| [1]Zielinski SM, Keijsers NL, Praet SF, et al. Functional outcome after successful internal fixation versus salvage arthroplasty of patients with a femoral neck fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 2014.
[2]Andruszkow H, Scharff B, Zapf A, et al. [Influence of comorbidities and delay in surgical treatment on mortality following femoral neck fracture]. Z Orthop Unfall.2013;151(4): 338-342.
[3]O'Toole RV, Dancy L, Dietz AR, et al. Diagnosis of femoral neck fracture associated with femoral shaft fracture: blinded comparison of computed tomography and plain radiography. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(6): 325-330.
[4]Cao L, Wang B, Li M, et al. Closed reduction and internal fixation versus total hip arthroplasty for displaced femoral neck fracture. Chin J Traumatol. 2014;17(2): 63-68.
[5]Pauyo T, Drager J, Albers A, et al. Management of femoral neck fractures in the young patient: A critical analysis review. World J Orthop. 2014;5(3): 204-217.
[6]Zhou GQ, Pang ZH, Chen QQ, et al. Reconstruction of the biomechanical transfer path of femoral head necrosis: a subject-specific finite element investigation. Comput Biol Med. 2014;52:96-101.
[7]Unger AC, Dirksen B, Renken FG, et al. Treatment of femoral neck fracture with a minimal invasive surgical approach for hemiarthroplasty - clinical and radiological results in 180 geriatric patients. Open Orthop J. 2014;8:225-231.
[8]Mei J. A brief history of internal fixation of femoral neck fracture. Zhonghua Yi Shi Za Zhi. 2014;44(2): 101-105.
[9]Zhao W, Liu L, Zhang H, et al. Effect of dynamic hip screw on the treatment of femoral neck fracture in the elderly. Chin J Traumatol. 2014;17(2): 69-72.
[10]Wani IH, Sharma S, Latoo I, et al. Primary total hip arthroplasty versus internal fixation in displaced fracture of femoral neck in sexa- and septuagenarians. J Orthop Traumatol. 2014;15(3): 209-214.
[11]Johansson T. Internal fixation compared with total hip replacement for displaced femoral neck fractures: a minimum fifteen-year follow-up study of a previously reported randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014; 96(6): e46.
[12]Fisher MA, Matthei JD, Obirieze A, et al. Open reduction internal fixation versus hemiarthroplasty versus total hip arthroplasty in the elderly: a review of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database. J Surg Res. 2013; 181(2): 193-198.
[13]Laurer HL, Wutzler S, Possner S, et al. Outcome after operative treatment of Vancouver type B1 and C periprosthetic femoral fractures: open reduction and internal fixation versus revision arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(7): 983-989.
[14]Seitz WH Jr, Berardis JM, Giannaris T, et al. Perforation of the rectum by a Smith-Petersen nail. J Trauma.1982;22(4): 339-340.
[15]Ji SC. [Application of self-made wire guide apparatus for Smith-Petersen nailing (author's transl)]. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1981;19(4): 239-241.
[16]Burton KG. Fractures of the femoral neck: primary treatment with a smith-petersen nail and primary autogenous-bone graft. A long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1964;46: 1659-1675.
[17]Svendsen RN, Hermansson S, Noer HH. Osteosynthesis of medial femoral neck fractures with 2 Hansson nails. Ugeskr Laeger. 1991;153(12): 847-849.
[18]Toriumi H, Miyasaka T, Uchiyama S, et al. Utilization of a partially threaded Kirschner wire in the treatment of femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1998;12(5): 320-323.
[19]He W, Zhang W. The Curative Effect Comparison Between Prolonged Third Generation of Gamma Nail and Prolonged Dynamic Hip Screw Internal Fixation in Treating Femoral Intertrochanteric Fracture and the Effect on Infection. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014.
[20]Schwartsmann CR, Jacobus LS, Spinellilde F, et al. Dynamic hip screw for the treatment of femoral neck fractures: a prospective study with 96 patients. ISRN Orthop. 2014;2014: 257871.
[21]Friedl W, Ruf W. Experimental studies of the effectiveness of the sliding principle in dynamic hip screw osteosynthesis and its value in managing unstable pertrochanteric femoral fractures. Chirurg. 1987;58(2): 106-112.
[22]Claes L, Becker C, Simnacher M, et al. [Improvement in the primary stability of the dynamic hip screw osteosynthesis in unstable, pertrochanteric femoral fractures of osteoporotic bones by a new glass ionomer cement]. Unfallchirurg. 1995; 98(3): 118-123.
[23]Griffin XL, Parsons N, Achten J, et al. the Targon femoral neck hip screw versus cannulated screws for internal fixation of intracapsular fractures of the hip: a randomised controlled trial. Bone Joint J. 2014; 96-B(5): 652-657.
[24]Kaplan T, Akesen B, Demirag B, et al. Comparative results of percutaneous cannulated screws, dynamic compression type plate and screw for the treatment of femoral neck fractures. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2012;18(1): 65-70.
[25]Tian W, Cui Z, Kan S. [Comparison of cannulated screws fixation with different reduction methods at different time points for displaced femoral neck fractures in terms of fracture healing]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009; 23(4): 440-443.
[26]Robinson CM, Adams CI, Craig M, et al. Implant-related fractures of the femur following hip fracture surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002;84-A(7): 1116-1122.
[27]Kelly DW, Kelly BD. A novel diagnostic sign of hip fracture mechanism in ground level falls: two case reports and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2012;6:136.
[28]Vecsei V, Manninger J. [Diagnostic measures and therapeutic procedure in dislocated medial femoral neck fracture with the aim of saving the head before the age of prosthesis]. Z Unfallchir Versicherungsmed Berufskr. 1983;76(3):151-154.
[29]Aggarwal A, Singh M, Aggarwal AN, et al. Assessment of interobserver variation in Garden classification and management of fresh intracapsular femoral neck fracture in adults. Chin J Traumatol. 2014;17(2): 99-102.
[30]Frandsen PA, Andersen E, Madsen F, et al. Garden's classification of femoral neck fractures. An assessment of inter-observer variation. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1988;70(4): 588-590.
[31]Mao YJ, Wei J, Zhou L, et al. [Related factor analysis of avascular necrosis of the femoral head after internal fixation with cannulated screws in femoral neck fractures]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2005;85(46): 3256-3259.
[32]Eliasson P, Hansson LI, Karrholm J. Displacement in femoral neck fractures. A numerical analysis of 200 fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 1988;59(4): 361-364.
[33]Holmberg S, Thorngren KG. Statistical analysis of femoral neck fractures based on 3053 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987; 218: 32-41.
[34]Yu YX, Ma JZ, Zhu LB, et al. Failure of internal fixation on displaced femoral neck fractures in adults under fifty-five years old. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(7): 542-545.
[35]Yang H, Zhou F, Tian Y, et al. Analysis of the failure reason of internal fixation in peritrochanteric fractures. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011;43(5): 699-702.
[36]Saglam N, Kucukdurmaz F, Kivilcim H, et al. Biomechanical comparison of antirotator compression hip screw and cannulated screw fixations in the femoral neck fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(2): 196-201.
[37]Zhang Y, Tian L, Yan Y, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the expansive cannulated screw for fixation of femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2011;42(11): 1372-1376.
[38]Chen Z, Wang G, Lin J, et al. [Efficacy comparison between dynamic hip screw combined with anti-rotation screw and cannulated screw in treating femoral neck fractures]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(1): 26-29.
[39]Karanicolas PJ, Bhandari M, Walter SD, et al. Interobserver reliability of classification systems to rate the quality of femoral neck fracture reduction. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(6): 408-412.
[40]Papanastassiou ID, MAvrogenis AF, Kokkalis ZT, et al. Fixation of femoral neck fractures using divergent versus parallel cannulated screws. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2011;21(1): 63-69.
[41]Kumar MN, Belehalli P, Ramachandra P. PET/CT study of temporal variations in blood flow to the femoral head following low-energy fracture of the femoral neck. Orthopedics. 2014; 37(6): e563-570.
[42]AL-ani AN, Neander G, Samuelsson B, et al. Risk factors for osteoporosis are common in young and middle-aged patients with femoral neck fractures regardless of trauma mechanism . Acta Orthop. 2013;84(1): 54-59.
[43]Zhong B, Zhang Y, Zhang C, et al. A comparison of proximal femoral locking compression plates with dynamic hip screws in extracapsular femoral fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014;100(6): 663-668.
[44]Bumpass DB, Ricci WM, Mcandrew CM, et al. A Prospective Study of Pain Reduction and Knee Dysfunction Comparing Femoral Skeletal Traction and Splinting in Adult Trauma Patients. J Orthop Trauma. 2014.
[45]Dayton P, Feilmeier M, Hensley NL. Technique for minimally invasive reduction of calcaneal fractures using small bilateral external fixation. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014;53(3): 376-382.
[46]Wu XB, Yang MH, Zhu SW, et al. Surgical resection of severe heterotopic ossification after open reduction and internal fixation of acetabular fractures: A case series of 18 patients. Injury. 2014;45(10): 1604-1610.
[47]Yang JJ, Lin LC, Chao KH, et al. Risk factors for nonunion in patients with intracapsular femoral neck fractures treated with three cannulated screws placed in either a triangle or an inverted triangle configuration. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95(1): 61-69.
[48]Huang TW, Hsu WH, Peng KT, et al. Effect of integrity of the posterior cortex in displaced femoral neck fractures on outcome after surgical fixation in young adults. Injury. 2011; 42(2): 217-222. |
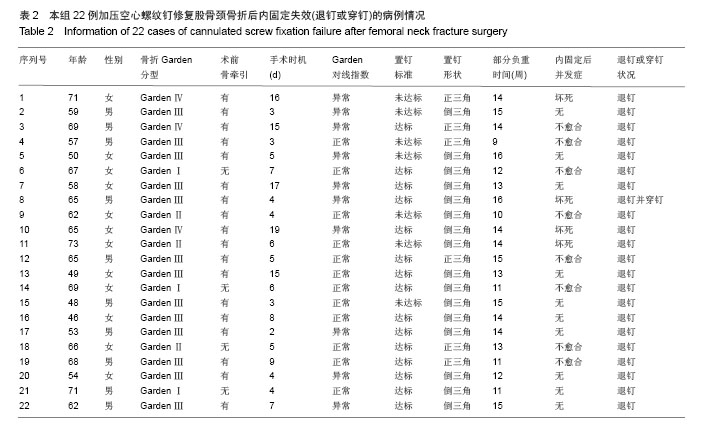
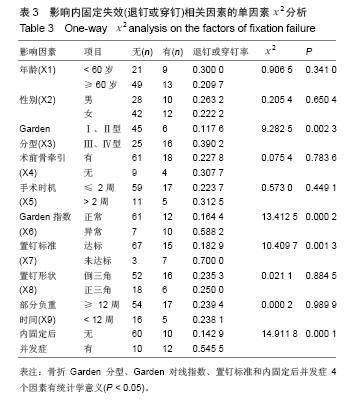
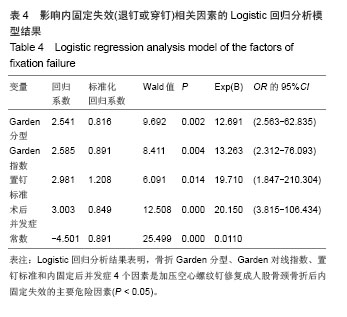
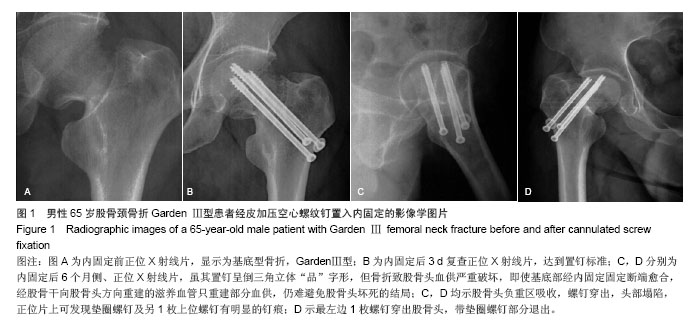
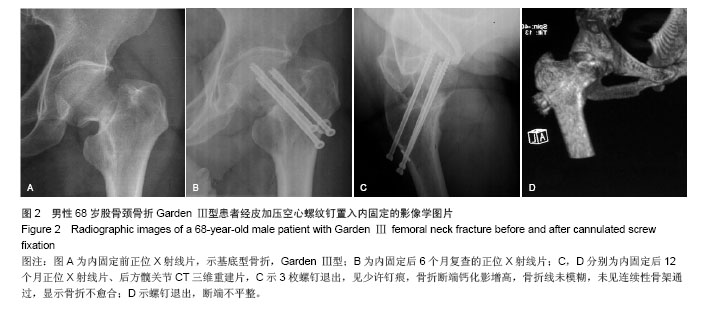
.jpg)