| [1] Widuchowski W, Widuchowski J, Trzaska T. Articular cartilage defects: study of 25,124 knee arthroscopies. Knee. 2007; 14(3):177-182.
[2] Dewan AK, Gibson MA, Elisseeff JH, et al. Evolution of autologous chondrocyte repair and comparison to other cartilage repair techniques. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014: 272481.
[3] 李海鹏,刘玉杰.关节软骨损伤治疗的最新进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(14):1076-1078.
[4] Miller BS, Steadman JR, Briggs KK, et al. Patient satisfaction and outcome after microfracture of the degenerative knee. J Knee Surg. 2004;17(1):13-17.
[5] Steadman JR, Briggs KK, Rodrigo JJ, et al. Outcomes of microfracture for traumatic chondral defects of the knee: average 11-year follow-up.Arthroscopy. 2003;19(5):477-484.
[6] Steadman JR, Miller BS, Karas SG, et al. The microfracture technique in the treatment of full-thickness chondral lesions of the knee in National Football League players. J Knee Surg. 2003;16(2):83-86.
[7] Russlies M, Behrens P, Wünsch L,et al. A cell-seeded biocomposite for cartilage repair. Ann Anat. 2002;184(4): 317-323.
[8] Trattnig S, Ba-Ssalamah A, Pinker K, et al. Matrix-based autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage repair: noninvasive monitoring by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;23(7): 779-787.
[9] 杜志坡,贝抗胜.干细胞在骨科疾病治疗中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(36):6817-6820.
[10] Hernigou P, Beaujean F. Treatment of osteonecrosis with autologous bone marrow grafting. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002;(405):14-23.
[11] Kreuz PC, Erggelet C, Steinwachs MR, et al. Is microfracture of chondral defects in the knee associated with different results in patients aged 40 years or younger. Arthroscopy. 2006;22(11):1180-1186.
[12] Kreuz PC, Steinwachs MR, Erggelet C, et al. Results after microfracture of full-thickness chondral defects in different compartments in the knee. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(11):1119-1125.
[13] Steadman JR, Briggs KK, Rodrigo JJ, et al. Outcomes of microfracture for traumatic chondral defects of the knee: average 11-year follow-up. Arthroscopy. 2003;19(5):477-484.
[14] Mithoefer K, Williams RJ 3rd, Warren RF, et al. The microfracture technique for the treatment of articular cartilage lesions in the knee. A prospective cohort study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(9):1911-1920.
[15] Brittberg M, Lindahl A, Nilsson A, et al. Treatment of deep cartilage defects in the knee with autologous chondrocyte transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1994;331(14):889-895.
[16] Marcacci M, Zaffagnini S, Kon E, et al. Arthroscopic autologous chondrocyte transplantation: technical note. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2002;10(3):154-159.
[17] Xing L, Jiang Y, Gui J, et al. Microfracture combined with osteochondral paste implantation was more effective than microfracture alone for full-thickness cartilage repair. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(8):1770-1776.
[18] Lane JG, Healey RM, Chen AC, et al. Can osteochondral grafting be augmented with microfracture in an extended-size lesion of articular cartilage. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(7): 1316-1323.
[19] Tegner Y, Lysholm J. Rating systems in the evaluation of knee ligament injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;(198):43-49.
[20] Shapiro F, Koide S, Glimcher MJ. Cell origin and differentiation in the repair of full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(4):532-553.
[21] Gomoll AH, Madry H, Knutsen G, et al. The subchondral bone in articular cartilage repair: current problems in the surgical management.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(4):434-447.
[22] Williams RJ 3rd, Harnly HW. Microfracture: indications, technique, and results. Instr Course Lect. 2007;56:419-428.
[23] Gill TJ, Asnis PD, Berkson EM. The treatment of articular cartilage defects using the microfracture technique. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2006;36(10):728-738.
[24] Truong MD, Chung JY, Kim YJ, et al. Histomorphochemical comparison of microfracture as a first-line and a salvage procedure: is microfracture still a viable option for knee cartilage repair in a salvage situation. J Orthop Res. 2014; 32(6):802-810.
[25] Wang Q, Li ZL, Fu YM, et al. Effect of low-energy shock waves in microfracture holes in the repair of articular cartilage defects in a rabbit model. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011;124(9): 1386-1394.
[26] Kon E, Gobbi A, Filardo G, et al. Arthroscopic second-generation autologous chondrocyte implantation compared with microfracture for chondral lesions of the knee: prospective nonrandomized study at 5 years. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(1):33-41.
[27] Peterson L, Brittberg M, Kiviranta I, et al. Autologous chondrocyte transplantation. Biomechanics and long-term durability. Am J Sports Med. 2002;30(1):2-12.
[28] Saris DB, Vanlauwe J, Victor J, et al. Characterized chondrocyte implantation results in better structural repair when treating symptomatic cartilage defects of the knee in a randomized controlled trial versus microfracture. Am J Sports Med. 2008;36(2):235-246.
[29] Knutsen G, Drogset JO, Engebretsen L, et al. A randomized trial comparing autologous chondrocyte implantation with microfracture. Findings at five years. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(10):2105-2112.
[30] Knutsen G, Engebretsen L, Ludvigsen TC, et al. Autologous chondrocyte implantation compared with microfracture in the knee. A randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(3): 455-464.
[31] Yoo JU, Barthel TS, Nishimura K, et al. The chondrogenic potential of human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998;80(12): 1745-1757.
[32] Nejadnik H, Hui JH, Feng Choong EP, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells versus autologous chondrocyte implantation: an observational cohort study. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(6):1110-1116.
[33] 任杰,郑荣琴,黄冬梅,等.膝关节软骨退行性变的声像学表现[J].中国超声医学杂志,2006,22(2):151-153.
[34] 王万宗,陈宗雄,刘晓强.骨髓间充质干细胞与关节软骨细胞Transwell共培养诱导形成软骨[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(38):7041-7044.
[35] Coleman RM, Case ND, Guldberg RE. Hydrogel effects on bone marrow stromal cell response to chondrogenic growth factors. Biomaterials. 2007;28(12):2077-2086.
[36] Gille J, Schuseil E, Wimmer J, et al. Mid-term results of Autologous Matrix-Induced Chondrogenesis for treatment of focal cartilage defects in the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(11):1456-1464.
[37] Siclari A, Mascaro G, Gentili C, et al. A cell-free scaffold-based cartilage repair provides improved function hyaline-like repair at one year. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(3):910-919.
[38] 赵卫民,聂振洪,张书玲. 关节镜下微骨折术治疗膝关节软骨损伤的临床观察[J].疑难病杂志,2010,9(6):456-457. |
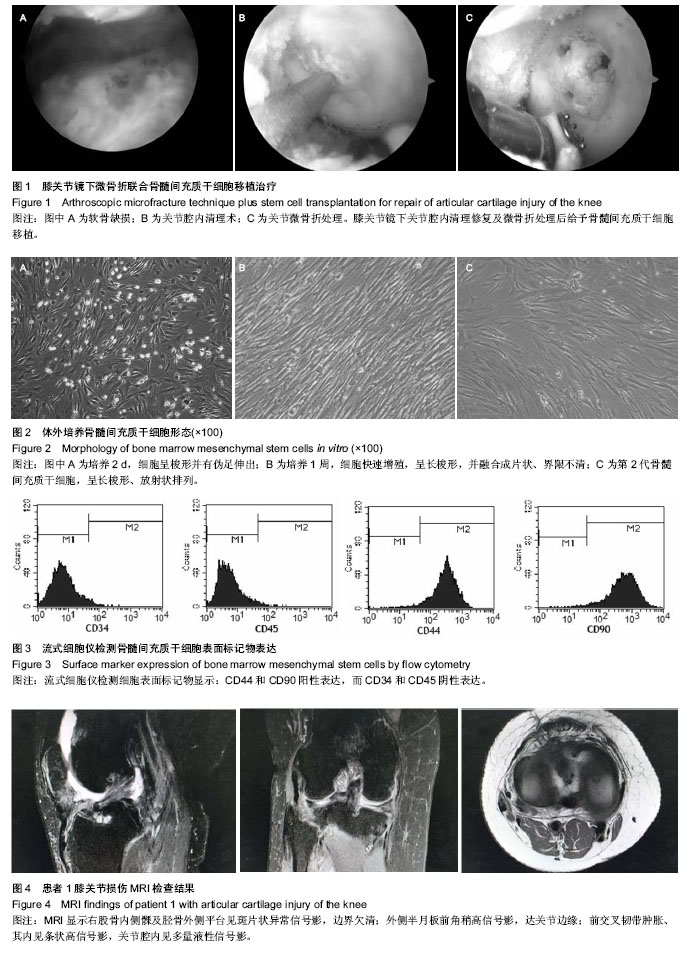
.jpg)
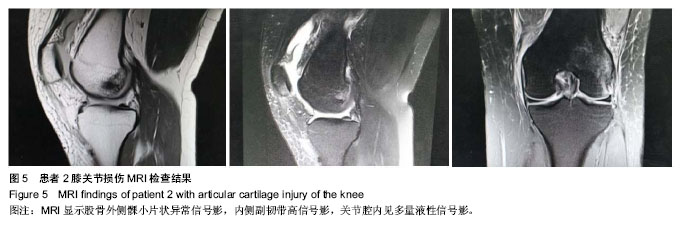
.jpg)