| [1] Floratou K, Giannopoulou E, Antonacopoulou A,et al. Oxidative stress due to radiation in CD34(+) hematopoietic progenitor cells: protection by IGF-1.J Radiat Res. 2012; 53(5):672-685.
[2] Wang Y, Liu L, Pazhanisamy SK,et al.Total body irradiation causes residual bone marrow injury by induction of persistent oxidative stress in murine hematopoietic stem cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;48(2):348-356.
[3] Tominaga H, Kodama S, Matsuda N,et al.Involvement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the induction of genetic instability by radiation.J Radiat Res. 2004;45(2):181-188.
[4] Huang L, Snyder AR, Morgan WF.Radiation-induced genomic instability and its implications for radiation carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2003;22(37):5848-5854.
[5] Bowler DA, Moore SR, Macdonald DA, et al.Bystander- mediated genomic instability after high LET radiation in murine primary haemopoietic stem cells.Mutat Res. 2006; 597(1-2):50-61.
[6] Jain AK, Bloom DA, Jaiswal AK.Nuclear import and export signals in control of Nrf2.J Biol Chem. 2005;280(32):29158- 29168.
[7] Simon HU, Haj-Yehia A, Levi-Schaffer F.Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction.Apoptosis. 2000;5(5):415-418.
[8] Samuni AM, Kasid U, Chuang EY,et al.Effects of hypoxia on radiation-responsive stress-activated protein kinase, p53, and caspase 3 signals in TK6 human lymphoblastoid cells.Cancer Res. 2005;65(2):579-586.
[9] Qi LW, Wang CZ, Yuan CS.Ginsenosides from American ginseng: chemical and pharmacological diversity. Phytochemistry. 2011;72(8):689-699.
[10] Liu Q, Kou JP, Yu BY.Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in PC12 cells via inhibiting NF-κB activation.Neurochem Int. 2011;58(1): 119-125.
[11] Wang Y, Li X, Wang X,et al.Ginsenoside Rd attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via Akt/GSK-3β signaling and inhibition of the mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathway.PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e70956.
[12] Mauch P, Constine L, Greenberger J,et al.Hematopoietic stem cell compartment: acute and late effects of radiation therapy and chemotherapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31(5):1319-1339.
[13] Campbell BA, Voss N, Woods R,et al.Long-term outcomes for patients with limited stage follicular lymphoma: involved regional radiotherapy versus involved node radiotherapy. Cancer. 2010;116(16):3797-3806.
[14] Ma L, Liu H, Xie Z,et al.Ginsenoside Rb3 protects cardiomyocytes against ischemia-reperfusion injury via the inhibition of JNK-mediated NF-κB pathway: a mouse cardiomyocyte model.PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e103628.
[15] Dreiem A, Gertz CC, Seegal RF.The effects of methylmercury on mitochondrial function and reactive oxygen species formation in rat striatal synaptosomes are age-dependent. Toxicol Sci. 2005;87(1):156-162.
[16] Cho YS, Challa S, Moquin D,et al.Phosphorylation-driven assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 complex regulates programmed necrosis and virus-induced inflammation.Cell. 2009;137(6): 1112-1123.
[17] Hayashi T, Hayashi I, Shinohara T,et al.Radiation-induced apoptosis of stem/progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood is associated with alterations in reactive oxygen and intracellular pH.Mutat Res. 2004;556(1-2):83-91.
[18] Summers RW, Maves BV, Reeves RD,et al.Irradiation increases superoxide dismutase in rat intestinal smooth muscle.Free Radic Biol Med. 1989;6(3):261-270.
[19] Paroni G, Henderson C, Schneider C,et al. Caspase-2- induced apoptosis is dependent on caspase-9, but its processing during UV- or tumor necrosis factor-dependent cell death requires caspase-3.J Biol Chem. 2001;276(24): 21907-21915.
[20] Johnson JA, Johnson DA, Kraft AD,et al.The Nrf2-ARE pathway: an indicator and modulator of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1147:61-69.
[21] Ludtmann MH, Angelova PR, Zhang Y,et al.Nrf2 affects the efficiency of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation.Biochem J. 2014;457(3):415-424.
[22] Lü JM, Yao Q, Chen C. Ginseng Compounds: an update on their molecular mechanisms and medical applications. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2009;7(3):293-302. |
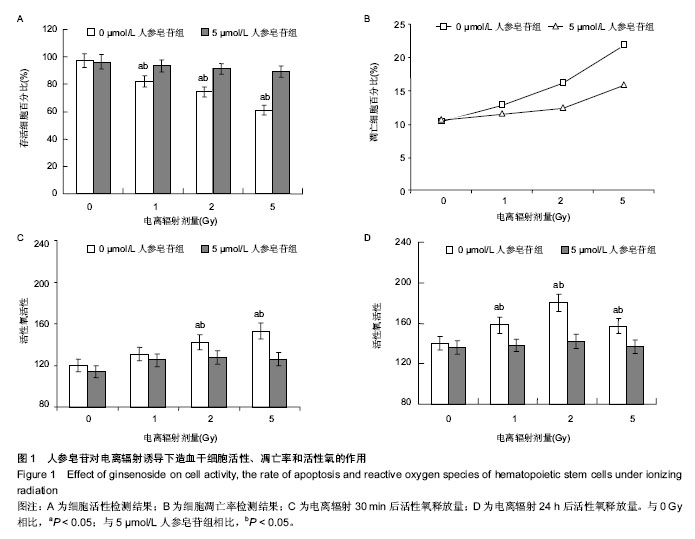
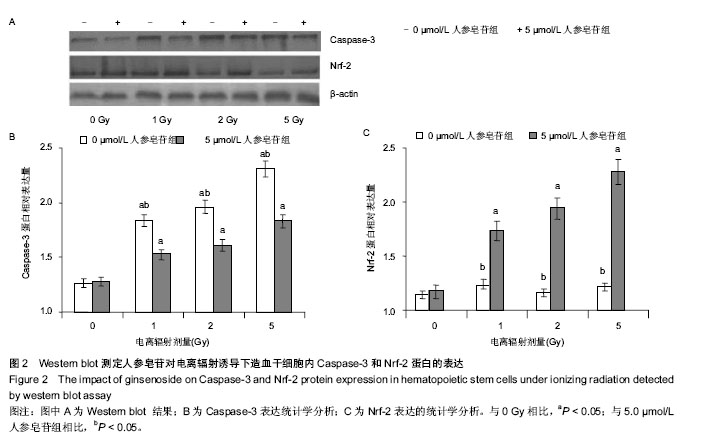
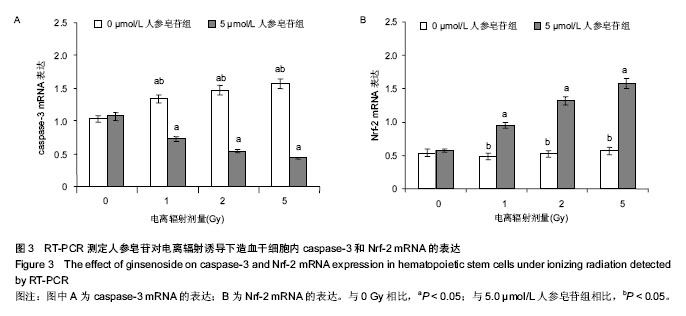
.jpg)