中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (37): 6019-6023.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.37.021
• 干细胞与中医药 stem cells and traditional Chinese medicine • 上一篇 下一篇
红景天苷诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞分化中的Ca2+/CaM信号通路
赵 玲1,赵红斌2,潘 茜2,李 根2,王九娜2,唐俊杰2
- 1甘肃中医学院,甘肃省兰州市 730000
2解放军兰州军区兰州总医院,甘肃省兰州市 730000
Salidroside induces the differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neuron-like cells mediated by calcium/calmodulin signaling pathway
Zhao Ling1, Zhao Hong-bin2, Pan Qian2, Li Gen2, Wang Jiu-na2, Tang Jun-jie2
- 1Gansu College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
2Institute of Orthopaedics, Lanzhou General Hospital of Lanzhou Military Region, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
摘要:
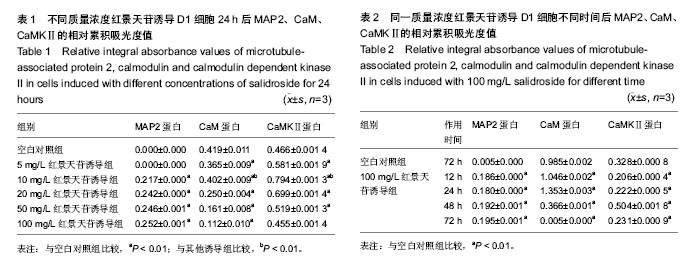
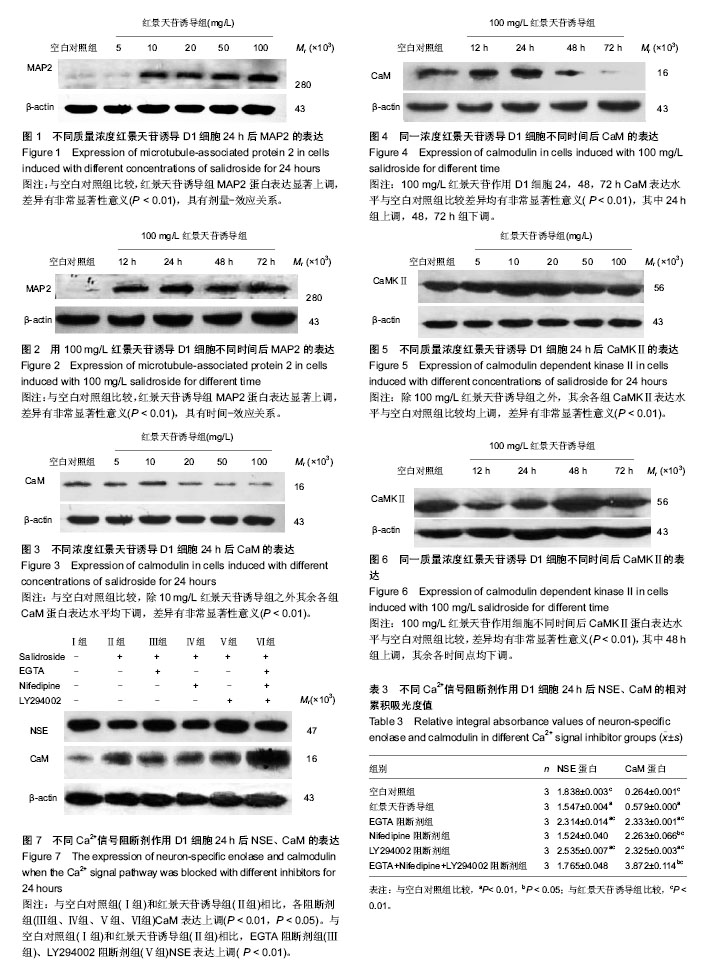
背景:课题组前期研究表明,红景天苷能诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元样细胞定向分化,Ca2+信号是实现其生物学信号传导的重要途径之一 目的:探讨Ca2+/CaM 信号通路在红景天苷诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞定向分化中的作用及机制。 方法:实验分为空白对照组和红景天苷诱导组,红景天苷诱导组将不同质量浓度红景天苷(5,10,20,50,100 mg/L)作用骨髓间充质干细胞24 h和100 mg/L红景天苷作用骨髓间充质干细胞12,24,48,72 h。采用Western blot方法分别检测红景天苷诱导骨髓间充质干细胞后神经标志分子MAP2和Ca2+/CaM信号通路中关键蛋白CaM、CaMKⅡ的表达水平。另外实验设阻断剂组,分别加Ca2+信号通路特异性阻断剂:500 µmol/L EGTA (细胞外Ca2+螯合剂)、1 mmol/L Nifedipine (L型Ca2+通道阻断剂)、10 mmol/L LY294002 (PI3K抑制剂)分别作用细胞30 min后,再加入100 mg/L红景天苷作用细胞24 h,采用Western blot方法检测阻断Ca2+/CaM信号通路后NSE、CaM的表达情况。 结果与结论:①红景天苷诱导后,MAP2的表达上调(P < 0.01),说明红景天苷可诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为神经细胞。②不同质量浓度红景天苷诱导骨髓间充质干细胞24 h后,10 mg/L红景天苷组CaM、CaMKⅡ的表达与其他诱导组比较显著上调(P < 0.01);同一质量浓度红景天苷诱导72 h后CaM、CaMKⅡ表达明显下调(P < 0.01)。③阻断细胞外Ca2+和PI3K信号通路后,NSE与CaM的表达水平较红景天苷诱导组上调(P < 0.05)。结果表明,红景天苷通过抑制Ca2+/CaM信号通路实现骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞定向分化。
中图分类号: