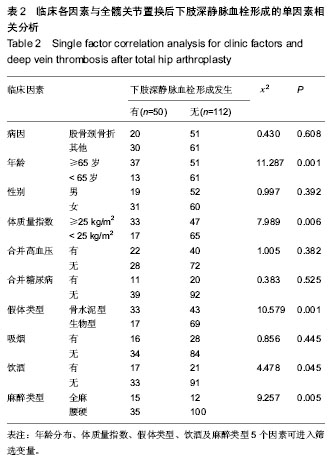
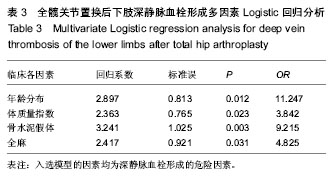
| [1] 李亮,赵阳,王志强.多孔金属钽髋臼在全髋关节置换术后髋臼翻修中的应用[J].中国骨与关节杂志, 2013, 2(8):470-473.
[2] 王睿铸,纪斌平,杨贵成.特殊髋关节义体术前测量的临床体会[J]. 实用医技杂志, 2014, 21(3):301-302.
[3] 刘辉,张育明,姚建锋,等.两种评估方法在全髋关节置换术后的比较研究[J].中国骨与关节外科,2011,4(6):450-454.
[4] 姜宇,杨玉生,朱国兴,等.中年患者128例生物型全髋置换和骨水泥全髋置换后的随访比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(17): 3069-3072.
[5] 钟群杰,林剑浩,武迎宏. 2010年北京地区全髋关节置换术手术部位感染目标性监测分析[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2012, 22(16): 3517-3520.
[6] 杨秋军,方玲,郝占元,等.全髋关节置换术后假体松动原因分析及防治[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2013,16(9):1572-1574.
[7] 曾容.早期功能锻炼对髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓的预防效果观察[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2014,22(8):55-56.
[8] 韩艳.人工膝髋关节置换术后下肢深静脉栓塞的预防[J].陕西医学杂志,2011,40(2):232-233.
[9] 尹知训.骨科大手术后静脉血栓栓塞症预防的进展[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2012, 6(6):971-975.
[10] 吕厚山,徐斌.人工关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成[J].中华骨科杂志,1999,19(3):155-156.
[11] 刘俊,赵银必,周忠华,等.骨科创伤手术后患者并发下肢深静脉血栓的预防和治疗[J].中国美容医学, 2014,4(16):240-241.
[12] 刘洪.下肢深静脉血栓形成的治疗进展[J].海南医学,2005,16(10): 153-155.
[13] 董尔丹,石山.血栓的实验方法与评价[J].中国药理学通报,1992, 8(6):422.
[14] 段曼,杜建时,马鹰,等. ABO血型与患者下肢深静脉血栓形成的关系[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(18):5265-5266.
[15] 柳剑,李玉军.静脉血栓栓塞症的物理预防[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2012,6(2):329-333.
[16] 盛颂颂.下肢深静脉血栓形成的诊断和治疗进展[J].上海医药,2013,34(2):37-39.
[17] 刘畅,刘玉杰.骨科患者深静脉血栓形成危险因素与预防的研究进展[J].中国全科医学,2013,16(2):593-597.
[18] 张金辉,冯曜宇,金辉.静脉血栓栓塞患者携带Leiden V因子杂合子病例报告[J].中国血管外科杂志:电子版,2014,7(3):170-174.
[19] 李洁,辛晓敏,刘娅娜.血浆蛋白C、蛋白S在静脉血栓病人诊断及治疗中的应用[J]. 微循环技术杂志:临床与实验, 2004, 8(5): 317.
[20] 潘以锋,孙敏莉,张皓,等.深静脉血栓形成与凝血因子Ⅷ及蛋白C、蛋白S的相关性[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010,27(5):575-576.
[21] 李方超,靳会敏,佟倩.静脉血栓栓塞症患者蛋白C和蛋白S基因单核苷酸多态性分析[J].中国老年学杂志, 2014,34(3):859-860.
[22] 程志鹏,唐亮,陆铉,等.遗传性抗凝血酶及遗传性蛋白C联合缺乏症家系研究[J].临床血液学杂志,2014,27(3):375-378.
[23] 李蕾,王培昌.蛋白C抗凝系统及生物学作用最新研究进展[J].四川医学,2012,33(9):1685-1686.
[24] 刘芳,诸兰艳,陈平,等.蛋白C、蛋白S缺乏症相关肺动脉血栓栓塞2例并文献复习[J].中南大学学报,2013,38(9):971-976.
[25] Watanabe H, Takahashi K, Takenouchi K, et al. Pseudotumor an-d deep venous thrombosis due to crevice corrosion of the head–ne-ck junction in metal-on-polyethylene total hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2014. [Epub ahead of print]
[26] 王艳红,马平.麻醉对髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的影响[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2006,12(2):137-140.
[27] 李光辉,李锋,陈超,等.麻醉方式对全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(21):1-2.
[28] 顾海伦,王欢,段景柱.人工全髋关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的多因素分析[J].中国骨伤, 2007,20(9):611-613.
[29] 唐孝明,裴福兴,沈彬.麻醉对人工全髋置换术后深静脉血栓形成的影响[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2002,17(3):201-202.
[30] Semchuk W, Backstein D, Komari N, et al. Adherence with inje-ctable prophylaxis for venous thromboembolism (VTE) following to-tal hip (THR) and total knee (TKR) replacement surgery: complete registry. Res Matt.2013:28.
[31] 魏亦兵,夏军,王思群,等.综合预防全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的发生[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2011,5(2):236-239.
[32] Meftah M, John M, Lendhey M, et al.Safety and Efficacy of Non-Cemented Femoral Fixation in Patients 75 Years of Age and Older. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(8):1378-1380.
[33] 万仑,胡豇,刘仲前.骨水泥对全髋置换术后深静脉血栓形成的影响[J].四川医学,2002,23(8):798-799.
[34] 陈东峰,白波,卢伟杰,等.骨水泥激活兔血小板促进下肢深静脉血栓形成的实验研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2007, 1(1): 42-44.
[35] 马骊,王欣,蒋丽华.人工髋关节置换后的深静脉血栓形成:发生因素及其预防策略[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(9): 1677-1680.
[36] 马俊,沈彬,杨静,等.人工全髋关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的危险因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(13):965-969.
[37] 温辉林,王友华,顾永强,等.全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的危险因素分析[J].江苏医药,2009,35(2):84-87.
[38] 查振刚,臧学慧,姚平,等.全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的临床研究及危险因素分析[J].中华外科杂志, 2005, 43(8):511-512.
[39] 张清,杨静,裴福兴,等.75 岁以上老年患者髋关节置换围术期合并症的处理及安全性评估[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2014, 13(6): 408-413.
[40] 张劲松,李琳.老年人静脉血栓栓塞症的流行病学[J].实用老年医学, 2013,28(10):806-809. |