| [1] Bydon M,De la Garza-Ramos R,Macki M,et al.Lumbar fusion versus nonoperative management for treatment of discogenic low back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2014;27(5): 297-304.
[2] 于铁淼,苗会玲,靳宪辉,等.钛网融合器与自体髂骨植骨在胸腰椎爆裂骨折前路手术中的应用比较研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013,28(3):210-212.
[3] 殷鹏,刘秀珍,吴延平,等.不同植骨材料在退变性腰椎病脊柱融合术中的应用与疗效比较[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012,26(7): 778-782.
[4] 袁振灿,郑燕平,刘新宇,等.不同植骨材料椎间融合效果的实验研究[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2008,46(3):276-279,283.
[5] Lawrence JP,Waked W,Gillon TJ,et al.rhBMP-2 (ACS and CRM formulations) overcomes pseudarthrosis in a New Zealand white rabbit posterolateral fusion model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2007;32(11):1206-1213.
[6] Schils F,Rilliet B,Payer M.Implantation of an empty carbon fiber cage or a tricortical iliac crest autograft after cervical discectomy for single-level disc herniation: a prospective comparative study. J Neurosurg Spine.2006;4(4):292-299.
[7] Bagby GW.Arthrodesis by the distraction-compression method using a stainless steel implant. Orthopedics.1988; 11(6):931-934.
[8] Kuslich SD,Danielson G,Dowdle JD,et al.Four-year follow-up results of lumbar spine arthrodesis using the Bagby and Kuslich lumbar fusion cage.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(20):2656-2662.
[9] Brantigan JW,Steffee AD,Geiger JM.A carbon fiber implant to aid interbody lumbar fusion. Mechanical testing.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1991;16(6):S277-282.
[10] Ohtori S,Ito T,Yamashita M,et al. Evaluation of low back pain using the Japanese Orthopaedic Association Back Pain Evaluation Questionnaire for lumbar spinal disease in a multicenter study: differences in scores based on age, sex, and type of disease.J Orthop Sci.2010;15(1):86-91.
[11] Freeman BC,Licina P,Mehdian SH. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion combined with instrumented posterior-lateral fusion: 5-year results in 60 patients.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000; 81:572-586.
[12] 张立国,朱裕昌,徐玉良,等.退变腰椎不稳的诊断和治疗[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2002,12(5):335.
[13] Ueno M,Imura T,Inoue G,et al.Posterior corrective fusion using a double-trajectory technique (cortical bone trajectory combined with traditional trajectory) for degenerative lumbar scoliosis with osteoporosis: technical note.J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(5):600-607.
[14] Schulz R,Melcher RP,Garib MC,et al.Does kyphotic deformity correlate with functional outcomes in fractures at the thoracolumbar junction treated by 360° instrumented fusion? Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2014;24(1):S93-101.
[15] Lammli J,Whitaker MC,Moskowitz A,et al.Stand-alone anterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative disc disease of the lumbar spine: results with a 2-year follow-up.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2014;39(15):E894-901.
[16] Kim DH,Jeong ST,Lee SS.Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using a unilateral single cage and a local morselized bone graft in the degenerative lumbar spine.Clin Orthop Surg.2009; 1(4):214-221.
[17] 丁悦,秦础强,黄东生,等.原位自体骨与同种异体骨混合移植在腰椎后外侧融合术中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009, 23(5):524-526.
[18] Ray CD.Threaded titanium cages for lumbar interbody fusions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997;22(6):667-680.
[19] Zhang JQ,Dong LQ,Jin CY,et al.Clinical control study in treating degenerative lumbar instability with single or double carbon fiber cages.Zhongguo Gu Shang.2009;22(10): 733-737.
[20] Lee HS,Lee JH,Lee JH.A comparison of dynamic views using plain radiographs and thin-section three-dimensional computed tomography in the evaluation of fusion after posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery.Spine J.2013;13(10): 1200-1207.
[21] 郑安华,徐正生,方崇斌.椎弓根螺钉固定联合与非联合伤椎置钉治疗单节段胸腰椎骨折的对比研究[J].中医正骨,2012,24(12): 20-22.
[22] Zucherman JF,Zdeblick TA,Bailey SA,et al.Instrumented laparoscopic spinal fusion. Preliminary Results.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1995;20(18):2029-2035.
[23] van der Haven I,van Loon PJ,Bartels RH,et al.Anterior cervical interbody fusion with radiolucent carbon fiber cages: clinical and radiological results.Acta Orthop Belg.2005; 71(5): 604-609.
[24] Kim SM,Rhee W,Ha S,et al.Influence of alendronate and endplate degeneration to single level posterior lumbar spinal interbody fusion.Korean J Spine. 2014;11(4):221-226.
[25] De la Garza-Ramos R,Bydon M,Abt NB,et al.The Impact of Obesity on Short- and Long-term Outcomes After Lumbar Fusion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2015;40(1):56-61.
[26] Bydon M,Macki M,De la Garza-Ramos R,et al.Smoking as an independent predictor of reoperation after lumbar laminectomy: a study of 500 cases.J Neurosurg Spine. 2015(2):1-6.
[27] Yoo M,Kim WH,Hyun SJ,et al.Comparison between Two Different Cervical Interbody Fusion Cages in One Level Stand-alone ACDF: Carbon Fiber Composite Frame Cage Versus Polyetheretherketone Cage.Korean J Spine.2014; 11(3):127-135.
[28] Bartels RH,Donk RD,Feuth T.Subsidence of stand-alone cervical carbon fiber cages. Neurosurgery. 2006;58(3): 502-508.
[29] Hasegawa K,Abe M,Washio T,et al.An experimental study on the interface strength between titanium mesh cage and vertebra in reference to vertebral bone mineral density. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(8):957-963. |
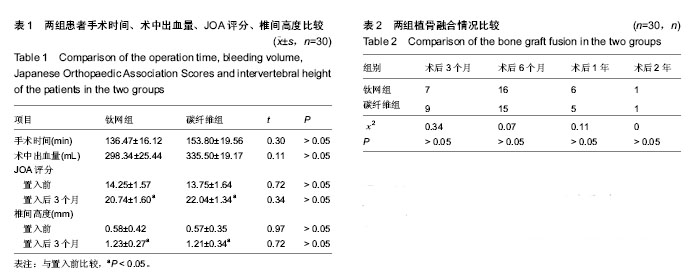
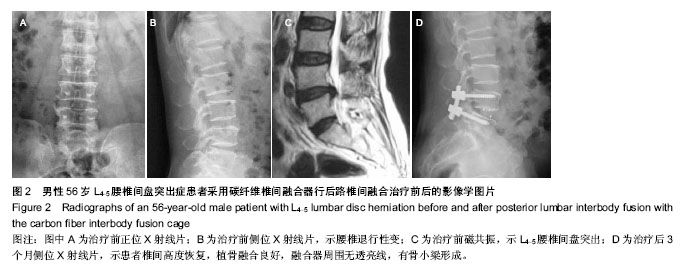
.jpg)