| [1]曹谊林.组织工程学研究进展[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版, 2008, 28(7):763-766.
[2]Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H,et al.Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.
[3]Mouras R, Bagnaninchi P, Downes A,et al.Non linear optical microscopy of adipose-derived stem cells induced towards osteoblasts and adipocytes.Proc SPIE. 2011;8:8086.
[4]Estes BT, Diekman BO, Gimble JM,et al.Isolation of adipose-derived stem cells and their induction to a chondrogenic phenotype.Nat Protoc. 2010;5(7):1294-1311.
[5]Kim HJ, Park SH, Durham J,et al. In vitro chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells with silk scaffolds.J Tissue Eng. 2012;3(1):1-8.
[6]Cao Y, Sun Z, Liao L,et al. Human adipose tissue-derived stem cells differentiate into endothelial cells in vitro and improve postnatal neovascularization in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;332(2):370-379.
[7]郭峘杉,颜玲.无血清培养促进脂肪干细胞向血管内皮细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(36):6443-6448.
[8]胡翰青,邢红艳,马行健,等.体外诱导小鼠脂肪来源干细胞向内皮细胞分化的实验研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2013,13(25): 4857-4860.
[9]Uysal AC, Mizuno H. Differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells for tendon repair. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;702:443-451.
[10]刘刘.腱组织提取物对大鼠脂肪来源间充质干细胞增殖和向肌腱细胞分化的影响[D].长沙:中南大学,2011.
[11]Fraser JK, Schreiber R, Strem B,et al.Plasticity of human adipose stem cells toward endothelial cells and cardiomyocytes. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2006;3 Suppl 1: S33-37.
[12]闫小宾,李琼,郭志坤,等.兔脂肪来源间充质干细胞的生物表型及其心肌样细胞的分化潜能[J].解剖学报,2013,44(1):55-61.
[13]王晓明,聂良明,许林海,等.两个部位脂肪来源干细胞的心肌细胞分化潜能比较[J].中华移植杂志(电子版),2011,5(4):304-308.
[14]P B, N G, H G. Differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells towards the epithelial lineage.J Stem Cells Regen Med. 2010; 6(2):61.
[15]刘荣福,高加胜,杨宇峰.脂肪间充质干细胞分化为肾小管上皮细胞的实验研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2013,2(2):175-179.
[16]Al Battah F, De Kock J, Vanhaecke T,et al.Current status of human adipose-derived stem cells: differentiation into hepatocyte-like cells.Scientific World Journal. 2011;11: 1568-1581.
[17]李晏,刘再毅,梁长虹,等.超顺磁氧化铁标记对大鼠脂肪干细胞向肝样细胞诱导分化的影响[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2012, 35(6):337-342.
[18]殷莉波,赵文秀,尹震宇,等.体内外人脂肪间充质干细胞向肝样细胞分化的实验研究[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2011,17(4): 322-327.
[19]张秀霞,蒋良福.无血清诱导脂肪间充质干细胞向雪旺细胞分化的实验研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(4):322-325.
[20]江丽,朱家恺,刘小林,等.大鼠脂肪干细胞诱导分化为类许旺细胞的表型和功能特征[J].中华显微外科杂志,2007,30(6):430-432.
[21]毕晓娟,马艳,江明.大鼠腹股沟脂肪间充质干细胞的分离、培养、鉴定及活体标记[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(14): 2512-2516.
[22]张雪莲,马依彤,王常勇,等.大鼠脂肪干细胞的分离培养及基本生物学性状研究[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2010, 26(12): 1217-1219.
[23]刘娜,张博,李芳菲,等.大鼠脂肪间充质干细胞膜片的生物学特点研究[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2013,11(2):65-69.
[24]石金鑫,刘剑锋,王海滨,等.棕色脂肪干细胞与白色脂肪干细胞移植对心肌梗死大鼠心功能的影响[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(15): 18-21.
[25]王清富,陈庄洪,蔡贤华,等.兔脂肪干细胞的多向诱导分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(49): 162-167.
[26]杨光,赵占志,朱新兵,等.兔脂肪干细胞体外诱导分化为胰岛β样细胞的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究,2012, 16(23):4232-4236.
[27]刘琴,王丽平,喻晶,等.组织块贴壁法扩增兔脂肪干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(1):88-93.
[28]谢永辉,陈庄洪,蔡贤华,等.兔脂肪间充质干细胞的生物学特性及其成骨诱导分化的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(2): 358-360.
[29]高大宽,章翔,费舟,等.脂肪干细胞诱导神经干细胞分化的体外实验研究[J]. 中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2010,9(2):120-123.
[30]宋丽娟,毕晓娟,马艳,等.小鼠脂肪源干细胞的生物学特性及增殖特点[J].新疆医科大学学报 2014,37(4):479-483.
[31]Bradley A.Mining the mouse genome. Nature. 2002; 420 (6915): 512-514.
[32]王萍,房佰俊,宋永平,等.小鼠脂肪源间充质干细胞在重型再生障碍性贫血中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(43): 8426-8430.
[33]任红苗,王宜南,陈继川,等.脂肪源性神经干细胞诱导分化为γ-氨基丁酸能神经元的体外研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2012, 34(11): 1067-1070.
[34]刘晓潭,徐海斌,路坦. 小鼠脂肪来源干细胞向成骨及软骨细胞的诱导分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(14): 2525-2531.
[35]Abdanipour A,Tiraihi T, Delshad A.Trans-differentiation of the adipose tissue-derived stem cells into neuron-like cells expressing neurotrophins by selegiline.Iranian Biomedical Journal. 2011; 15(4):113-121.
[36]Campagnoli C, Roberts IA, Kumar S,et al. Identification of mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in human first-trimester fetal blood, liver, and bone marrow.Blood. 2001;98(8): 2396-2402.
[37]王福科,赵德萍,代晓明,等.不同类型血清对大鼠脂肪干细胞分离培养的影响[J]. 昆明医学院学报, 2010,31(3): 4-10.
[38]Lin G, Garcia M, Ning H,et al.Defining stem and progenitor cells within adipose tissue. Stem Cells Dev. 2008;17(6): 1053-1063.
[39]Lin K, Matsubara Y, Masuda Y, et al. Characterization of adipose tissue-derived cells isolated with the Celution system. Cytotherapy. 2008;10(4):417-426.
[40]Varma MJ, Breuls RG, Schouten TE,et al. Phenotypical and functional characterization of freshly isolated adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2007;16(1):91-104.
[41]Gronthos S, Franklin DM, Leddy HA,et al. Surface protein characterization of human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells.J Cell Physiol. 2001;189(1):54-63.
[42]Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al.Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295.
[43]De Ugarte DA, Morizono K, Elbarbary A,et al. Comparison of multi-lineage cells from human adipose tissue and bone marrow. Cells Tissues Organs. 2003;174(3):101-109.
[44]Aust L, Devlin B, Foster SJ,et al.Yield of human adipose-derived adult stem cells from liposuction aspirates. Cytotherapy. 2004;6(1):7-14.
[45]Strem BM, Hicok KC, Zhu M, et al.Multipotential differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells.Keio J Med. 2005; 54(3): 132-141.
[46]Qayyum AA, Haack-Sørensen M, Mathiasen AB, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for chronic myocardial ischemia (MyStromalCell Trial): study design. Regen Med. 2012;7(3):421-428.
[47]Rodriguez AM, Elabd C, Amri EZ,et al.The human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells.Biochimie. 2005; 87(1):125-128.
[48]Boquest AC, Shahdadfar A, Frønsdal K,et al. Isolation and transcription profiling of purified uncultured human stromal stem cells: alteration of gene expression after in vitro cell culture. Mol Biol Cell. 2005;16(3):1131-1141.
[49]Hu K, Shi H, Zhu J,et al.Compressed collagen gel as the scaffold for skin engineering.Biomed Microdevices. 2010; 12(4):627-635.
[50]Lin Z, Solomon KL, Zhang X,et al. In vitro evaluation of natural marine sponge collagen as a scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Sci. 2011;7(7):968-977.
[51]Pang Y, Greisler HP. Using a type 1 collagen-based system to understand cell-scaffold interactions and to deliver chimeric collagen-binding growth factors for vascular tissue engineering. J Investig Med. 2010;58(7):845-848. |
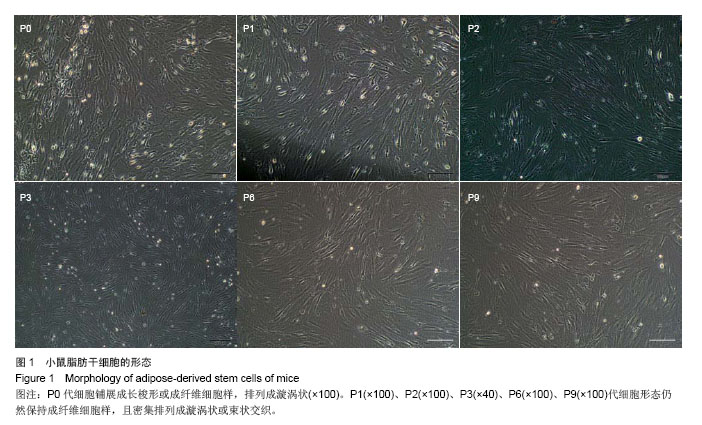
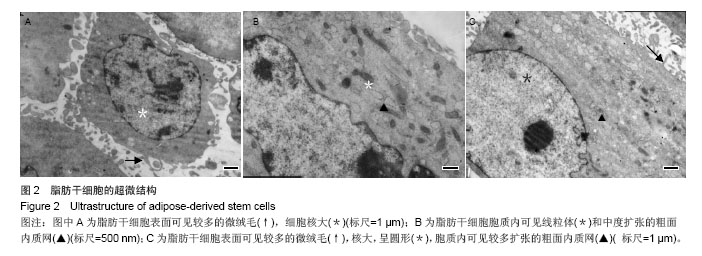
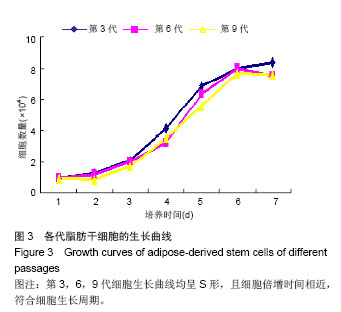
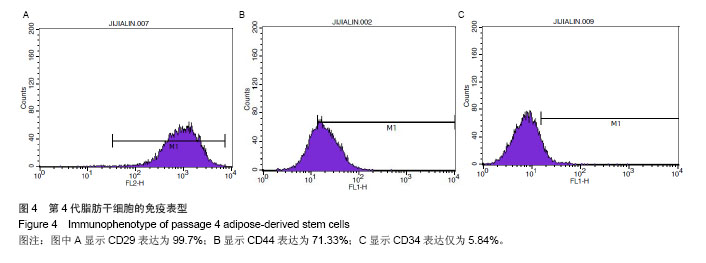

.jpg)