| [1] World Health Organization.Global status report on noncommunicable disaeses 2010. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2011.
[2] World Health Organization.Global atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control. Geneva, World Health Organization, 2011.
[3] 卫生部心血管病防治研究中心. 中国心血管病报告2011[M]. 北京:中国大百科全书出版社, 2011.
[4] Pittenger MF, Martin BJ.Mesenchymal stem cells and their potential as cardiac therapeutics.Circ Res. 2004;95(1):9-20.
[5] Dai W, Hale SL, Martin BJ,et al.Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in postinfarcted rat myocardium: short-and long-term effects.Circulation. 2005;112(2): 214-223.
[6] Wang T, Tang W, Sun S,et al.Intravenous infusion of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves myocardial function in a rat model of myocardial ischemia.Crit Care Med. 2007;35(11):2587-2593.
[7] Wang T, Tang W, Sun S,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells improve outcomes of cardiopulmonary resuscitation in myocardial infarcted rats.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009;46(3): 378-384.
[8] van der Bogt KE, Sheikh AY, Schrepfer S,et al.Comparison of different adult stem cell types for treatment of myocardial ischemia.Circulation. 2008;118(14 Suppl):S121-129.
[9] Chen SL, Fang WW, Ye F,et al.Effect on left ventricular function of intracoronary transplantation of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Am J Cardiol. 2004;94(1):92-95.
[10] Mohyeddin-Bonab M, Mohamad-Hassani MR, Alimoghaddam K,et al.Autologous in vitro expanded mesenchymal stem cell therapy for human old myocardial infarction.Arch Iran Med. 2007;10(4):467-473.
[11] Hare JM, Traverse JH, Henry TD,et al.A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study of intravenous adult human mesenchymal stem cells (prochymal) after acute myocardial infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009; 54(24): 2277-2286.
[12] Williams AR, Trachtenberg B, Velazquez DL,et al. Intramyocardial stem cell injection in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: functional recovery and reverse remodeling. Circ Res. 2011;108(7):792-796.
[13] Trachtenberg B, Velazquez DL, Williams AR,et al.Rationale and design of the Transendocardial Injection of Autologous Human Cells (bone marrow or mesenchymal) in Chronic Ischemic Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Heart Failure Secondary to Myocardial Infarction (TAC-HFT) trial: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of safety and efficacy.Am Heart J. 2011;161(3):487-493.
[14] Wen Z, Zheng S, Zhou C,et al.Repair mechanisms of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in myocardial infarction.J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(5):1032-1043.
[15] Abdel-Latif A, Bolli R, Tleyjeh IM,et al.Adult bone marrow-derived cells for cardiac repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(10):989-997.
[16] Zhu W, Chen J, Cong X, et al.Hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cells. 2006;24(2):416-425.
[17] Saini U, Gumina RJ, Wolfe B,et al.Preconditioning mesenchymal stem cells with caspase inhibition and hyperoxia prior to hypoxia exposure increases cell proliferation.J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(11):2612-2623.
[18] Chavakis E, Koyanagi M, Dimmeler S.Enhancing the outcome of cell therapy for cardiac repair: progress from bench to bedside and back.Circulation. 2010;121(2):325-335.
[19] Huang XP, Sun Z, Miyagi Y,et al. Differentiation of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells induces immunogenicity and limits their long-term benefits for myocardial repair.Circulation. 2010; 122(23):2419-2429.
[20] Wen Z, Zheng S, Zhou C,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells for post-myocardial infarction cardiac repair: microRNAs as novel regulators.J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16(4): 657-671.
[21] Urbich C, Kuehbacher A, Dimmeler S.Role of microRNAs in vascular diseases, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79(4):581-588.
[22] Matkovich SJ, Hu Y, Dorn GW 2nd. Regulation of cardiac microRNAs by cardiac microRNAs.Circ Res. 2013;113(1): 62-71.
[23] Naga Prasad SV, Duan ZH, Gupta MK,et al.Unique microRNA profile in end-stage heart failure indicates alterations in specific cardiovascular signaling networks.J Biol Chem. 2009; 284(40):27487-27499.
[24] Lee DY, Deng Z, Wang CH,et al.MicroRNA-378 promotes cell survival, tumor growth, and angiogenesis by targeting SuFu and Fus-1 expression.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007; 104 (51): 20350-20355.
[25] Chen LT, Xu SD, Xu H,et al.MicroRNA-378 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis by promoting cell migration, invasion and tumor angiogenesis.Med Oncol. 2012; 29(3):1673-1680.
[26] Amsalem Y, Mardor Y, Feinberg MS,et al.Iron-oxide labeling and outcome of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in the infarcted myocardium.Circulation. 2007;116(11 Suppl):I38-45.
[27] 孔宏亮,刘宁宁,霍鑫,等. 缺氧对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、凋亡及葡萄糖摄取和Akt表达的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2008, 18(10): 1374-1378,1382.
[28] 徐巧岩,夏琳,王吉昌.低氧预处理骨髓间充质干细胞耐受缺血缺氧的能力[J].中国组织工程研究, 2013, 17(49): 8474-8480.
[29] Cao W, Guo XW, Chen K,et al.Inhibition of hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis by salvianolic acid in rat mesenchymal stem cells.J Tradit Chin Med. 2012;32(2): 222-228.
[30] Xie X, Sun A, Zhu W,et al.Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells preconditioned with hydrogen sulfide enhances repair of myocardial infarction in rats.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2012; 226(1):29-36.
[31] McGinley L, McMahon J, Strappe P,et al.Lentiviral vector mediated modification of mesenchymal stem cells & enhanced survival in an in vitro model of ischaemia.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011;2(2):12.
[32] Tsubokawa T, Yagi K, Nakanishi C,et al.Impact of anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidative effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells with transient overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 on myocardial ischemia.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010;298(5):H1320-1329.
[33] Yu B, Gong M, He Z,et al.Enhanced mesenchymal stem cell survival induced by GATA-4 overexpression is partially mediated by regulation of the miR-15 family.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(12):2724-2735.
[34] Eichner LJ, Perry MC, Dufour CR,et al.miR-378(∗) mediates metabolic shift in breast cancer cells via the PGC-1β/ERRγ transcriptional pathway.Cell Metab. 2010;12(4):352-361.
[35] Deng H, Guo Y, Song H,et al.MicroRNA-195 and microRNA-378 mediate tumor growth suppression by epigenetical regulation in gastric cancer.Gene. 2013;518(2): 351-359.
[36] Fang J, Song XW, Tian J,et al.Overexpression of microRNA-378 attenuates ischemia-induced apoptosis by inhibiting caspase-3 expression in cardiac myocytes. Apoptosis. 2012;17(4):410-423.
[37] Knezevic I, Patel A, Sundaresan NR,et al. A novel cardiomyocyte-enriched microRNA, miR-378, targets insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor: implications in postnatal cardiac remodeling and cell survival.J Biol Chem. 2012;287 (16): 12913-12926.
[38] Kim SW, Kim HW, Huang W,et al.Cardiac stem cells with electrical stimulation improve ischaemic heart function through regulation of connective tissue growth factor and miR-378.Cardiovasc Res. 2013;100(2):241-251.
[39] Bonauer A, Boon RA, Dimmeler S.Vascular microRNAs.Curr Drug Targets. 2010;11(8):943-949.
[40] Skrzypek K, Tertil M, Golda S,et al.Interplay between heme oxygenase-1 and miR-378 affects non-small cell lung carcinoma growth, vascularization, and metastasis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19(7):644-660. |
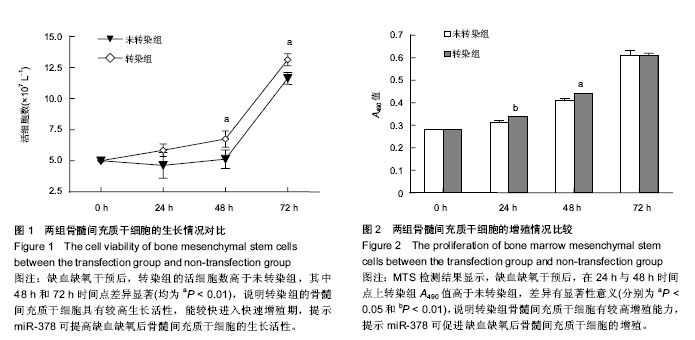

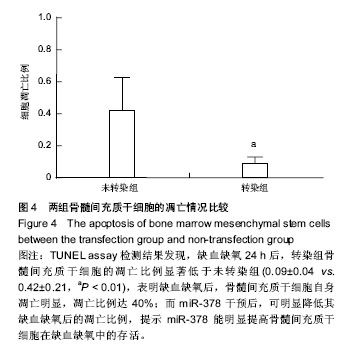
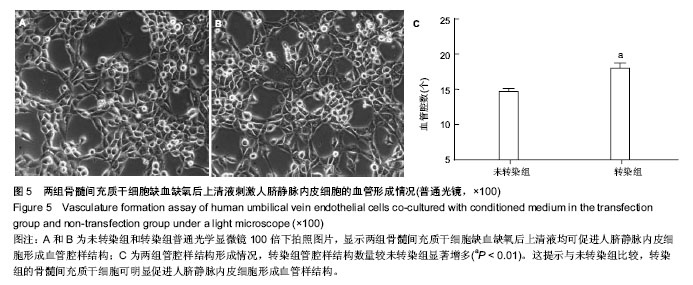
.jpg)