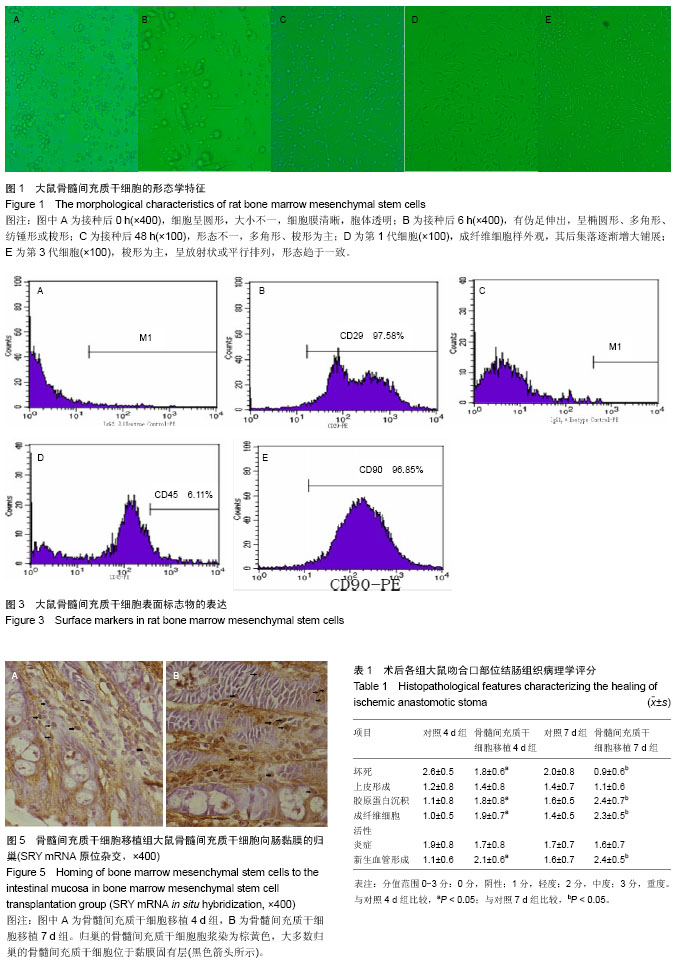
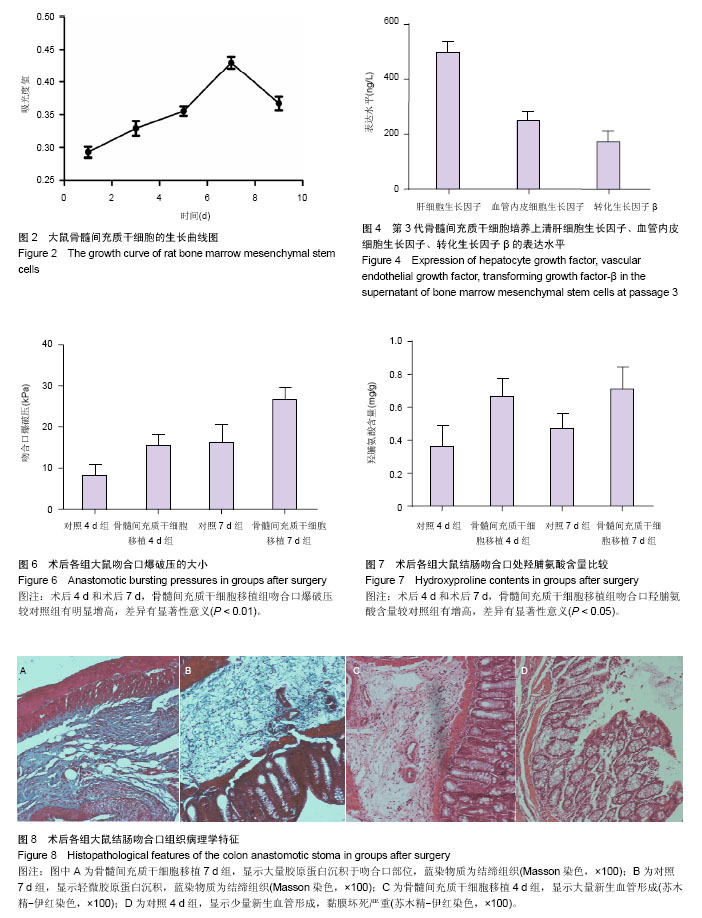
| [1] Egger B, Inglin R, Zeeh J, et al. Insulin-like growth factor I and truncated keratinocyte growth factor accelerate healing of left-sided colonic anastomoses.Br J Surg. 2001;88(1): 90-98.
[2] Thornton FJ, Barbul A.Healing in the gastrointestinal tract.Surg Clin North Am. 1997;77(3):549-573.
[3] Mast BA.Healing in other tissues.Surg Clin North Am. 1997; 77(3):529-547.
[4] Thompson SK, Chang EY, Jobe BA.Clinical review: Healing in gastrointestinal anastomoses, part I.Microsurgery. 2006;26(3): 131-136.
[5] Enestvedt CK, Thompson SK, Chang EY,et al.Clinical review: Healing in gastrointestinal anastomoses, part II.Microsurgery. 2006;26(3):137-143.
[6] Quaedackers JS, Beuk RJ, Bennet L,et al.An evaluation of methods for grading histologic injury following ischemia/ reperfusion of the small bowel.Transplant Proc. 2000;32(6): 1307-1310.
[7] Yo LS, Consten EC, Quarles van Ufford HM,et al.Buttressing of the staple line in gastrointestinal anastomoses: overview of new technology designed to reduce perioperative complications. Dig Surg. 2006;23(5-6):283-291.
[8] Pommergaard HC, Achiam MP, Rosenberg J.External coating of colonic anastomoses: a systematic review.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012;27(10):1247-1258.
[9] van der Ham AC, Kort WJ, Weijma IM,et al.Effect of antibiotics in fibrin sealant on healing colonic anastomoses in the rat.Br J Surg. 1992;79(6):525-528.
[10] Nguyen NT, Nguyen CT, Stevens CM,et al.The efficacy of fibrin sealant in prevention of anastomotic leak after laparoscopic gastric bypass.J Surg Res. 2004;122(2): 218-224.
[11] Binnebösel M, Junge K, Kaemmer DA,et al.Intraperitoneally applied gentamicin increases collagen content and mechanical stability of colon anastomosis in rats.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009;24(4):433-440.
[12] Junge K, Klinge U, Rosch R,et al.Improved collagen type I/III ratio at the interface of gentamicin-supplemented polyvinylidenfluoride mesh materials.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2007;392(4):465-471.
[13] Khanna A, Rossman J, Caty MG,et al.Beneficial effects of intraluminal nitroglycerin in intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Surg Res. 2003;114(1):15-24.
[14] 冯涛,考晓明,嵇武.干细胞的临床应用:缺少大动物模型和人体试验[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(14):2269-2274.
[15] Wu Y, Chen L, Scott PG,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing through differentiation and angiogenesis.Stem Cells. 2007;25(10):2648-2659.
[16] Hayashi Y, Tsuji S, Tsujii M,et al.Topical implantation of mesenchymal stem cells has beneficial effects on healing of experimental colitis in rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008; 326(2):523-531.
[17] Huang Y, Chang C, Zhang JW, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells increase dopamine synthesis in the injured striatum. Neural Regen Res. 2012; 7(34): 2653-2662.
[18] Piao H, Youn TJ, Kwon JS,et al.Effects of bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation in acutely infarcting myocardium.Eur J Heart Fail. 2005;7(5):730-738.
[19] Adas G, Arikan S, Karatepe O,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells improve the healing of ischemic colonic anastomoses (experimental study).Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2011;396(1): 115-126.
[20] Rabau M, Eyal A, Kluger Y,et al.Bursting pressure in anastomotic healing in experimentally induced colitis in rats.Dis Colon Rectum. 1998;41(4):468-472.
[21] Kingham TP, Pachter HL.Colonic anastomotic leak: risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment.J Am Coll Surg. 2009; 208(2):269-278.
[22] Tadros T, Wobbes T, Hendriks T.Blood transfusion impairs the healing of experimental intestinal anastomoses.Ann Surg. 1992;215(3):276-281.
[23] Guzel S, Sunamak O, AS A,et al.Effects of hyperbaric oxygen and Pgg-glucan on ischemic colon anastomosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12(9):1421-1425.
[24] Azevedo LA, Parra RS, Da Rocha JJ, et al.Hyperbaric oxygen on the healing of ischemic colonic anastomosis--an experimental study in rats.Undersea Hyperb Med. 2010; 37(6):405-411.
[25] Cronin K, Jackson DS, Dunphy JE.Changing bursting strength and collagen content of the healing colon.Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1968;126(4):747-753.
[26] Jiang H, Qu L, Li Y,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells reduce intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injuries in rats.J Surg Res. 2011;168(1):127-134.
[27] Gao J, Dennis JE, Muzic RF,et al.The dynamic in vivo distribution of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells after infusion.Cells Tissues Organs. 2001;169(1):12-20.
[28] Voswinkel J, Francois S, Gorin NC,et al.Gastro-intestinal autoimmunity: preclinical experiences and successful therapy of fistulizing bowel diseases and gut Graft versus host disease by mesenchymal stromal cells.Immunol Res. 2013;56(2-3):241-248.
[29] Forraz N, Wright KE, Jurga M,et al.Experimental therapies for repair of the central nervous system: stem cells and tissue engineering.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(7):523-536.
[30] Adas G, Kemik O, Eryasar B,et al.Treatment of ischemic colonic anastomoses with systemic transplanted bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(17):2275-2285.
[31] Sémont A, François S, Mouiseddine M,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells increase self-renewal of small intestinal epithelium and accelerate structural recovery after radiation injury.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;585:19-30.
[32] 高光周,李大伟,李欣,等. 同种异体大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞移植在肠缺血-再灌注损伤肠道中的定植及其分化效应[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(23): 4262-4266.
[33] Månsson P, Zhang XW, Jeppsson B,et al.Anastomotic healing in the rat colon: comparison between a radiological method, breaking strength and bursting pressure.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2002;17(6):420-425.
[34] Tadauchi A, Narita Y, Kagami H,et al.Novel cell-based therapeutic strategy for ischemic colitis with use of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells in rats.Dis Colon Rectum. 2009;52(8):1443-1451.
[35] Gao F, He T, Wang H,et al.A promising strategy for the treatment of ischemic heart disease: Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer in rats.Can J Cardiol. 2007;23(11):891-898.
[36] François S, Bensidhoum M, Mouiseddine M,et al.Local irradiation not only induces homing of human mesenchymal stem cells at exposed sites but promotes their widespread engraftment to multiple organs: a study of their quantitative distribution after irradiation damage.Stem Cells. 2006;24(4): 1020-1029.
[37] Sémont A, Mouiseddine M, François A,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells improve small intestinal integrity through regulation of endogenous epithelial cell homeostasis.Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(6):952-961.
[38] Shackleton M.Normal stem cells and cancer stem cells: similar and different.Semin Cancer Biol. 2010;20(2):85-92.
[39] Peters BA, Diaz LA, Polyak K,et al.Contribution of bone marrow-derived endothelial cells to human tumor vasculature. Nat Med. 2005;11(3):261-262.
[40] Potten CS, Booth C, Hargreaves D.The small intestine as a model for evaluating adult tissue stem cell drug targets.Cell Prolif. 2003;36(3):115-129.
[41] Secko D.Do stem cells cause gastric cancer. CMAJ. 2005; 172(3):325-326.
[42] Studeny M, Marini FC, Dembinski JL,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells: potential precursors for tumor stroma and targeted-delivery vehicles for anticancer agents.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96(21):1593-1603 |