| [1]Evans MJ, Kaufman MH.Establishment in culture of pluripotential cells from mouse embryos.Nature. 1981;292 (5819):154-156.
[2]Amit M, Carpenter MK, Inokuma MS,et al.Clonally derived human embryonic stem cell lines maintain pluripotency and proliferative potential for prolonged periods of culture.Dev Biol. 2000;227(2):271-278.
[3]Kubo A, Shinozaki K, Shannon JM,et al.Development of definitive endoderm from embryonic stem cells in culture. Development. 2004;131(7):1651-1662.
[4]Bai H, Wang ZZ.Directing human embryonic stem cells to generate vascular progenitor cells.Gene Ther. 2008;15(2): 89-95.
[5]Levenberg S.Engineering blood vessels from stem cells: recent advances and applications.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2005;16(5):516-523.
[6]Kusuma S, Gerecht S.Engineering blood vessels using stem cells: innovative approaches to treat vascular disorders. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2010;8(10):1433-1445.
[7]Sun G, Gerecht S.Vascular regeneration: engineering the stem cell microenvironment. Regen Med. 2009;4(3):435-447.
[8]Wang ZZ, Au P, Chen T,et al.Endothelial cells derived from human embryonic stem cells form durable blood vessels in vivo.Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(3):317-318.
[9]Levenberg S, Ferreira LS, Chen-Konak L,et al. Isolation, differentiation and characterization of vascular cells derived from human embryonic stem cells.Nat Protoc. 2010;5(6): 1115-1126.
[10]Vodyanik MA, Bork JA, Thomson JA,et al.Human embryonic stem cell-derived CD34+ cells: efficient production in the coculture with OP9 stromal cells and analysis of lymphohematopoietic potential.Blood. 2005;105(2):617-626.
[11]Levenberg S, Golub JS, Amit M,et al.Endothelial cells derived from human embryonic stem cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(7):4391-4396.
[12]Goldman O, Feraud O, Boyer-Di Ponio J,et al.A boost of BMP4 accelerates the commitment of human embryonic stem cells to the endothelial lineage.Stem Cells. 2009;27(8): 1750-1759.
[13]Nourse MB, Halpin DE, Scatena M,et al.VEGF induces differentiation of functional endothelium from human embryonic stem cells: implications for tissue engineering. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(1):80-89.
[14]Simon MC, Liu L, Barnhart BC,et al.Hypoxia-induced signaling in the cardiovascular system.Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:51-71.
[15]邹志兵,毛淑章,郑澜. 低氧训练大鼠骨骼肌组织低氧诱导因子1对血管新生的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(20):3654- 3658.
[16]刘城,吴平生,王月刚,等. 野生型低氧诱导因子1α对人微血管内皮细胞增殖、迁移及成管的影响[J].中华生物医学工程杂志, 2013, 19(4):261-265.
[17]邹多宏,黄远亮. 低氧诱导因子1在血管形成及血管重塑中的作用[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2011,46(3):190-192.
[18]魏璇,陶宇,裴静娴,等. 重组腺病毒三突变型低氧诱导因子-1α对血管新生的影响[J].南方医科大学学报,2010,30(4):686-689.
[19]曲伟栋,赵华强. 低氧条件下HIF-1促进血管生成作用的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2009,25(2):234-236.
[20]石晓明,吴胜春,唐雷,等. 缺氧对血管内皮细胞低氧诱导因子-1α表达及增殖能力的影响[J].广东医学,2013,34(5):661-664.
[21]苏位君,王宝玉,宋祥和,等. 改良三维条件下人胚胎干细胞向内皮细胞的分化及功能[J].中国医学科学院学报,2012,34(6): 539-544.
[22]高斌,符伟国,竺挺,等. 二维法和三维法诱导小鼠胚胎干细胞定向分化为内皮细胞[J].中国临床医学,2012,19(3):193-197.
[23]罗敏,耿菊敏,梁道明,等. 人胚胎干细胞接种在鼠尾胶原包被培养板上定向分化为血管内皮细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(41):7642-7646.
[24]王彦,钱德俭,尉真,等. 人胚胎干细胞定向分化为血管内皮细胞的初步研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2010,6(2):66-69.
[25]Fischer B, Bavister BD.Oxygen tension in the oviduct and uterus of rhesus monkeys, hamsters and rabbits.J Reprod Fertil. 1993;99(2):673-679.
[26]Ezashi T, Das P, Roberts RM.Low O2 tensions and the prevention of differentiation of hES cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(13):4783-4788.
[27]Ramírez-Bergeron DL, Simon MC.Hypoxia-inducible factor and the development of stem cells of the cardiovascular system. Stem Cells. 2001;19(4):279-286.
[28]董红燕,王强,张中明,等. 低氧反应元件调控缺血心肌转染hVEGF165基因表达对新生血管的影响[J].徐州医学院学报, 2009, 29(11):704-707.
[29]董红燕,姜波,张中明,等. 低氧反应元件对缺血心肌转染人血管内皮生长因子165基因表达的调控作用[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2008,25(9):1095-1097.
[30]姜波,张中明,董红燕.低氧反应元件对缺血心肌转导hVEGF165基因表达的调控[J].徐州医学院学报,2006,26(5):381-385.
[31]张宜乾,张中明,闫英群,等. 低氧反应元件调控下h-VEGF165基因表达及其蛋白产物的延迟消失[J].生理学报,2006, 58(3): 281-286.
[32]张中明,姜波,董红燕,等.低氧反应元件对低氧复氧状态下心肌细胞转染人血管内皮生长因子165基因表达的调控作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(12):1510-1512.
[33]Prado-Lopez S, Conesa A, Armiñán A,et al.Hypoxia promotes efficient differentiation of human embryonic stem cells to functional endothelium.Stem Cells. 2010;28(3):407-418. |
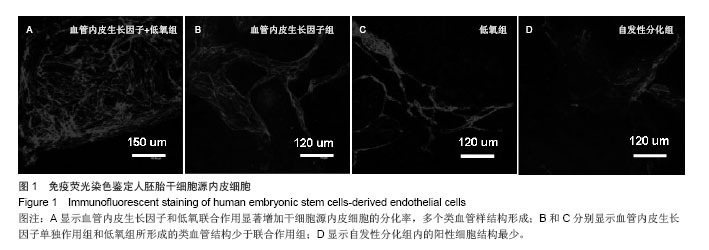
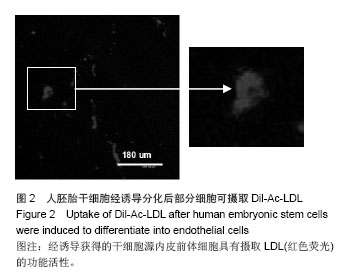
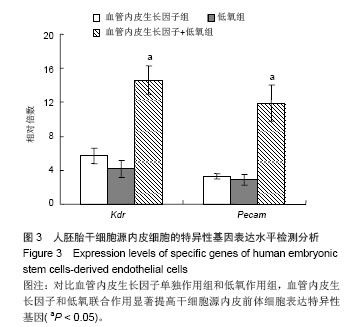
.jpg)