| [1] 任远,李泽桂.基于乳腺癌干细胞的临床治疗进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(6):1103-1106.
[2] 侯国芳,张瑾.乳腺癌干细胞研究进展[J].中华乳腺病杂志:电子版, 2012,6(4):441-446.
[3] 燕丽.5Fu对乳腺癌细胞向肿瘤干细胞样细胞逆向分化的作用[D]. 郑州:郑州大学,2011.
[4] 郑国沛.旁分泌或自分泌细胞因子在乳腺癌上皮—间质转化(EMT)及耐药和转移中的作用[D].长沙:中南大学,2013.
[5] 李静,欧周罗,邵志敏,等.微环境中间质细胞通过趋化因子对乳腺癌生长和转移的影响[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2008,15(5): 494-496,500.
[6] 王欣荣.乳腺癌干细胞研究现状[J].国际肿瘤学杂志,2009, 36(11): 846-850.
[7] Lengerke C, Fehm T, Kurth R, et al. Expression of the embryonic stem cell marker SOX2 in early-stage breast carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2011;11:42.
[8] Debeb BG, Xu W, Mok H,et al. Differential radiosensitizing effect of valproic acid in differentiation versus self-renewal promoting culture conditions.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;76(3):889-895.
[9] Ricardo S, Vieira AF, Gerhard R, et al. Breast cancer stem cell markers CD44, CD24 and ALDH1: expression distribution within intrinsic molecular subtype.J Clin Pathol. 2011;64(11): 937-946.
[10] Xing F, Saidou J, Watabe K.Cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in tumor microenvironment.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010;15:166-179.
[11] 尚文博,范忠林,马力.乳腺癌干细胞研究现状[J].临床肿瘤学杂志,2007,12(8):628-630.
[12] 刘为军,王昆华,龚昆梅,等.乳腺癌研究及治疗新靶点-乳腺癌干细胞的研究进展[J].中国癌症杂志,2010,20(1):66-69.
[13] Polyak K, Kalluri R.The role of the microenvironment in mammary gland development and cancer.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2(11):a003244.
[14] Korkaya H, Liu S, Wicha MS.Breast cancer stem cells, cytokine networks, and the tumor microenvironment.J Clin Invest. 2011;121(10):3804-3809.
[15] 林叔陈,张凤春,张雁云,等.乳腺癌干细胞的研究进展[J].肿瘤, 2008,28(8):719-722.
[16] Sneddon JB, Zhen HH, Montgomery K,et al.Bone morphogenetic protein antagonist gremlin 1 is widely expressed by cancer-associated stromal cells and can promote tumor cell proliferation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(40):14842-14847.
[17] 屈洪波,韩明利,范原铭,等.阻断PI3K/Akt信号通路对低氧微环境中BCSCs微球体细胞增殖的影响[J].肿瘤,2013,33(1):36-41.
[18] Römer AM, Lühr I, Klein A,et al.Normal mammary fibroblasts induce reversion of the malignant phenotype in human primary breast cancer.Anticancer Res. 2013;33(4):1525- 1536.
[19] 王荣,羊晓勤,吕青.乳腺癌组织CD44+CD24-/LowESA+Lin-干细胞比例及影响因素分析[J].四川大学学报:医学版,2014,45(1): 53-56.
[20] 许立生,王水,黄中晶,等. CD44+/CD24-/low/ABCG2-乳腺癌干细胞与临床治疗及预后的关系[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(21): 3877-3879.
[21] 王岫,吴捷,彭旭佳,等.乳腺癌组织中干细胞CD44+/CD24-表型与预后的关系[J].中外医疗,2014,33(6):57-59.
[22] Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,et al.Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(7):3983-3988.
[23] 王洪海,李连宏,毛俊,等.乳腺癌中干细胞标志物ALDH1及VHL/HIF-1α的表达及意义[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2013, 29(6):598-602.
[24] 朱玉芬,任美敬,谷峰,等.肿瘤微环境对乳腺癌干细胞样微球体培养鉴定的影响[J].中国肿瘤临床,2014,41(22):1417-1421.
[25] Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC,et al.Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 2005;121(3):335-348.
[26] 李治.乳腺癌干细胞的分离与鉴定及其自我更新和耐药机制的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2006.
[27] 屈洪波,范原铭,韩明利,等.沉默HIF-2α表达对低氧下乳腺癌干细胞微球体富集的影响[J].中国肿瘤临床,2013,40(2):67-71.
[28] 付钰洁,常徽,糜漫天.乳腺癌干细胞的研究进展[J].重庆理工大学学报(自然科学版),2011,25(1):23-28.
[29] 张远起.乳腺癌干细胞的研究进展[J].广东医学院学报,2011, 29(6): 675-677.
[30] 张凤春,林叔陈,宋彩丽,等.乳腺癌干细胞的研究进展[C].哈尔滨:第十届全国临床肿瘤学大会暨2007年CSCO学术年会,2007: 106-113.
[31] 曹峰琦,陈翀,刘妍,等. 肿瘤pH微环境通过激活β-catenin/ TCF4增强人乳腺癌肿瘤细胞的干性[J].基础医学与临床,2014, 34(5): 622-627.
[32] 徐琦璘,王椋,赵春华,等.人脂肪来源间充质干细胞诱导人乳腺癌MCF-7细胞上皮间质转化[J].基础医学与临床,2012,32(6):623- 627.
[33] Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,et al.ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell. 2007; 1(5):555-567.
[34] 谢国柱.通过对肿瘤细胞致瘤潜能及上皮—间充质转化的研究探讨肿瘤干细胞假说的本质[D].广州:南方医科大学,2012.
[35] 陈颖欣,李连宏,孙杰,等.人乳腺病变组织乳腺癌耐药蛋白及细胞角蛋白8和嗜铬蛋白A的表达:可能与多向分化潜能干细胞相关[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(1):57-62.
[36] 赵阳.人脂肪干细胞与乳腺癌MCF-7、BT474细胞旁分泌机制影响的体外实验研究[D]. 广州:南方医科大学,2013.
[37] 何亚琴.人乳腺肿瘤干细胞的分离培养鉴定及低氧对乳腺肿瘤干细胞特性影响的研究[D]. 银川:宁夏医科大学,2013.
[38] 赵志正.复方苦参注射液干预BMSCs与乳腺癌细胞交互作用机理的体外实验研究[D].北京:中国中医科学院,2012.
[39] 宣恒华.干细胞微环境对小鼠卵母细胞体外成熟、胚胎发育的影响及其生物活性因子分析[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2012.
[40] 康健豪,杨光,赵世光.肿瘤干细胞与肿瘤微环境的相互作用[J].临床神经外科杂志,2013,10(6):380-382.
[41] 王椋. 乳腺癌肿瘤环境中的间充质干细胞通过调节TGF-β1促进乳腺癌细胞的转移[D]. 北京:北京协和医学院(中国医学科学院),2011.
[42] 刘珊,张巍,刘夏,等.雄激素受体阳性乳腺癌干细胞的富集及其特性鉴定[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(1):67-69.
[43] 陈刚,谢丽,刘宝瑞,等.以肿瘤干细胞为靶点的肿瘤治疗新策略[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2008,30(11):801-803.
[44] 张凤春,南飞飞,徐海燕,等.原代乳腺癌干细胞富集及其与临床病理特征的相关性分析[J].肿瘤,2012,32(9):724-730. |
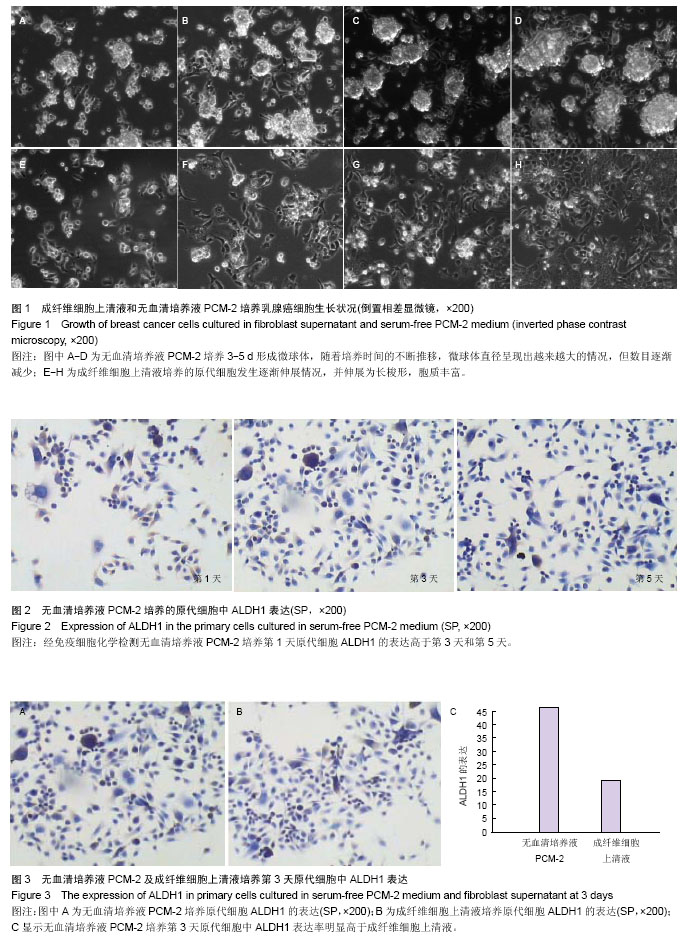
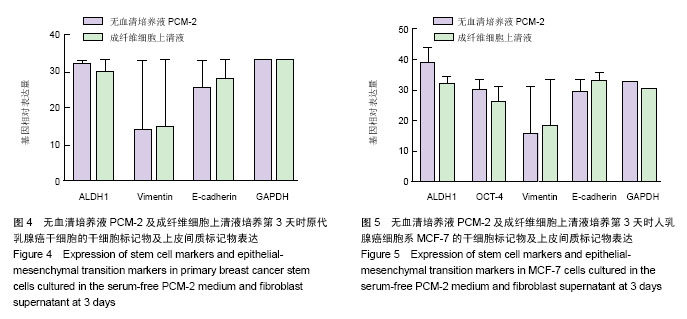
.jpg)
.jpg)