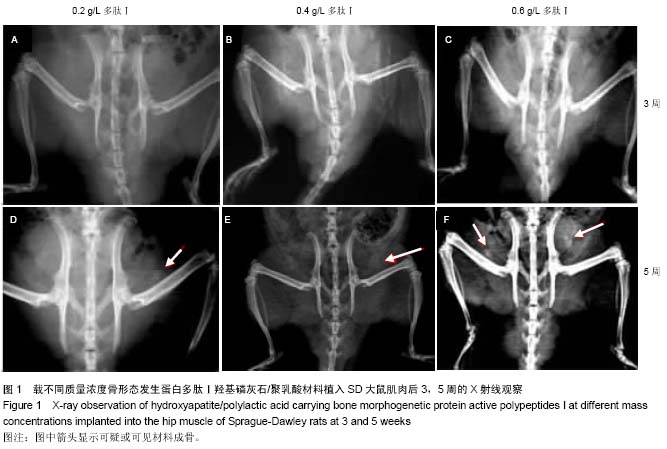
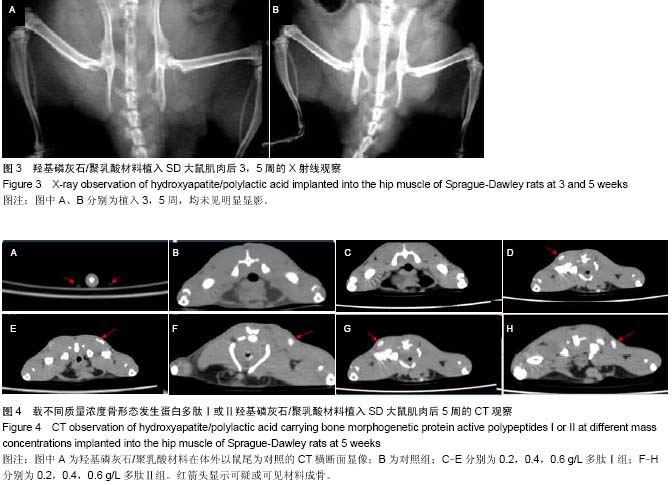
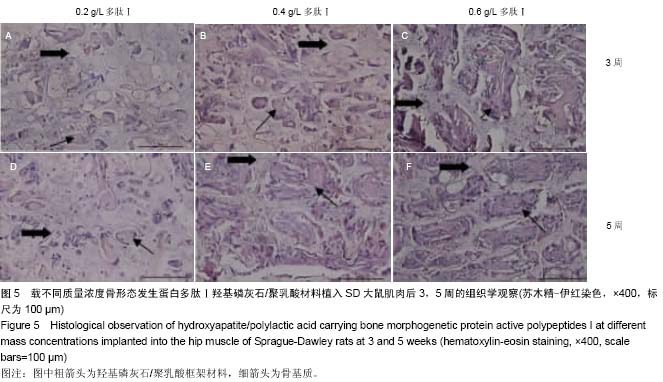
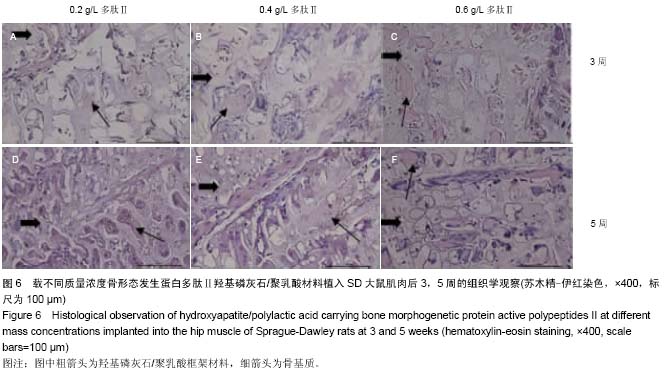
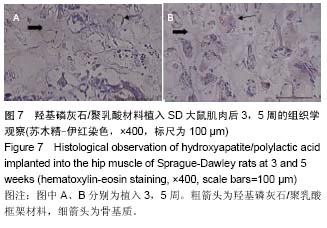
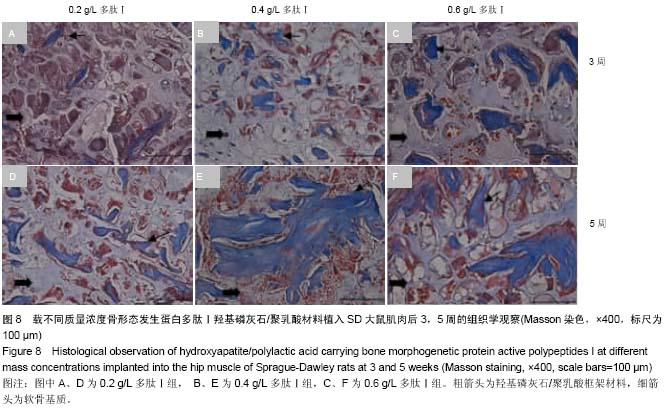
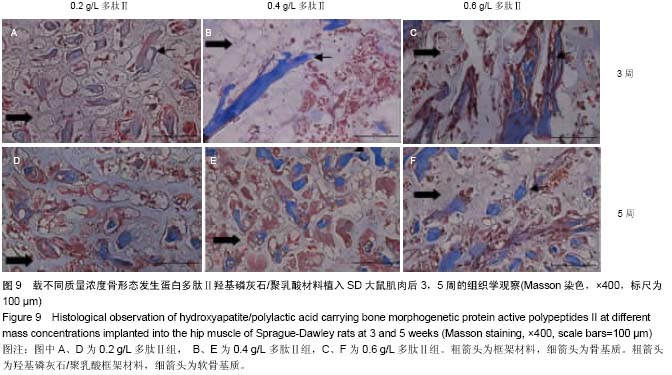
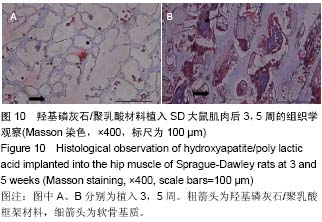
| [1] Mussano F,Gccone G,Ceccardli M,et al.Bone morphogenetie proteins and bone defects:a systematic review.Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(7):824-830.
[2] Jianfeng Wang,Jing Guo,Jingsong Liu,et al. BMP-Functionalised Coatings to Promote Osteogenesis for Orthopaedic Implants.Int J Mol Sci.2014;15(6): 10150-10168.
[3] 王弘毅,郝平,王晋申,等.rhBMP-2 在兔桡骨远端骨缺损模型中成骨效应研究[J].国际骨科学杂志,2013,34(5):362-367.
[4] 段智霞,郑启新,郭晓东,等.骨形态蛋白2活性多肽体外定向定向诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨方向分化的剂量依赖性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(10):1118-1122.
[5] Yang W,Maolin H,Jinmin Z,et al.High expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor 4: correlation with clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis of osteosarcoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2014;140(3): 419-426.
[6] 王俊艳,梁玉.试用Masson染色评价骨组织的成熟程度[J].解剖科学进展,2004,10(Suppl):17-18.
[7] 郭建刚,赵然,侯桂英,等.骨组织成分与Masson三色染色反应的关系分析[J].中医正骨,2001,13(11):5-6.
[8] Rose FR,Oreffo RO.Bone tissue engineering: hope vs hype.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;292(1):1-7.
[9] Cook SD,Rueger DC.Osteogenic protein-1: biology and applications.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1996;(324):29-38.
[10] La WG,Jin M,Park S,et al.Delivery of bone morphogenetic protein-2 and substance P using graphene oxide for bone regeneration.Int J Nanomedicine.2014;9 Suppl 1:107-116.
[11] 张春,魏琴,王雪梅,等.BMP-2 体外诱导OPG小鼠BMSCs向成骨方向分化的实验研究[J].动物与比较医学,2012,32(3): 186-190.
[12] 宁江海,刘洪臣,王会信,等.纤维连接蛋白模拟肽P19的实验研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2005,30(6):475-478.
[13] 段智霞,郑启新,郭晓东,等.BMP-2活性多肽体外定向诱导大鼠BMSCs 向成骨方向分化的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2007,15(21):1647-1650.
[14] 刘虹丽,丁晓颖,张鹏,等.成骨生长肽羧基端片段及其衍生物对成骨细胞作用的体外研究[J].天津医科大学学报,2005,11(3): 349-352.
[15] Tang S,Zhao J,Xu S,et al.Bone induction through controlled release of novel BMP-2- related peptide from PTMC11 -F127-PTMC11 hydrogels.Biomed Mater.2012;7(1):015008.
[16] 李景峰,郑启新,郭晓东,等.BMP2活性多肽/鼠尾Ⅰ型胶原复合物植入异位成骨的实验研究[J].中国医学生物工程学报,2010, 29(2):295-299.
[17] 吴斌,郑启新,郭晓东,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2活性多肽修饰的重组胶原矿化骨对骨髓基质干细胞生物学行为的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(12):1157-1160.
[18] Bose S,Tarafder S.Calcium phosphate ceramic systems in growth factor and drug delivery for bone tissue engineering: areview.Acta Biomater.2012;8(4):1401-1421.
[19] 张晓燕,李正强,孙莹,等.丝素蛋白/左旋聚乳酸复合组织工程纳米材料的生物相容性及安全性评价[J].吉林大学学报,2014, 40(3):578-582.
[20] Todo M,Park SD,Arakawa K,et al.Relationship between microstructure and fracture behavior of bioabs0rbable HA/PLLA composites.Compos Part A Appl Sci Manufac. 2006;37(12):2221-2225.
[21] 杜欧,盖丽婷,王民艳,等.聚乳酸/羟基磷灰石复合材料的机械性能及其细胞毒性[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2014,40(2): 300-305.
[22] Hu Y,Zou S,Chen W,et al.Mineralization and drug release of hydroxyapatite/poly(l-lactic acid) nanocomposite scaffolds prepared by Pickering emulsion templating.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2014;122:559-565.
[23] 游永刚,徐永清,唐辉,等.三种骨移植材料的骨诱导活性对比实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(4):297-300.
[24] Wozney JM,Seeherman HJ.Protein-based tissueengineering in bone and cartilage repair.Curr Opin Biotechnol.2004;15(5):392-398.
[25] Takigami H,Kumagai K,Latson L,et al.Bone formation following OP-1 implantation is improved by addition of autogenous bone marrow cells in a canine femur defect model. J Orthop Res.2007;25(10):1333-1342.
[26] Mariner PD,WudelJM,Miller DE,et al.Synthetic hydrogel scaffold is an effective vehicle for delivery of INFUSE (rhBMP2) to critical-sized calvaria bone defects in rats.J Orthop Res.2013;31(3):401-406. |