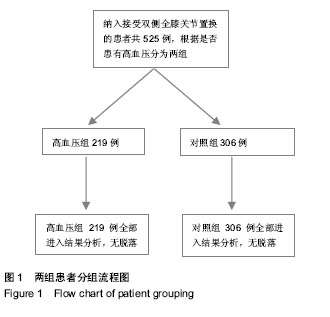
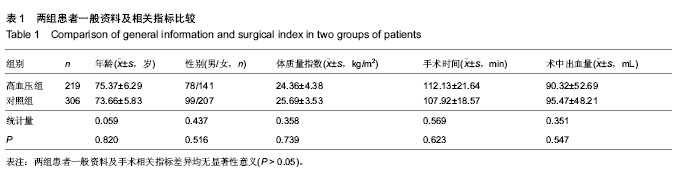
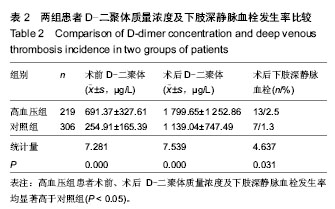
| [1] 王少华,连鸿凯,宋树春,等.骨科大手术围手术期血浆D-二聚体检测的临床意义[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2012,18(2): 153-156.
[2] 中华医学会骨科学分会.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(6):602-604.
[3] 邱贵兴,杨庆铭,余楠生.低分子肝素预防髋、膝关节手术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的多中心研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(12):819-822.
[4] Geerts WH,Heit JA,Clagett GP,et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism. Chest. 2001;119(Suppl):132-175.
[5] 陈群,林强,林赛梅.原发性高血压外周静脉血流动力学研究[J].临床心血管病杂志,2002,18(11):553-555.
[6] 吕厚山.人工关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成[J].中华骨科杂志,1999,19(3):155-157.
[7] 张小平,胡豫.急性下肢深静脉血栓形成危险因素的评估[J].中华普通外科杂志,2008,23(3):168-170.
[8] 杨中良,张彩萍,王乃玲.老年原发性高血压患者血压变异性与血栓前状态关系的研究[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2012,14(7):691-693.
[9] 罗兰,胡滨.原发性高血压患者血管内皮功能的超声检测[J].中华医学超声杂志,2004,1(2):69-71.
[10] Richad B. Left ventricular hypetophy in hypertension:Prevalen and relationsh:Pto Patho Physiologic variales. Hypertension. 1987;9(2suppl):53.
[11] 盛筠.原发性高血压与高粘、高凝、高脂血症的血液流变性关系[J].中国血液流变学杂志,2003,13(3):262-263.
[12] 吴芳丽,孟延丰.人工关节置换术后并发深静脉血栓的危险因素评估[J].医学研究杂志,2011,40(5):109-111.
[13] 刘刚,韩一生,赵建宁.髋膝关节置换术后的深静脉血栓形成[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(4):237-239.
[14] 杨力,李建国.人工关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的彩色多普勒超声诊断[J].临床超声医学杂志,2007,9(11):651-654.
[15] 沈骏,蒋矗.全膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓发生的中期随访研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(7):639-641.
[16] 唐辉,齐保闯,徐永清.骨科手术后深静脉血栓形成的研究进展[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2011,13(1):84-85.
[17] 张阳,钱齐荣.止血带对全膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的影响[J].中华骨科杂志.2009,29(10):910-913.
[18] 钱东阳,白波.髋膝关节置换围手术期下肢深静脉血栓形成与D-二聚体及抗凝药的关系[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014, 8(2):181-184.
[19] 陈哨军.髋、膝置换术后深静脉血栓临床流行病学研究进展[J].中华外科杂志,2006, 44(8):568-570.
[20] 中国高血压防治指南修订委员会. 中国高血压防治指南2010[J]. 中华心血管病杂志,2011,39(7):579-616
[21] 闫沛云,宋朝基,苗生龙,等.全髋人工关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓的早期诊断[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2013,12(8):444-447.
[22] Cooper HJ, Sanders SA, Berger RA. Risk of Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism Associated With Flying in the Early Postoperative Period Following Elective Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014: 1119-1122.
[23] Levy YD, Hardwick ME, Copp SN, et al. Thrombosis Incidence in Unilateral vs. Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty with Compression Device Prophylaxis. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(3): 474-478.
[24] Fujita S, Hirota S, Oda T, et al. Deep venous thrombosis after total hip or total knee arthroplasty in patients in Japan. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000;(375):168-174.
[25] Struijk-Mulder MC, Ettema HB, Verheyen CC, et al. Comparing consensus guidelines on thromboprophylaxis in orthopedic surgery. J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 8(4) :678-683.
[26] Pulido Pamela A, Copp Steven N, Walker Richard H, et al. The efficacy of a single daily dose of enoxaparin for deep vein thrombosis prophylaxis following total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2004;27 (11):1185-1187.
[27] McAndrew Christopher M, Fitzgerald Steven J, Kraay Matthew J, et al. Incidence of postthrombotic syndrome in patients undergoing primary total knee arthroplasty for osteoarthritis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(1):178-181.
[28] 李佩佳,高玉镭,王东辰.利伐沙班与低分子肝素在预防人工全膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(11):998.
[29] 范少地,王晓坤,白峰,等.膝关节置换后应用药物预防血栓形成的对比研究与国际分析[J],中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9): 1661-1670
[30] 闵令田,翁文杰,邱勇,等. 关节腔内灌注氨甲环酸降低全膝关节置换手术出血的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014,8(4):482-486.
[31] 裴征,关振鹏,郭卫,等.髋膝关节置换术前预测深静脉血栓形成的多因素分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012, 20(11):1001-1005.
[32] 余霄.择期髋膝关节置换患者静脉血栓栓塞性疾病预防的AAOS指南[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2012, 6(4):84-87.
[33] Westrich GH,Schneider R,Ghelman B. Comparison between color Doppler imaging and ascending venography in the detection of deep venous thrombosis following total joint arthroplasty:A prospective study. Contemporary Surg. 1997: 225-234.
[34] 中华医学会骨科学分会. 预防骨科大手术深静脉血栓形成指南(草案)[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(2):118-119.
[35] 周一新.骨科标准新突破,手术技术指导规范-人工髋、膝关节置换术解读[J].中国卫生标准管理, 2011,2(4):22-24.
[36] 刘宝,谢小平,高悦,等. 阿哌沙班和依诺肝素用于骨科大手术后静脉血栓预防的成本效果分析[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2014, 8(5):677-681.
[37] 权冬,朱锦宇,王华溢,等. 利伐沙班与低相对分子质量肝素预防人工髋膝关节置换术后静脉血栓栓塞症的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2010, 12(12):1130-1133.
[38] 中华医学会骨科学分会.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006, 26(12): 819-822.
[39] 杨力,吕厚山,张万蕾,等.原发性深静脉瓣膜功能不全对全膝关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的影响[J]. 中华外科杂志, 2009, 47(5):356-358.
[40] 喻林.关节置换后下肢静脉血栓形成及髋膝关节病变中彩色多普勒超声的应用价值[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(22):4078-4081.
[41] 阮佳丽,吕涛,苗菁菁,等. 利伐沙班、达比加群与肝素在全髋或全膝置换后的抗凝治疗[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(13): 2390-2397.
[42] 姚尧,张成绩,戴小宇,等.关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的解剖分布[J].中华骨科杂志,2013, 33(9):912-916.
[43] 王峰,姚晨,史冬泉. 全髋关节置换术后深静脉血栓发生的随机对照研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2010,30(4):381-385.
[44] Chan WS,Spencer FA,Ginsberg JS. Anatomic distribution of deep vein thrombosis in pregnancy. CMAJ. 2010;(7):657-660.
[45] 杨明辉,朱仕文,孙旭,等.骨盆髋臼骨折后深静脉血栓形成的诊断:彩色多普勒超声与静脉造影的比较研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志, 2012, 14(5):391-394. |