| [1] Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957;16(4):485-493.
[2] Mareddy S, Crawford R, Brooke G, et al. Clonal isolation and characterization of bone marrow stromal cells from patients with osteoarthritis. Tissue Eng. 2007;13(4):819-829.
[3] Madry H, Cucchiarini M. Clinical potential and challenges of using genetically modified cells for articular cartilage repair. Croat Med J. 2011;52(3):245-261.
[4] Evans CH, Robbins PD, Ghivizzani SC, et al. Gene transfer to human joints: progress toward a gene therapy of arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(24):8698-8703.
[5] Centeno CJ, Busse D, Kisiday J, et al. Increased knee cartilage volume in degenerative joint disease using percutaneously implanted, autologous mesenchymal stem cells. Pain Physician. 2008;11(3):343-353.
[6] Emadedin M, Aghdami N, Taghiyar L, et al. Intra-articular injection of autologous mesenchymal stem cells in six patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arch Iran Med. 2012;15(7):422-428.
[7] Vangsness CT Jr, Farr J 2nd, Boyd J, et al. Adult human mesenchymal stem cells delivered via intra-articular injection to the knee following partial medial meniscectomy: a randomized, double-blind, controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(2):90-98.
[8] Krampera M, Cosmi L, Angeli R, et al. Role for interferon-gamma in the immunomodulatory activity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2006; 24(2): 386-398.
[9] Liang C, Chen SL, Wang M, et al. Synergistic immunomodulatory effects of interferon-gamma and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2013;34(3):213-216.
[10] Ren G, Zhang L, Zhao X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(2):141-150.
[11] Ghannam S, Bouffi C, Djouad F, et al. Immunosuppression by mesenchymal stem cells: mechanisms and clinical applications. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1(1):2.
[12] Wang M, Shen J, Jin H, et al. Recent progress in understanding molecular mechanisms of cartilage degeneration during osteoarthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2011; 1240:61-69.
[13] Németh K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PS, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 2009;15(1): 42-49.
[14] Spaggiari GM, Abdelrazik H, Becchetti F, et al. MSCs inhibit monocyte-derived DC maturation and function by selectively interfering with the generation of immature DCs: central role of MSC-derived prostaglandin E2. Blood. 2009;113(26):6576- 6583.
[15] Sitcheran R, Cogswell PC, Baldwin AS Jr. NF-kappaB mediates inhibition of mesenchymal cell differentiation through a posttranscriptional gene silencing mechanism. Genes Dev. 2003;17(19):2368-2373.
[16] Murakami S, Lefebvre V, de Crombrugghe B. Potent inhibition of the master chondrogenic factor Sox9 gene by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(5): 3687-3692.
[17] Garnero P, Rousseau JC, Delmas PD. Molecular basis and clinical use of biochemical markers of bone, cartilage, and synovium in joint diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43(5):953- 968.
[18] Halász K, Kassner A, Mörgelin M, et al. COMP acts as a catalyst in collagen fibrillogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(43): 31166-31173.
[19] 王晓滨,薛庆云.骨关节炎患者滑液中COMP水平与病情严重程度的相关性研究[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2012,5(1):60-64.
[20] Horie M, Sekiya I, Muneta T, et al. Intra-articular Injected synovial stem cells differentiate into meniscal cells directly and promote meniscal regeneration without mobilization to distant organs in rat massive meniscal defect. Stem Cells. 2009;27(4):878-887.
[21] Horie M, Choi H, Lee RH, et al. Intra-articular injection of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) promote rat meniscal regeneration by being activated to express Indian hedgehog that enhances expression of type II collagen. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(10):1197-1207.
[22] Rubio D, Garcia-Castro J, Martín MC, et al. Spontaneous human adult stem cell transformation. Cancer Res. 2005; 65(8):3035-3039.
[23] Bernardo ME, Zaffaroni N, Novara F, et al. Human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells do not undergo transformation after long-term in vitro culture and do not exhibit telomere maintenance mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2007;67(19):9142-9149.
[24] In 't Anker PS, Scherjon SA, Kleijburg-van der Keur C, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells of fetal or maternal origin from human placenta. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1338-1345.
[25] Wang S, Qu X, Zhao RC. Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells. J Hematol Oncol. 2012;5:19.
[26] Jo CH, Lee YG, Shin WH, et al. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a proof-of-concept clinical trial. Stem Cells. 2014; 32(5):1254-1266. |
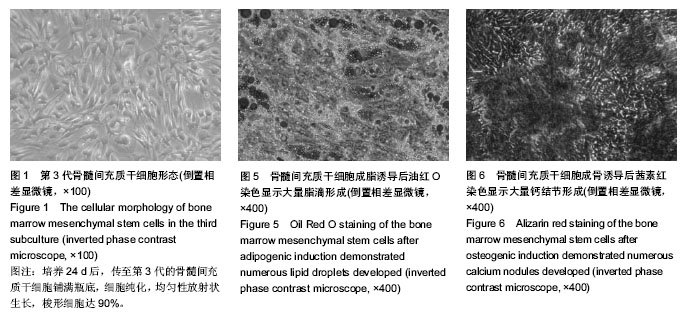
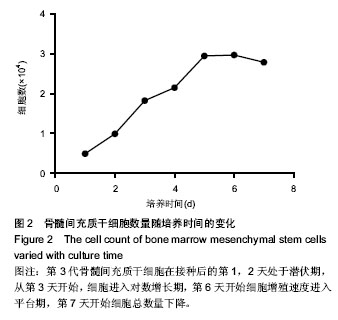
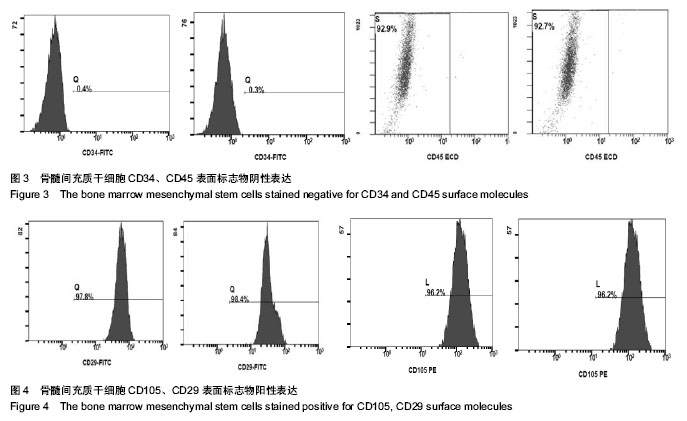
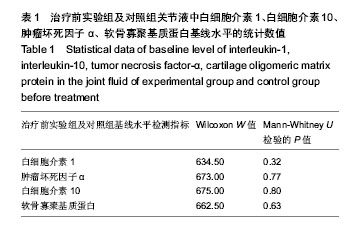
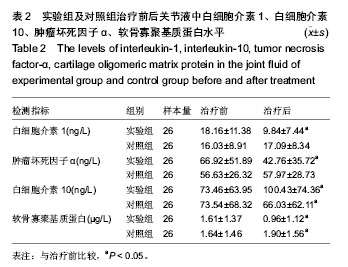
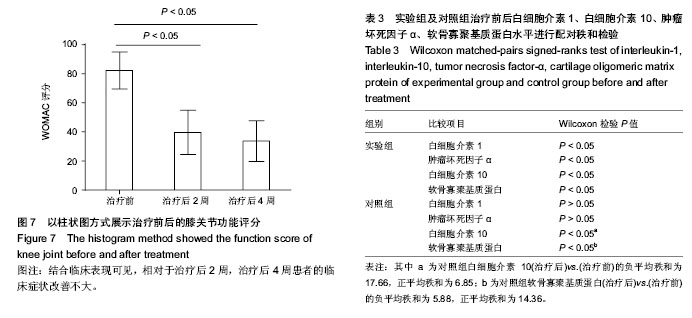
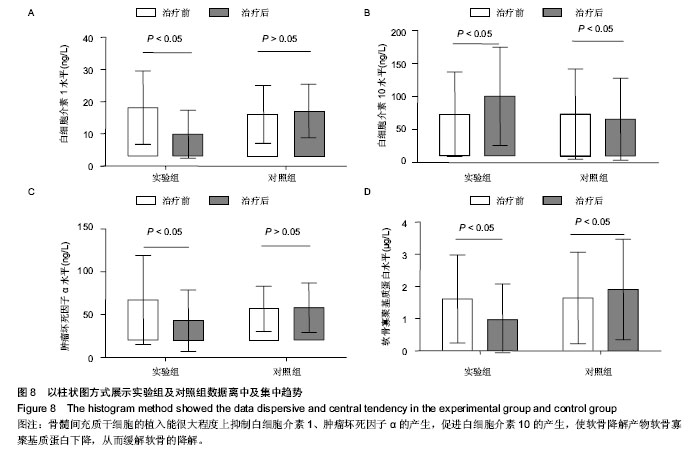
.jpg)