中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (14): 2283-2290.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.14.026
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
骨髓微环境对造血干细胞命运的调控
杜 华,师迎旭
- 内蒙古医科大学附属医院检验科,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010050
-
修回日期:2015-03-07出版日期:2015-04-02发布日期:2015-04-02 -
通讯作者:师迎旭,博士,助理研究员,内蒙古医科大学附属医院检验科,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010050 -
作者简介:杜华,女,1978年生,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市人,汉族,2012年内蒙古医科大学毕业,硕士,讲师,主要从事肿瘤病理学方面的研究。 -
基金资助:内蒙古医科大学科技百万工程基金(YKD2012KJBW006);内蒙古自治区高等学校科学研究项目(NJZY12145)
Bone marrow microenvironment controls the “fate” of hematopoietic stem cells
Du Hua, Shi Ying-xu
- Department of Laboratory Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Hohhot 010050, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2015-03-07Online:2015-04-02Published:2015-04-02 -
Contact:Shi Ying-xu, M.D., Assistant researcher, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Hohhot 010050, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Du Hua, Master, Lecturer, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, Hohhot 010050, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the “One Million” Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. YKD2012KJBW006; the Higher Research Project in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. NJZY12145
摘要:
背景:研究表明造血微环境主要通过细胞-细胞、细胞-可溶性因子、细胞-细胞外基质3种模式对造血干细胞进行调控。
中图分类号:
引用本文
杜 华,师迎旭. 骨髓微环境对造血干细胞命运的调控[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(14): 2283-2290.
Du Hua, Shi Ying-xu . Bone marrow microenvironment controls the “fate” of hematopoietic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(14): 2283-2290.
| [1] Till JE, McCulloch EA. A direct measurement of the radiation sensitivity of normal mouse bone marrow cells. Radiat Res. 1961;14:213-222. [2] Kiel MJ, Yilmaz OH, Iwashita T, et al. SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell. 2005;121(7): 1109-1121. [3] Hoover-Plow J, Gong Y. Challenges for heart disease stem cell therapy.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2012;8:99-113. [4] Schofield R. The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells. 1978;4(1-2):7-25. [5] Winkler IG, Sims NA, Pettit AR, et al. Bone marrow macrophages maintain hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niches and their depletion mobilizes HSCs. Blood. 2010;116(23): 4815-4828. [6] Boisset JC, van Cappellen W, Andrieu-Soler C, et al. In vivo imaging of haematopoietic cells emerging from the mouse aortic endothelium. Nature. 2010 4;464(7285):116-120. [7] Bertrand JY, Chi NC, Santoso B, et al. Haematopoietic stem cells derive directly from aortic endothelium during development. Nature. 2010;464(7285):108-111. [8] Garrett RW, Emerson SG. Bone and blood vessels: the hard and the soft of hematopoietic stem cell niches. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4(6):503-506. [9] Kiel MJ, Morrison SJ. Uncertainty in the niches that maintain haematopoietic stem cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(4): 290-301. [10] Butler JM, Nolan DJ, Vertes EL, et al. Endothelial cells are essential for the self-renewal and repopulation of Notch-dependent hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;6(3):251-264. [11] Chow A, Lucas D, Hidalgo A, et al. Bone marrow CD169+ macrophages promote the retention of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the mesenchymal stem cell niche. J Exp Med. 2011;208(2):261-271. [12] Sipkins DA, Wei X, Wu JW, et al. In vivo imaging of specialized bone marrow endothelial microdomains for tumour engraftment. Nature. 2005;435(7044):969-973. [13] Christopher MJ, Rao M, Liu F, et al. Expression of the G-CSF receptor in monocytic cells is sufficient to mediate hematopoietic progenitor mobilization by G-CSF in mice. J Exp Med. 2011;208(2):251-260. [14] Kobayashi H, Butler JM, O'Donnell R,et al. Angiocrine factors from Akt-activated endothelial cells balance self-renewal and differentiation of haematopoietic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2010;12(11):1046-1056. [15] Méndez-Ferrer S, Michurina TV, Ferraro F, et al. Mesenchymal and haematopoietic stem cells form a unique bone marrow niche. Nature. 2010;466(7308):829-834. [16] Omatsu Y, Sugiyama T, Kohara H,et al. The essential functions of adipo-osteogenic progenitors as the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell niche. Immunity. 2010;33(3):387-399. [17] Ehninger A1, Trumpp A.The bone marrow stem cell niche grows up: mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages move in. J Exp Med. 2011;208(3):421-428. [18] Gertz MA. Current status of stem cell mobilization. Br J Haematol. 2010;150(6):647-662. [19] Ito K, Hirao A, Arai F, et al. Reactive oxygen species act through p38 MAPK to limit the lifespan of hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Med. 2006;12(4):446-451. [20] Tothova Z, Kollipara R, Huntly BJ, et al. FoxOs are critical mediators of hematopoietic stem cell resistance to physiologic oxidative stress. Cell. 2007;128(2):325-339. [21] Trumpp A, Essers M, Wilson A. Awakening dormant haematopoietic stem cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10(3): 201-209. [22] Takizawa H, Regoes RR, Boddupalli CS, et al. Dynamic variation in cycling of hematopoietic stem cells in steady state and inflammation. J Exp Med. 2011;208(2):273-284. [23] Grassinger J, Haylock DN, Williams B, et al. Phenotypically identical hemopoietic stem cells isolated from different regions of bone marrow have different biologic potential. Blood. 2010;116(17):3185-3196. [24] Bari S, Chu PP, Lim A, et al. Protective role of functionalized single walled carbon nanotubes enhance ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Nanomedicine. 2013;9(8):1304-1316. [25] Jung Y, Wang J, Havens A, et al. Cell-to-cell contact is critical for the survival of hematopoietic progenitor cells on osteoblasts. Cytokine. 2005;32(3-4):155-162. [26] Papayannopoulou T. Current mechanistic scenarios in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell mobilization. Blood. 2004;103(5):1580-1585. [27] Zohren F, Toutzaris D, Klärner V, et al. The monoclonal anti-VLA-4 antibody natalizumab mobilizes CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells in humans. Blood. 2008;111(7): 3893-3895. [28] Scott LM, Priestley GV, Papayannopoulou T. Deletion of alpha4 integrins from adult hematopoietic cells reveals roles in homeostasis, regeneration, and homing. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(24):9349-9360. [29] Grunwald GB, Pratt RS, Lilien J. Enzymic dissection of embryonic cell adhesive mechanisms. III. Immunological identification of a component of the calcium-dependent adhesive system of embryonic chick neural retina cells. J Cell Sci. 1982;55:69-83. [30] Chiba H, Ataka K, Iba K, et al. Diabetes impairs the interactions between long-term hematopoietic stem cells and osteopontin-positive cells in the endosteal niche of mouse bone marrow. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2013;305(7): C693-703. [31] Arai F, Hosokawa K, Toyama H, et al. Role of N-cadherin in the regulation of hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow niche. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2012;1266:72-77. [32] Bromberg O, Frisch BJ, Weber JM, et al. Osteoblastic N-cadherin is not required for microenvironmental support and regulation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood. 2012;120(2):303-313. [33] Greenbaum AM, Revollo LD, Woloszynek JR, et al. N-cadherin in osteolineage cells is not required for maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2012; 120(2):295-302. [34] Arai F, Hirao A, Ohmura M, et al. Tie2/angiopoietin-1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche. Cell. 2004;118(2):149-161. [35] Kiel MJ, Radice GL, Morrison SJ. Lack of evidence that hematopoietic stem cells depend on N-cadherin-mediated adhesion to osteoblasts for their maintenance. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1(2):204-217. [36] Haug JS, He XC, Grindley JC, et al. N-cadherin expression level distinguishes reserved versus primed states of hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;2(4):367-379. [37] Kiel MJ, Acar M, Radice GL, et al. Hematopoietic stem cells do not depend on N-cadherin to regulate their maintenance. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4(2):170-179. [38] Hosokawa K, Arai F, Yoshihara H, et al. Knockdown of N-cadherin suppresses the long-term engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 2010;116(4):554-563. [39] Zhang K, Zhang YQ, Ai WB, et al. Hes1, an important gene for activation of hepatic stellate cells, is regulated by Notch1 and TGF-β/BMP signaling.World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21(3):878-887. [40] Kim AD, Melick CH, Clements WK, et al. Discrete Notch signaling requirements in the specification of hematopoietic stem cells. EMBO J. 2014;33(20):2363-2373. [41] Gerhardt DM, Pajcini KV, D'altri T, et al. The Notch1 transcriptional activation domain is required for development and reveals a novel role for Notch1 signaling in fetal hematopoietic stem cells. Genes Dev. 2014;28(6):576-593. [42] Tie G, Messina KE, Yan J, et al. Hypercholesterolemia induces oxidant stress that accelerates the ageing of hematopoietic stem cells. J Am Heart Assoc. 2014;3(1): e000241. [43] Tang Y, Bai H, Urs S, et al. Notch1 activation in embryonic VE-cadherin populations selectively blocks hematopoietic stem cell generation and fetal liver hematopoiesis. Transgenic Res. 2013;22(2):403-410. [44] Mancini SJ, Mantei N, Dumortier A, et al. Jagged1-dependent Notch signaling is dispensable for hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Blood. 2005;105(6): 2340-2342. [45] Chen S, Xu L, Lin N, et al. Activation of Notch1 signaling by marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through cell-cell contact inhibits proliferation of hepatic stellate cells. Life Sci. 2011;89(25-26):975-981. [46] Zeng Y, Broxmeyer HE, Staser K, et al. Pak2 regulates hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation, survival and differentiation. Stem Cells. 2015 Jan 13. doi: 10.1002/stem.1951. [Epub ahead of print]. [47] Zandstra PW, Conneally E, Petzer AL, et al. Cytokine manipulation of primitive human hematopoietic cell self-renewal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94(9):4698-4703. [48] Vegh P, Winckler J, Melchers F. Long-term "in vitro" proliferating mouse hematopoietic progenitor cell lines. Immunol Lett. 2010;130(1-2):32-35. [49] Ogawa M, Matsuzaki Y, Nishikawa S, et al. Expression and function of c-kit in hemopoietic progenitor cells. J Exp Med. 1991;174(1):63-71. [50] McCulloch EA, Siminovitch L, Till JE, et al. The cellular basis of the genetically determined hemopoietic defect in anemic mice of genotype Sl-Sld.Blood. 1965;26(4):399-410. [51] Kent D, Copley M, Benz C, et al. Regulation of hematopoietic stem cells by the steel factor/KIT signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(7):1926-1930. [52] Colmone A, Amorim M, Pontier AL, et al. Leukemic cells create bone marrow niches that disrupt the behavior of normal hematopoietic progenitor cells. Science. 2008;322 (5909):1861-1865. [53] Chou FS, Mulloy JC. The thrombopoietin/MPL pathway in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2011; 112(6):1491-1498. [54] Du J, Wang J, Kong G, et al. Signaling profiling at the single-cell level identifies a distinct signaling signature in murine hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cells. 2012;30(7):1447-1454. [55] Terskikh AV, Miyamoto T, Chang C, et al. Gene expression analysis of purified hematopoietic stem cells and committed progenitors. Blood. 2003;102(1):94-101. [56] Link KA, Chou FS, Mulloy JC. Core binding factor at the crossroads: determining the fate of the HSC. J Cell Physiol. 2010;222(1):50-56. [57] Olson TS, Caselli A, Otsuru S, et al. Megakaryocytes promote murine osteoblastic HSC niche expansion and stem cell engraftment after radioablative conditioning. Blood. 2013; 121(26):5238-5249. [58] Kidd S, Bueso-Ramos C, Jagan S, et al. In vivo expansion of the megakaryocyte progenitor cell population in adult CD26-deficient mice. Exp Hematol. 2011;39(5):580-590. [59] Davis S, Aldrich TH, Jones PF, et al. Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell. 1996;87(7):1161-1169. [60] Yuan J, Fang W, Lin A, et al. Angiopoietin-2/Tie2 signaling involved in TNF-α induced peritoneal angiogenesis. Int J Artif Organs. 2012;35(9):655-662. [61] Zhou ZH, Karnaukhova E, Rajabi M, et al. Oversulfated chondroitin sulfate binds to chemokines and inhibits stromal cell-derived factor-1 mediated signaling in activated T cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e94402. [62] Bleul CC, Fuhlbrigge RC, Casasnovas JM, et al. A highly efficacious lymphocyte chemoattractant, stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1). J Exp Med. 1996;184(3):1101-1109. [63] Tzeng YS, Li H, Kang YL, et al. Loss of Cxcl12/Sdf-1 in adult mice decreases the quiescent state of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells and alters the pattern of hematopoietic regeneration after myelosuppression. Blood. 2011;117(2): 429-439. [64] Bleul CC, Farzan M, Choe H, et al. The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature. 1996;382(6594):829-833. [65] Wang H, Beaty N, Chen S, et al. The CXCR7 chemokine receptor promotes B-cell retention in the splenic marginal zone and serves as a sink for CXCL12. Blood. 2012;119(2): 465-468. [66] Itkin T, Lapidot T. SDF-1 keeps HSC quiescent at home. Blood. 2011;117(2):373-374. [67] Konuma T, Takahashi S. Cord Blood Transplantation in Adults with Acute Leukemia[M]. INTECH Open Access Publisher, 2011. [68] Nishino T, Osawa M, Iwama A. New approaches to expand hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(6):743-756. [69] Zhang K, Zhang YQ, Ai WB, et al. Hes1, an important gene for activation of hepatic stellate cells, is regulated by Notch1 and TGF-β/BMP signaling. World J Gastroenterol. 2015; 21(3): 878-887. [70] Shiozawa Y, Jung Y, Ziegler AM, et al. Erythropoietin couples hematopoiesis with bone formation. PLoS One. 2010;5(5): e10853. [71] Essers MA, Offner S, Blanco-Bose WE, et al. IFNalpha activates dormant haematopoietic stem cells in vivo. Nature. 2009;458(7240):904-908. [72] Brakebusch C, Fillatreau S, Potocnik AJ, et al. Beta1 integrin is not essential for hematopoiesis but is necessary for the T cell-dependent IgM antibody response. Immunity. 2002;16(3): 465-477. [73] Schreiber TD, Steinl C, Essl M, et al. The integrin alpha9beta1 on hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells: involvement in cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation. Haematologica. 2009;94(11):1493-1501. [74] Qian H, Georges-Labouesse E, Nyström A, et al. Distinct roles of integrins alpha6 and alpha4 in homing of fetal liver hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood. 2007;110(7): 2399-2407. [75] Wilson A, Trumpp A. Bone-marrow haematopoietic-stem-cell niches. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(2):93-106. [76] Dao MA, Nolta JA. Cytokine and integrin stimulation synergize to promote higher levels of GATA-2, c-myb, and CD34 protein in primary human hematopoietic progenitors from bone marrow. Blood. 2007;109(6):2373-2379. [77] Zhang J, Grindley JC, Yin T, et al. PTEN maintains haematopoietic stem cells and acts in lineage choice and leukaemia prevention. Nature. 2006;441(7092):518-522. [78] Duncan AW, Rattis FM, DiMascio LN, et al. Integration of Notch and Wnt signaling in hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(3):314-322. [79] Parmar K, Mauch P, Vergilio JA, et al. Distribution of hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow according to regional hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(13): 5431-5436. [80] Nilsson SK, Johnston HM, Whitty GA, et al. Osteopontin, a key component of the hematopoietic stem cell niche and regulator of primitive hema topoietic progenitor cells. Blood. 20055;106(4):1232-1239. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | 张秀梅, 翟运开, 赵 杰, 赵 萌. 类器官模型国内外数据库近10年文献研究热点分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | 王正东, 黄 娜, 陈婧娴, 郑作兵, 胡鑫宇, 李 梅, 苏 晓, 苏学森, 颜 南. 丁酸钠抑制氟中毒可诱导小胶质细胞活化及炎症因子表达增多[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [5] | 汪显耀, 关亚琳, 刘忠山. 提高间充质干细胞治疗难愈性创面的策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [6] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [7] | 廖成成, 安家兴, 谭张雪, 王 倩, 刘建国. 口腔鳞状细胞癌干细胞的治疗靶点及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [8] | 谢文佳, 夏天娇, 周卿云, 刘羽佳, 顾小萍. 小胶质细胞介导神经元损伤在神经退行性疾病中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [9] | 李珊珊, 郭笑霄, 尤 冉, 杨秀芬, 赵 露, 陈 曦, 王艳玲. 感光细胞替代治疗视网膜变性疾病[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [10] | 焦 慧, 张一宁, 宋雨晴, 林 宇, 王秀丽. 乳腺癌类器官研究进展及临床应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [11] | 王诗琦, 张金生. 中医药调控缺血缺氧微环境对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化及衰老的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [12] | 曾燕华, 郝延磊. 许旺细胞体外培养及纯化的系统性综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [13] | 孔德胜, 何晶晶, 冯宝峰, 郭瑞云, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, 吕 飞, 张舒涵, 张晓琳, 马 隽, 崔慧先. 间充质干细胞修复大动物模型脊髓损伤疗效评价的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [14] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [15] | 史洋洋, 秦英飞, 吴福玲, 何 潇, 张雪静. 胎盘间充质干细胞预处理预防小鼠毛细支气管炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
1.1 资料来源 由第一作者分别以“Niche,HSC,VCAM-1,VLA-4,TPO,MPL,ECM,Integrin,N-cadherin,ANG-1,Tie2,ECM,VLA-5,Jagged-1,Notch,CXCL12,CXCR4,SCF,Kit,BMPs/TGF-β,TGF-βR,IFNα,IFNαR”为英文关键词,检索PubMed英文数据库中1965年1月至2015年1月的文献。
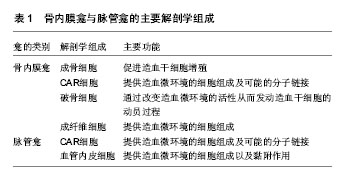
1 此问题的已知信息:骨髓腔内存在两类造血微环境:骨内膜造血微环境和脉管造血微环境,造血微环境通过信号分子调控造血干细胞的功能。
造血干细胞的自我更新能力也是相对有限的, 需要特定的细胞外环境来维持其相对稳态---使造血干细胞处于相对静止状态,允许造血干细胞自我更新但不分化。关于造血微环境的研究很多,但是确切的机制仍需要进一步研究。目前关于造血微环境主流上认为存在2个龛,一个是骨内膜龛,一个是脉管龛,但很多实验结果支持骨髓腔内可能存在其他的造血微环境。造血微环境主要通过3种途径:细胞-细胞、细胞-可溶性细胞因子、细胞-基质对造血干细胞的各种功能如分化、增殖、自我更新等进行调控。目前对于各途径的研究报道不断在更新,甚至有争论例如N-cadherin。了解、研究这些调控途径、调控分子、调控机制,将有助于找到确切的造血干细胞龛,为进一步揭示造血干细胞龛的本质奠定基础。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||