| [1]崔书章,寿松涛,柴艳芬.实用危重病医学[M].天津:天津科学技术出版社,2001:913-920
[2]Rabuel C,Mebazaa A. Septic shock:A heart story since the1960s.Intensive Care Med.2006;32(6):799-807.
[3]Zanotti-Cavazzoni SL,Hollenberg SM.Cardiac dysfunction in severe sepsis and septic shock.Curr Opin Crit Care. 2009; 15(5):392-397.
[4]Li XJ, Wang XW,Du YJ. Protective effects of erythropoietin on myocardial infarction in rats: the role of AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Am J Med Sci. 2011;342(2): 153-159.
[5]Merelli A, Caltana L,Lazarowshi A,et al. Experimental evidence of the potential use of erythropoietin by intranasal administration as a neuroprotective agent in cerebral hypoxia. Drug Metabol Drug Interact. 2011;26(2):65-69.
[6]You Shang, Yan Wu,Shanglong Yao,et al. Protective effect of erythropoietin against ketamine-induced apoptosis in cultured rat cortical neurons: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and GSK-3 beta pathway. Apotosis. 2007;12(11):2187-2195.
[7]Khan AI, Coldewey SM, Patel NS et al. Erythropoietin attenuates cardiac dysfunction in experimental sepsis in mice via activation of the β-common receptor. Dis Model Mech. 2013; 6(4):1021-1030.
[8]秦延军,张新亮,于悦卿,等.促红细胞生成素对脓毒症大鼠心肌损伤的保护作用[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2014,23(2):151-156.
[9]Katsanos KH, Tatsioni A, Natsi D, et al. Recombinant human erythropoietin in patients with inflammatory bowel disease and refractory anemia: a 15-year single center experience. J Crohns Colitis. 2012;6(1):56-61.
[10]苏绍红,张俊峰,李倩如,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植小鼠免疫系统CD4+T细胞亚群的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(1): 106-111.
[11]杨锐,马昭杰, 陈容平,等.间充质干细胞诱导糖尿病小型猪同种异体胰岛移植的免疫耐受[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013,17(14): 2558-2562.
[12]Németh K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PS, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 2009; 15(1):42-49.
[13]Gonzalez-Rey E, Anderson P, González MA, et al. Human adult stem cells derived from adipose tissue protect against experimental colitis and sepsis. Gut. 2009;58(7):929-39.
[14]Yagi H, Soto-Gutierrez A, Kitagawa Y, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate organ injury induced by LPS and burn. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(6):823-830.
[15]李娜,胡大海,王耀军,等.脂肪间充质干细胞对烧伤脓毒症小鼠肾脏损伤的作用[J].中华烧伤杂志,2013,29(3): 249-254.
[16]Chang CL, Leu S, Sung HC, et al. Impact of apoptotic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on attenuating organ damage and reducing mortality in rat sepsis syndrome induced by cecal puncture and ligation. J Transl Med. 2012; 10:244.
[17]Wichterman KA, Baue AE, Chaudry IH. Sepsis and septic shock: A review of laboratory models and a proposal. J Surg Res. 1980;29(2):189-201.
[18]Chittock DR, Russell JA. Oxygen delivery and consumption during sepsis.Clin Chest Med. 1996;17(2):263-268.
[19]Guest TM, Ramanathan JH,Tuteur PG, et al. Myocardial injury in critically ill patients . A frequently unrecognized complication. JAMA. 1995;273(24):1945-1949.
[20]Kollef MH, Ladenson JH, Eisenberg PR.Clinically recognized cardiac dysfunction: an independent determinant of mortality among critically ill patients. Is there a role for serial measurement of cardiac troponin I?Chest. 1997;111(5): 1340-1347.
[21]Ostermann M, Lo J, Toolan M,et al.A prospective study of the impact of serial troponin measurements on the diagnosis of myocardial infarction and hospital and 6-month mortality in patients admitted to ICU with non-cardiac diagnoses.Crit Care. 2014;18(2):R62.
[22]Turner A, Tsamitros M, Bellomo R. Myocardial cell injury in septic shock. Crit Care Med.1999;27(9):1775-1780.
[23]Soriano FG, Nogueira AC, Caldini EG, et al.Potential role of poly(adenosine 5'-diphosphate-ribose) polymerase activation in the pathogenesis of myocardial contractile dysfunction associated with human septic shock.Crit Care Med. 2006; 34(4): 1073-1079.
[24]Yip HK, Chang YC, Wallace CG, et al. Melatonin treatment improves adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell therapy for acute lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Pineal Res. 2013; 54(2):207-221.
[25]杨澄,张敏州,郭力.脓毒症大鼠早期心功能的变化[J].广东医学, 2010,31(18):2357-2358. |
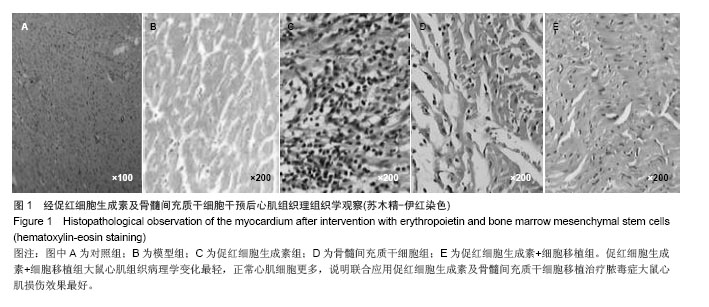
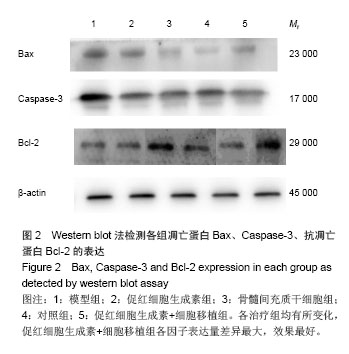
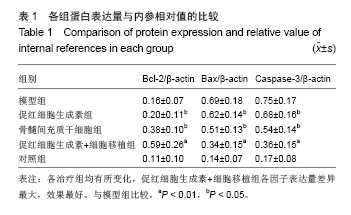
.jpg)