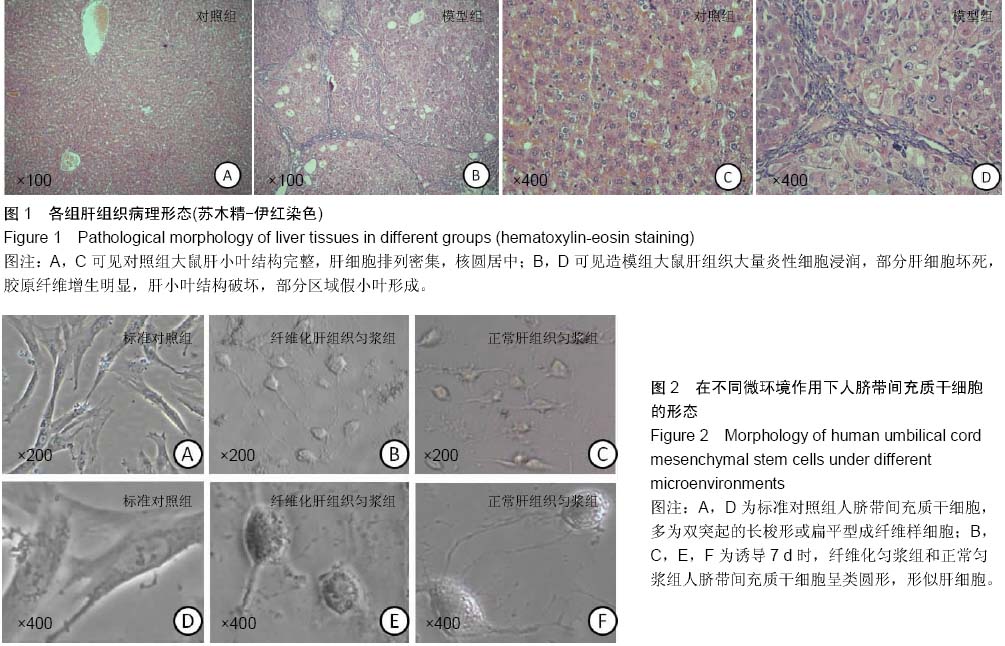
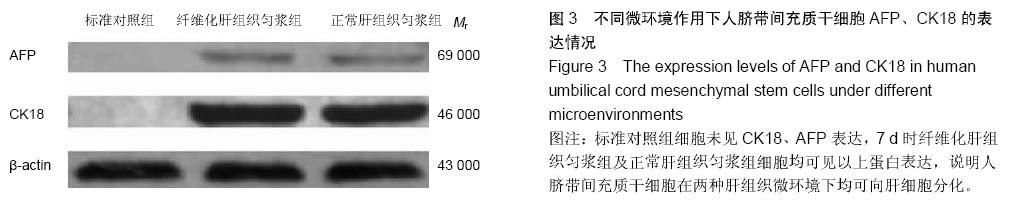
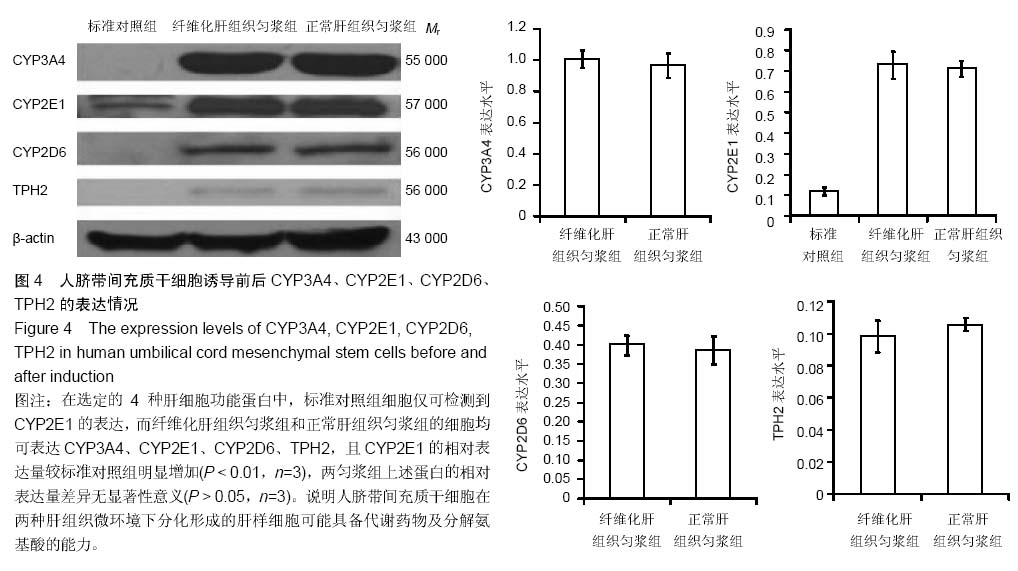
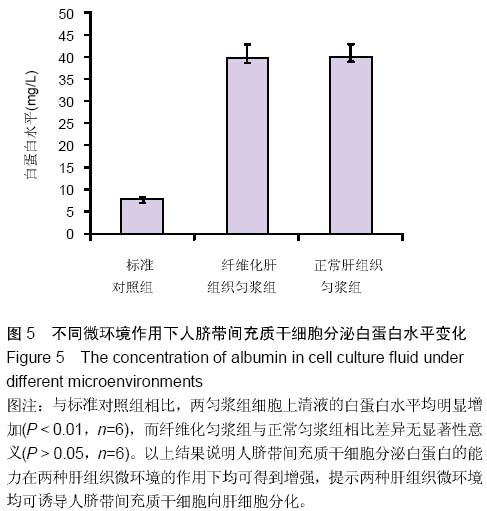
| [1] Park M, Kim YH, Woo SY, et al. Tonsil-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice via autophagy activation.Sci Rep. 2015;5:8616.
[2] Yu F, Ji S, Su L, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit activation of hepatic stellate cells in vitro and ameliorate rat liver fibrosis in vivo. J Formos Med Assoc. 2015; 114(2):130-138.
[3] Zheng L, Chu J, Shi Y, et al. Bone marrow-derived stem cells ameliorate hepatic fibrosis by down-regulating interleukin-17. Cell Biosci. 2013;3(1):46.
[4] Zhang Z, Lin H, Shi M, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells improve liver function and ascites in decompensated liver cirrhosis patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27 Suppl 2:112-120.
[5] Berardis S, Dwisthi Sattwika P, Najimi M, et al. Use of mesenchymal stem cells to treat liver fibrosis: current situation and future prospects. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21(3):742-758.
[6] Ahmed SK, Mohammed SA, Khalaf G, et al. Role of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of CCL4 Induced Liver Fibrosis in Albino Rats: A Histological and Immunohistochemical Study. Int J Stem Cells. 2014;7(2): 87-97.
[7] Salama H, Zekri AR, Medhat E, et al. Peripheral vein infusion of autologous mesenchymal stem cells in Egyptian HCV-positive patients with end-stage liver disease. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(3):70.
[8] Terai S, Takami T, Yamamoto N, et al. Status and prospects of liver cirrhosis treatment by using bone marrow-derived cells and mesenchymal cells. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(3): 206-210.
[9] Abdel Aziz M, Atta H, Roshdy N, et al. Amelioration of Murine Schistosoma mansoni Induced Liver Fibrosis by Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2012; 8(1): 28-34.
[10] Nikeghbalian S, Pournasr B, Aghdami N, et al. Autologous transplantation of bone marrow-derived mononuclear and CD133(+) cells in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Arch Iran Med. 2011;14(1):12-17.
[11] 范莎莎,石詠中,袁友红,等. 肝纤维化大鼠血清体外诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向肝细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(27):4959-4963.
[12] 马欣,薛改,刘建芳,等.肝匀浆上清液诱导人脐带间充质干细胞分化为肝样细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(45):7877-7884.
[13] Wang H, Wu G, Park HJ, et al. Protective effect of Phellinus linteus polysaccharide extracts against thioacetamide- induced liver fibrosis in rats: a proteomics analysis. Chin Med. 2012;7(1):23.
[14] Spradling A, Drummond-Barbosa D, Kai T. Stem cells find their niche. Nature. 2001;414(6859):98-104.
[15] 王韫芳,南雪,尉承泽,等.丙烯醇致肝损伤微环境定向诱导骨髓干细胞向肝细胞分化[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2005,13(4):274-277.
[16] Wang X, Wu H, Xue G, et al. Progesterone promotes neuronal differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in culture conditions that mimic the brain microenvironment. Neural Regen Res. 2012;7(25):1925-1930.
[17] 李昆,李世正,张蕴莉.心肌微环境对胎盘间充质干细胞向心肌细胞分化的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2012,22(29):16-20.
[18] 刘楠梅,田军,王巍巍,等.急性肾损伤微环境对培养骨髓间充质干细胞分化及分裂增殖的影响[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志,2010, 19(5):435-439,444.
[19] 刘芳,何援利.模拟子宫内膜微环境体外诱导兔骨髓间充质干细胞向子宫内膜上皮细胞分化的实验研究[J].现代妇产科进展, 2012,21(11):878-881.
[20] Ye JS, Su XS, Stoltz JF, et al. Signalling pathways involved in the process of mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into hepatocytes. Cell Prolif. 2015;48(2):157-165.
[21] Lu T, Yang C, Sun H, et al. FGF4 and HGF promote differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes via the MAPK pathway. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(1):415-424.
[22] Takata A, Otsuka M, Kogiso T, et al. Direct differentiation of hepatic cells from human induced pluripotent stem cells using a limited number of cytokines.Hepatol Int. 2011;5(4):890-898.
[23] Ye JS, Su XS, Stoltz JF, et al. Signalling pathways involved in the process of mesenchymal stem cells differentiating into hepatocytes. Cell Prolif. 2015;48(2):157-165.
[24] Li X, Yuan J, Li W, et al. Direct differentiation of homogeneous human adipose stem cells into functional hepatocytes by mimicking liver embryogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2014;229(6): 801-812.
[25] Kuai XL, Shao N, Lu H, et al. Differentiation of nonhuman primate embryonic stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells. J Dig Dis. 2014;15(1):27-34.
[26] Huang HI, Chen SK, Wang RY, et al. Human foreskin fibroblast-like stromal cells can differentiate into functional hepatocytic cells. Cell Biol Int. 2013;37(12):1308-1319.
[27] Alaimo G, Cozzoli E, Marfe G, et al. Blood-derived stem cells (BDSCs) plasticity: in vitro hepatic differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(6):1249-1254.
[28] 刘英,施占立,赵宗泽,等.人脐带源间充质干细胞移植改善四氯化碳诱导肝硬化大鼠的肝纤维化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(10):1837-1840.
[29] 张英杰,李玉云,郝晓娜,等.人脐带源间充质干细胞静脉移植治疗大鼠肝纤维化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(28):4485-4490.
[30] 曲鑫,王新超,韩璐,等.不同来源间质干细胞移植治疗大鼠肝纤维化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(6):926-931. |