| [1] Kita K, Gauglitz GG, Phan TT, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from the sub-amniotic human umbilical cord lining membrane. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(4):491-502.
[2] Yoon JH, Roh EY, Shin S, et al. Introducing pulsed low-intensity ultrasound to culturing human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2009;31(3):329-335.
[3] Kadivar M, Khatami S, Mortazavi Y, et al. In vitro cardiomyogenic potential of human umbilical vein-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;340(2):639-647.
[4] La Rocca G, Anzalone R, Corrao S, et al. Isolation and characterization of Oct-4+/HLA-G+ mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord matrix: differentiation potential and detection of new markers. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009;131(2): 267-282.
[5] Chambers I, Colby D, Robertson M, et al. Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2003;113(5):643-655.
[6] Ding DC, Shyu WC, Lin SZ, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells support nontumorigenic expansion of human embryonic stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(7): 1515-1527.
[7] Jo CH, Kim OS, Park EY, et al. Fetal mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord sustain primitive characteristics during extensive expansion. Cell Tissue Res. 2008;334(3):423-433.
[8] Kaptanoglu E, Tuncel M, Palaoglu S, et al. Comparison of the effects of melatonin and methylprednisolone in experimental spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg. 2000;93(1 Suppl):77-84.
[9] Muñoz-Elías G, Woodbury D, Black IB. Marrow stromal cells, mitosis, and neuronal differentiation: stem cell and precursor functions. Stem Cells. 2003;21(4):437-448.
[10] 冯善伟,姚晓黎,李中,等. Brdu体外标记大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的研究[J]. 第一军医大学学报, 2005, 25(2):184-186.
[11] Anzalone R, Lo Iacono M, Corrao S, et al. New emerging potentials for human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells: immunological features and hepatocyte-like differentiative capacity. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(4):423-438.
[12] 孙丽,于丽,张华芳,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的分离培养及生物学特性[J]. 解剖科学进展,2011,17(2): 131-134.
[13] Huang P, Lin LM, Wu XY, et al. Differentiation of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells into germ-like cells in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2010;109(4): 747-754.
[14] Anzalone R, Lo Iacono M, Loria T, et al. Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells as candidates for beta cells regeneration: extending the differentiative and immunomodulatory benefits of adult mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Stem Cell Rev. 2011;7(2): 342-363.
[15] Weiss ML, Medicetty S, Bledsoe AR, et al. Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells: preliminary characterization and effect of transplantation in a rodent model of Parkinson's disease. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):781-792.
[16] Ding DC, Shyu WC, Chiang MF, et al. Enhancement of neuroplasticity through upregulation of beta1-integrin in human umbilical cord-derived stromal cell implanted stroke model. Neurobiol Dis. 2007;27(3):339-353.
[17] Yang CC, Shih YH, Ko MH, et al. Transplantation of human umbilical mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton's jelly after complete transection of the rat spinal cord. PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3336.
[18] Li Z,Qin HJ,Feng ZS,et al.Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-loaded amniotic membrane for the repair of radial nerve injury.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8 (36): 3441-3448.
[19] 朱玉海,冯世庆,王雪.大鼠脐带华通胶来源MSCS修复脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009, 23(12): 1491-1496.
[20] Chen H,Zhang Y,Yang ZJ,et al.Human umbilical cord Wharton’s jelly-derived oligodendrocyte precursor-like cells for axon and myelin sheath regeneration.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8 (10): 890-899.
[21] 冯大雄,钟德君,阳运康,等.静脉移植骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠脊髓损伤后轴突再生的作用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(12): 937-941.
[22] Maikos JT, Shreiber DI. Immediate damage to the blood-spinal cord barrier due to mechanical trauma. J Neurotrauma. 2007;24(3):492-507.
[23] Vaquero J, Zurita M, Oya S, et al. Cell therapy using bone marrow stromal cells in chronic paraplegic rats: systemic or local administration. Neurosci Lett. 2006;398(1-2):129-134.
[24] Kuan WL, Barker RA. New therapeutic approaches to Parkinson's disease including neural transplants. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2005;19(3):155-181.
[25] Lu P, Jones LL, Snyder EY, et al. Neural stem cells constitutively secrete neurotrophic factors and promote extensive host axonal growth after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2003;181(2):115-129.
[26] Hofstetter CP, Schwarz EJ, Hess D, et al. Marrow stromal cells form guiding strands in the injured spinal cord and promote recovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(4): 2199-2204.
[27] Kang SK, Jun ES, Bae YC, et al. Interactions between human adipose stromal cells and mouse neural stem cells in vitro. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2003;145(1):141-149.
[28] Gerdoni E, Gallo B, Casazza S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells effectively modulate pathogenic immune response in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Ann Neurol. 2007;61(3):219-227.
[29] Galli D, Gobbi G, Carrubbi C, et al. The role of PKCε-dependent signaling for cardiac differentiation. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013;139(1):35-46.
[30] Ruan ZB, Zhu L, Yin YG, et al. The mechanism underlying the differentiation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells into myocardial cells induced by 5-azacytidine. Indian J Med Sci. 2010;64(9):402-407. |
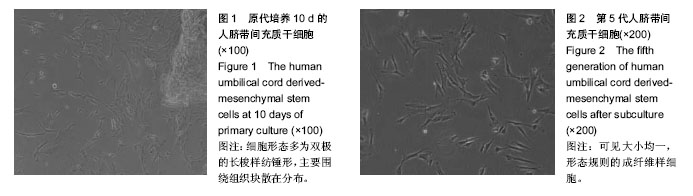
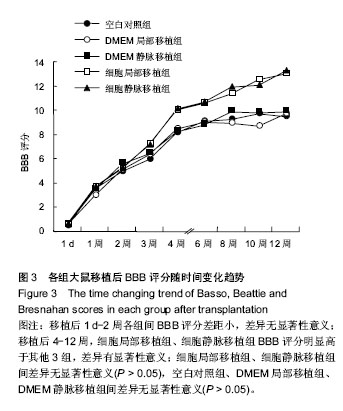

.jpg)
.jpg)