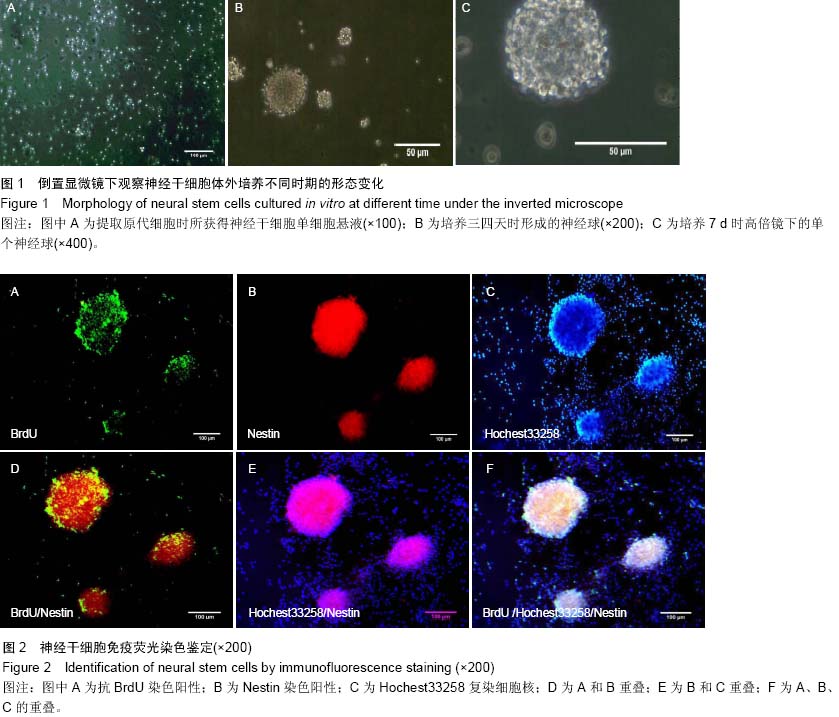
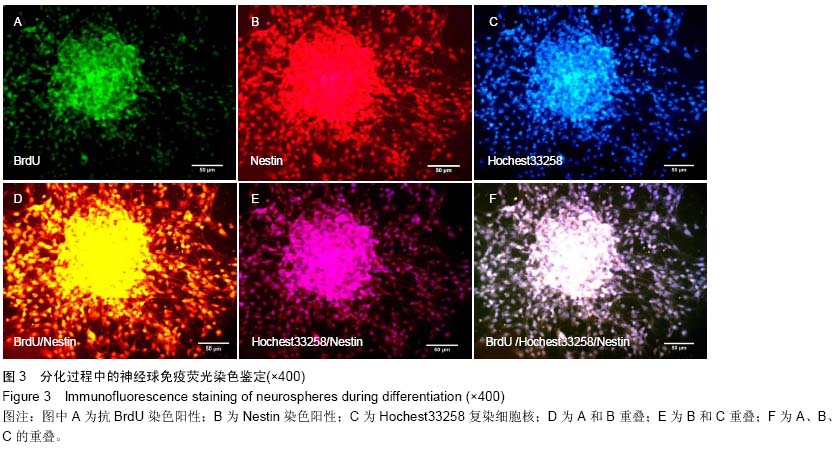
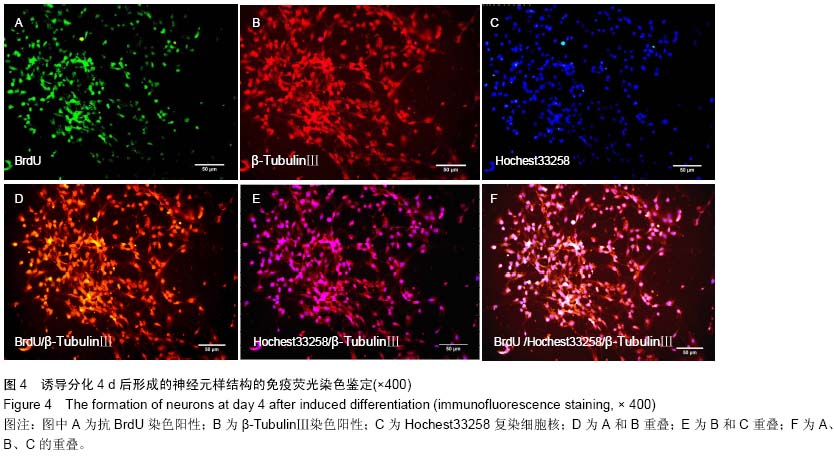
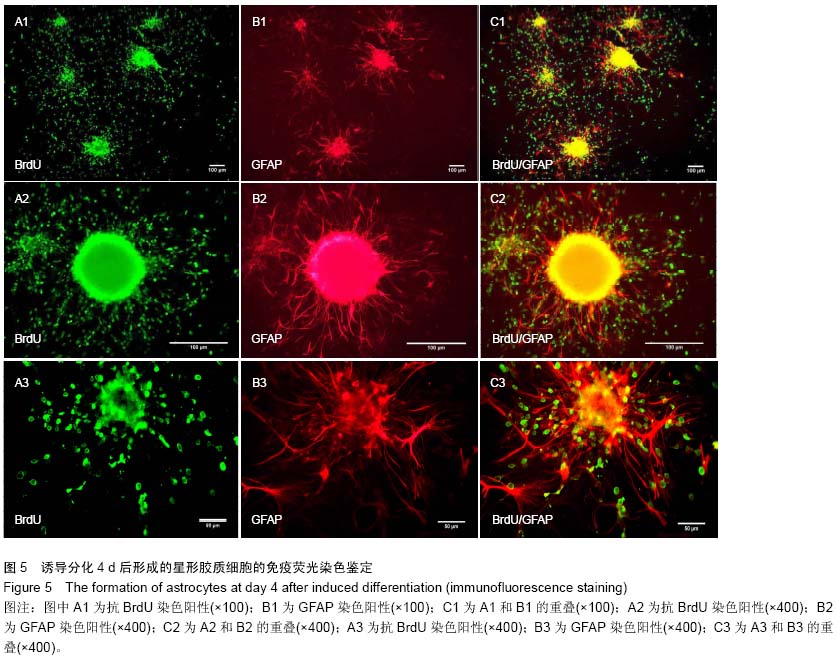
| [1] Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells.Science. 2000; 287 (5457):1433-1438.
[2] Gritti A, Bonfanti L, Doetsch F, et al. Multipotent neural stem cells reside into the rostral extension and olfactory bulb of adult rodents. J Neurosci. 2002;22(2):437-445.
[3] Walker MR, Patel KK, Stappenbeck TS. The stem cell niche. J Pathol. 2009;217(2):169-180.
[4] Ahmed S. The culture of neural stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2009;106(1):1-6.
[5] Crane JF, Trainor PA. Neural crest stem and progenitor cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:267-286.
[6] Miltiadous P, Kouroupi G, Stamatakis A,et al. Subventricular zone-derived neural stem cell grafts protect against hippocampal degeneration and restore cognitive function in the mouse following intrahippocampal kainic acid administration. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(3):185-198.
[7] Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, et al. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of intravascular neural stem cell transplantation in haemorrhagic stroke. Brain. 2008;131(Pt 3):616-629.
[8] Sakata H, Narasimhan P, Niizuma K, et al. Interleukin 6-preconditioned neural stem cells reduce ischaemic injury in stroke mice. Brain. 2012;135(Pt 11):3298-3310.
[9] Mine Y, Tatarishvili J, Oki K, et al. Grafted human neural stem cells enhance several steps of endogenous neurogenesis and improve behavioral recovery after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;52:191-203.
[10] Shetty AK. Hippocampal injury-induced cognitive and mood dysfunction, altered neurogenesis, and epilepsy: can early neural stem cell grafting intervention provide protection. Epilepsy Behav. 2014;38:117-124.
[11] Wang E, Gao J, Yang Q, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying effects of neural stem cells against traumatic axonal injury. J Neurotrauma. 2012;29(2):295-312.
[12] Karussis D, Petrou P, Kassis I. Clinical experience with stem cells and other cell therapies in neurological diseases. J Neurol Sci. 2013;324(1-2):1-9.
[13] Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Clonal and population analyses demonstrate that an EGF-responsive mammalian embryonic CNS precursor is a stem cell. Dev Biol. 1996;175(1):1-13.
[14] Su P, Zhang J, Zhao F, et al. The interaction between microglia and neural stem/precursor cells. Brain Res Bull. 2014;109:32-38.
[15] Ihrie RA, Alvarez-Buylla A. Lake-front property: a unique germinal niche by the lateral ventricles of the adult brain. Neuron. 2011;70(4):674-686.
[16] Drago D, Cossetti C, Iraci N, et al. The stem cell secretome and its role in brain repair. Biochimie. 2013;95(12):2271-2285.
[17] Baraniak PR, McDevitt TC. Stem cell paracrine actions and tissue regeneration. Regen Med. 2010;5(1):121-143.
[18] Qian X, Davis AA, Goderie SK, et al. FGF2 concentration regulates the generation of neurons and glia from multipotent cortical stem cells. Neuron. 1997;18(1):81-93.
[19] Ballarin C, Peruffo A. Primary cultures of astrocytes from fetal bovine brain. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;814:117-126.
[20] Jensen MB, Yan H, Krishnaney-Davison R, et al. Survival and differentiation of transplanted neural stem cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells in a rat stroke model. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;22(4):304-308.
[21] Dulin JN, Lu P.Bridging the injured spinal cord with neural stem cells. Neura Regen Res. 2014;9 (3): 229-231.
[22] Butti E, Cusimano M, Bacigaluppi M, et al. Neurogenic and non-neurogenic functions of endogenous neural stem cells. Front Neurosci. 2014;8:92.
[23] Song S,Park JT,Na JY,et al.Early expressions of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor increase the neuronal plasticity of activated endogenous neural stem cells after focal cerebral ischemia. Neura Regen Res. 2014;9(9): 912-918. |