| [1] Brott T, Bogousslavsky J. Treatment of acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(10):710-722.
[2] Antoine H, Roger S. Ischemic preconditioning: introduction. Stroke. 2004;35:2675.
[3] Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation. 1986;74(5):1124-1136.
[4] Kitagawa K, Matsumoto M, Kuwabara K, et al. 'Ischemic tolerance' phenomenon detected in various brain regions. Brain Res. 1991;561(2):203-211.
[5] Dempsey RJ, Sailor KA, Bowen KK, et al. Stroke-induced progenitor cell proliferation in adult spontaneously hypertensive rat brain: effect of exogenous IGF-1 and GDNF. J Neurochem. 2003;87(3):586-597.
[6] 王蘋,毕建忠.三七皂苷治疗脑血管病的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志, 2006,26(2):275.
[7] 周俊英,刘小利,罗祖明,三七三醇皂苷增进大鼠脑缺血耐受的作用及对GFAP和bFGF表达的影响[J].华西药学杂志,2005,20(6): 489-492.
[8] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导意见. 2006-09-30.
[9] Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[10] 郝玉曼,罗祖明,周东.局灶预缺血诱导脑缺血耐受的动物模型[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2003;20(2):129-131.
[11] Ara J, De Montpellier S. Hypoxic-preconditioning enhances the regenerative capacity of neural stem/progenitors in subventricular zone of newborn piglet brain. Stem Cell Res. 2013;11(2):669-686.
[12] Jin K, Minami M, Lan JQ, et al. Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(8):4710-4715.
[13] Wei L, Fraser JL, Lu ZY, et al. Transplantation of hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells enhances angiogenesis and neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;46(3):635-645.
[14] Dhodda VK, Sailor KA, Bowen KK, et al. Putative endogenous mediators of preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance in rat brain identified by genomic and proteomic analysis. J Neurochem. 2004;89(1):73-89.
[15] Hong SJ, Li H, Becker KG, et al. Identification and analysis of plasticity-induced late-response genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(7):2145-2150.
[16] Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, et al. VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest. 2003;111(12):1843-1851.
[17] Türeyen K, Vemuganti R, Bowen KK, et al. EGF and FGF-2 infusion increases post-ischemic neural progenitor cell proliferation in the adult rat brain. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(6): 1254-1263.
[18] Sakata H, Niizuma K, Yoshioka H, et al. Minocycline-preconditioned neural stem cells enhance neuroprotection after ischemic stroke in rats. J Neurosci. 2012;32(10):3462-3473.
[19] Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(24):1581-1587.
[20] Dharmasaroja PA, Pattaraarchachai J. Low vs standard dose of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in treating East Asian patients with acute ischemic stroke. Neurol India. 2011;59(2):180-184.
[21] Cremer S, Berliner Y, Warren D, et al. Successful treatment of pediatric stroke with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-PA): a case report and review of the literature. CJEM. 2008;10(6):575-578.
[22] Stemer AB, Huisa BN, Zivin JA. The evolution of transcranial laser therapy for acute ischemic stroke, including a pooled analysis of NEST-1 and NEST-2. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2010; 12(1): 29-33.
[23] Saver JL. Novel end point analytic techniques and interpreting shifts across the entire range of outcome scales in acute stroke trials. Stroke. 2007;38(11):3055-3062.
[24] Wardlaw JM, Murray V, Berge E, et al. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischaemic stroke: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2012;379 (9834): 2364-2372.
[25] Naylor M, Bowen KK, Sailor KA, et al. Preconditioning-induced ischemic tolerance stimulates growth factor expression and neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. Neurochem Int. 2005;47(8):565-572. |
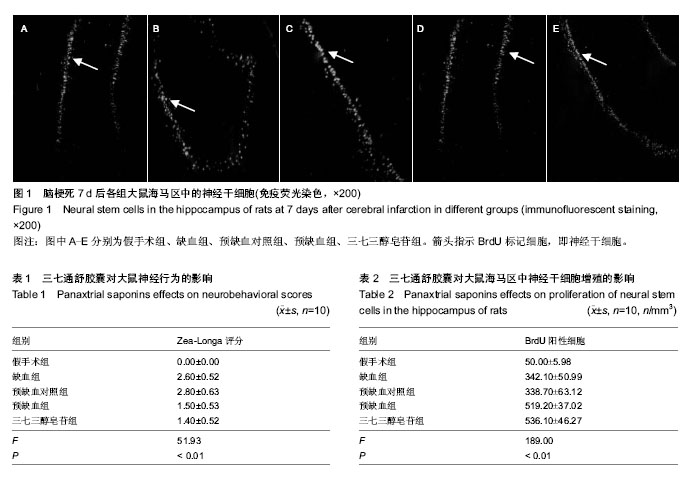
.jpg)