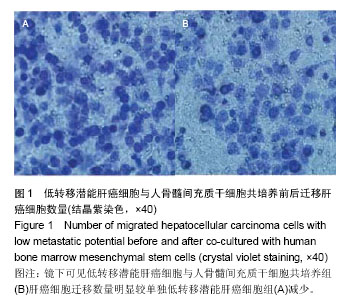
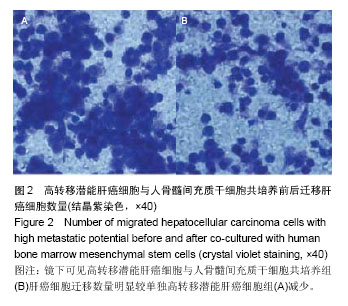
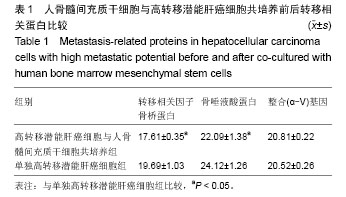
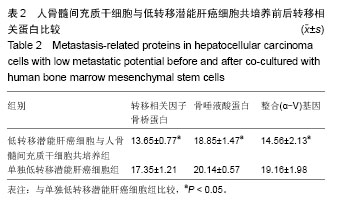
| [1]郑鹏翔,周欢,谭建明,等.间充质干细胞对肝癌细胞增殖、侵袭及生物学行为的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(36):6521- 6526.
[2]乔玲,赵铁军,山长亮,等.人间充质干细胞抑制肝癌细胞增殖的作用及其基因表达谱分析[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2007, 23(12):1037-1044.
[3]李天然,杜湘珂,宋斌,等.TGFβ1转染hMSC对MHCC97-H影响的实验研究[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2013,22(7):615-619.
[4]刘铮,马宏,史娟,等.间充质干细胞介导的TRAIL可控性表达及其杀伤人肝癌细胞的活性研究[J].中华医学杂志,2011,91(8): 544-548.
[5]李天然,杜湘珂,宋斌,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对高转移肝癌模型的干预[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(49):8498-8504.
[6]周思朗.肝癌大鼠肿瘤细胞与间充质干细胞药敏相关性研究[C]. 广州第一届国际肿瘤靶向治疗大会论文集,2006:207-211.
[7]李晓明.间充质干细胞对肝肿瘤细胞力生物学行为的影响及相关机理研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2014.
[8]罗敏.大鼠原发性肝癌肿瘤细胞与骨髓造血干细胞在肝癌个体化治疗应用中的实验研究[D]. 广州:第一军医大学,2007.
[9]李国才.人骨髓来源间充质干细胞对肝癌细胞增殖和侵袭能力的影响[D].上海:复旦大学,2008.
[10]韩志鹏,井莹莹,蔡雄,等.干细胞治疗与肝癌发生发展的研究与思考[C].呼和浩特:第18次全国干扰素与细胞因子学术会议论文集, 2013:26-28.
[11]王晓宇.间充质干细胞对肝癌细胞的抑制作用及其机制研究[D]. 北京:北京交通大学,2011.
[12]狄国虎.间充质干细胞(MSCs)用于肿瘤化疗辅助治疗及与肿瘤生长关系的实验研究[D]. 天津:天津大学,2012.
[13]郑鹏翔.人脐带间充质干细胞对肝癌细胞生长的影响[D]. 福州:福建医科大学,2013.
[14]周媛.大鼠原发性肝癌肿瘤细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞在肝癌药敏应用中的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2007.
[15]马博,任军,姜晗昉,等.肿瘤源性外切体负载的间充质干细胞抗肿瘤活性的实验研究[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2008,40(5): 494-499.
[16]李国才,武金才,孙冰生,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对人肝癌细胞系MHCC97-H增殖能力的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2008,25(7): 823-825.
[17]陈双庆,王培军,李铭华,等.磁标记骨髓间充质干细胞对肝细胞癌的抑制作用[J].临床放射学杂志,2009,28(10):1454-1458.
[18]吕昕蕾,张南征,陈复兴,等.骨髓间充质干细胞接种小鼠肝癌组织对小鼠生存期的影响[J].徐州医学院学报,2009,29(6):351-356.
[19]Wang F, Zhang YC, Zhou H, et al. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo osteogenic differentiation of nano-hydroxyapatite/ chitosan/poly(lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(3):760-768.
[20]Ng CP, Sharif AR, Heath DE, et al. Enhanced ex vivo expansion of adult mesenchymal stem cells by fetal mesenchymal stem cell ECM. iomaterials. 2014;35(13): 4046-4057.
[21]Dai J, Wang H, Liu G, et al. Dynamic compression and co-culture with nucleus pulposus cells promotes proliferation and differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomech. 2014;47(5):966-972.
[22]Rammal H, Beroud J, Gentils M, et al. Reversing charges or how to improve Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells culture on polyelectrolyte multilayer films. Biomed Mater Eng. 2013;23(4):299-309.
[23]游佳,焦艳,郑琦,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植干预大鼠肝纤维化/肝癌模型中转化生长因子-β1的作用[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2014, 31(10):2112-2114.
[24]王雪峰,梅佳玮,廖传文,等.骨髓间充质干细胞与小鼠肝癌肝移植术后复发关系的实验观察[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(6): 455-458.
[25]邵志红,王培军,李铭华,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞移植对Walker-256肝癌生长影响的实验研究[J].中华医学杂志, 2009, 89(7):491-496.
[26]周媛,罗敏,张婧,等.不同抗肿瘤机制药物对大鼠肝癌细胞成瘤性的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2007,27(3):290-292.
[27]Ma J, Both SK, Ji W, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells as monocultures or cocultures with human umbilical vein endothelial cells: performance in vitro and in rat cranial defects. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(4): 1026-1036.
[28]Tzameret A, Sher I, Belkin M, et al. Transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells as a thin subretinal layer ameliorates retinal degeneration in a rat model of retinal dystrophy. Exp Eye Res. 2014;118:135-144.
[29]Kim J, Kim HN, Lim KT, et al. Synergistic effects of nanotopography and co-culture with endothelial cells on osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(30):7257-7268.
[30]李天然,卢光明,宋斌,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对高低转移潜能肝癌细胞影响的实验研究[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2014,23(9): 1056-1060.
[31]赵文秀,张磊,刘建明,等.小鼠脂肪间充质干细胞的分离培养及其在肝内归巢[J].南方医科大学学报,2013,33(8):1151-1154.
[32]王骥,周海军,董红燕,等.人外周血间充质干细胞向肝样细胞诱导分化的实验研究[J].徐州医学院学报,2012,32(8):491-496.
[33]陈双庆,王培军,李铭华,等.磁标记大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞活体内移植后向肝癌细胞趋向性迁移的研究[J].中华放射学杂志,2009, 43(10):1102-1106.
[34]Sato Y, Araki H, Kato J, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells xenografted directly to rat liver are differentiated into human hepatocytes without fusion. Blood. 2005;106(2):756-763.
[35]Choi D, Kim JH, Lim M, et al. Hepatocyte-like cells from human mesenchymal stem cells engrafted in regenerating rat liver tracked with in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2008;14(1):15-23.
[36]Snykers S, Vanhaecke T, Papeleu P, et al. Sequential exposure to cytokines reflecting embryogenesis: the key for in vitro differentiation of adult bone marrow stem cells into functional hepatocyte-like cells. Toxicol Sci. 2006;94(2): 330-341.
[37]李国才.人骨髓来源间充质干细胞对肝癌细胞增殖和侵袭能力的影响[D].上海:复旦大学,2008.
[38]周佳美,向慧玲,朱争艳,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基对大鼠肝癌细胞系CBRH-7919增殖能力的影响[J].天津医科大学学报,2011,17(4):455-458.
[39]秦翔.肝癌细胞条件培养基对骨髓间充质干细胞迁移和增殖的影响及其分子机理[D]. 重庆:重庆大学,2013.
[40]袁博,陈昆仑,张岚,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞对RH-35肝癌细胞侵袭能力的影响[J].西安交通大学学报:医学版,2014,35(4): 455-459. |