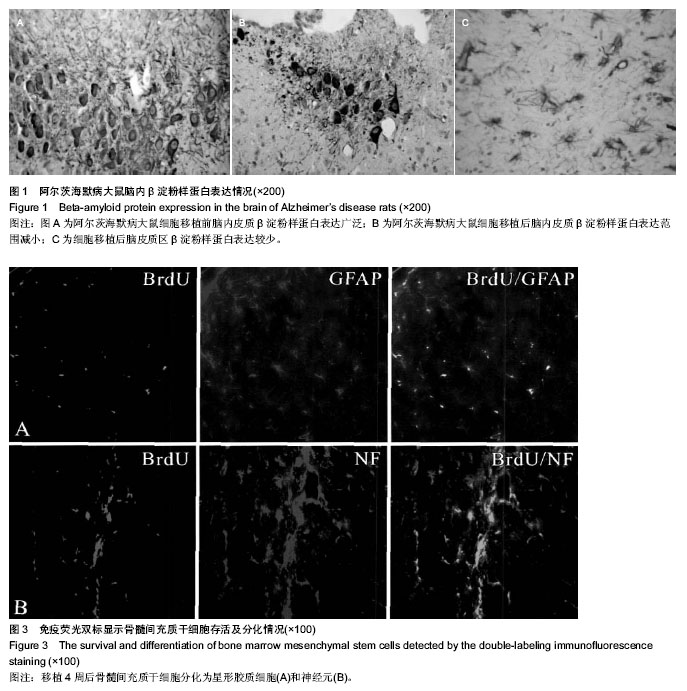
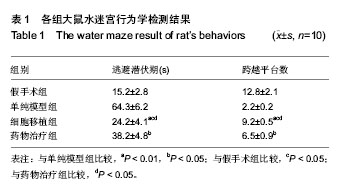
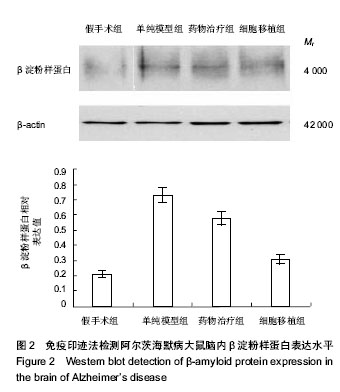
| [1] Lee JK, Jin HK, Bae JS.Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce brain amyloid-beta deposition and accelerate the activation of microglia in an acutely induced Alzheimer's disease mouse model.Neurosci Lett. 2009; 450(2):136-141.
[2] Simard AR, Soulet D, Gowing G,et al.Bone marrow-derived microglia play a critical role in restricting senile plaque formation in Alzheimer's disease.Neuron. 2006;49(4): 489-502.
[3] Li X, Li M, Li Y, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the action of ginsenoside Rg1 against Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2012; 7(36): 2860-2866.
[4] Schwarz SC, Schwarz J.Translation of stem cell therapy for neurological diseases.Transl Res. 2010;156(3):155-160.
[5] Baharnoori M, Brake WG, Srivastava LK.Prenatal immune challenge induces developmental changes in the morphology of pyramidal neurons of the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus in rats.Schizophr Res. 2009;107(1):99-109.
[6] Schmahmann JD, Weilburg JB, Sherman JC.The neuropsychiatry of the cerebellum - insights from the clinic. Cerebellum. 2007;6(3):254-67.
[7] Wolf U, Rapoport MJ, Schweizer TA.Evaluating the affective component of the cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome.J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2009;21(3):245-253.
[8] Bae JS, Furuya S, Shinoda Y,et al.Neurodegeneration augments the ability of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to fuse with Purkinje neurons in Niemann-Pick type C mice.Hum Gene Ther. 2005;16(8):1006-1011.
[9] Lee JK, Jin HK, Bae JS.Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuate amyloid β-induced memory impairment and apoptosis by inhibiting neuronal cell death.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2010;7(6):540-548.
[10] Biswas SC, Shi Y, Vonsattel JP,et al.Bim is elevated in Alzheimer's disease neurons and is required for beta-amyloid-induced neuronal apoptosis.J Neurosci. 2007;27(4):893-900.
[11] Cummings JL.Alzheimer's disease.N Engl J Med. 2004; 351(1): 56-67.
[12] Rosen WG, Mohs RC, Davis KL.A new rating scale for Alzheimer's disease.Am J Psychiatry. 1984;141(11):1356-1364.
[13] Selkoe DJ.Alzheimer's disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(2):741-766.
[14] Bantubungi K, Blum D, Cuvelier L,et al.Stem cell factor and mesenchymal and neural stem cell transplantation in a rat model of Huntington's disease.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;37(3): 454-470.
[15] Kim SU, de Vellis J.Microglia in health and disease.J Neurosci Res. 2005;81(3):302-313.
[16] Cho SR, Kim YR, Kang HS,et al.Functional recovery after the transplantation of neurally differentiated mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone barrow in a rat model of spinal cord injury.Cell Transplant. 2009;18(12):1359-1368.
[17] Kitada M, Dezawa M.Induction system of neural and muscle lineage cells from bone marrow stromal cells; a new strategy for tissue reconstruction in degenerative diseases.Histol Histopathol. 2009;24(5):631-642.
[18] Malm TM, Koistinaho M, Pärepalo M,et al.Bone-marrow-derived cells contribute to the recruitment of microglial cells in response to beta-amyloid deposition in APP/PS1 double transgenic Alzheimer mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2005;18(1):134-142.
[19] Lee HJ, Lee JK, Lee H,et al. The therapeutic potential of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in Alzheimer's disease.Neurosci Lett. 2010;481(1):30-35.
[20] Lee JK, Jin HK, Endo S,et al.Intracerebral transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduces amyloid-beta deposition and rescues memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease mice by modulation of immune responses. Stem Cells. 2010;28(2):329-343.
[21] Okada K, Okaichi H.The functional cooperation of the hippocampus and anterior thalamus via the fimbria-fornix in spatial memory in rats.Shinrigaku Kenkyu. 2006;77(3): 261-270.
[22] Vorhees CV, Williams MT.Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc. 2006;1(2):848-858. |