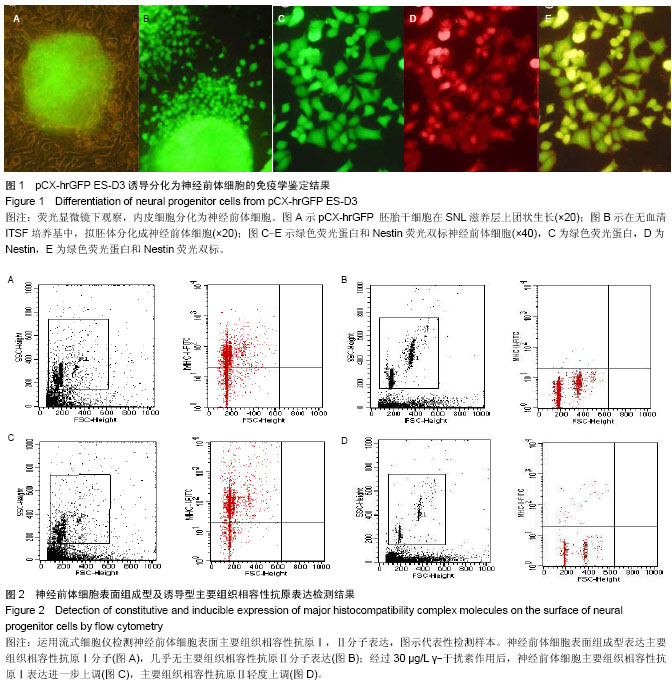
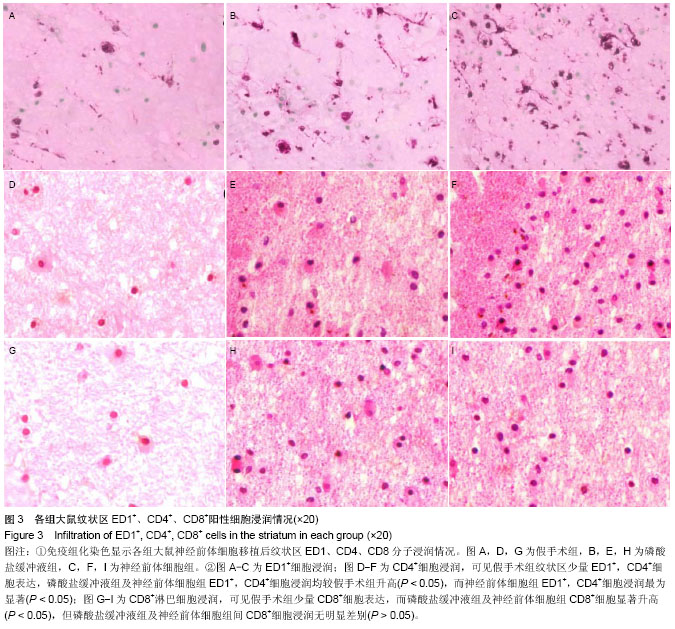
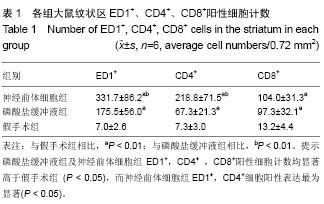
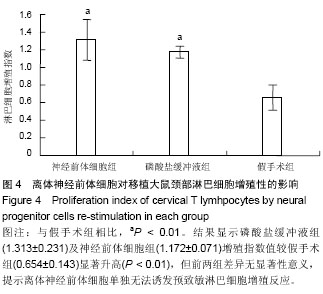
| [1] Bonnamain V, Neveu I, Naveilhan P. Neural stem/progenitor cells as promising candidates for regenerative therapy of the central nervous system. Front Cell Neurosci. 2012;6:17.
[2] Bonnamain V, Neveu I, Naveilhan P.In vitro analyses of the immunosuppressive properties of neural stem/progenitor cells using anti-CD3/CD28-activated T cells. Methods. 2011; 677: 233-243.
[3] Klassen H,Schwartz MR, Bailey AH, et al. Surface markers expressed by multipotent human and mouse neural progenitor cells include tetraspanins and non-protein epitopes. Neurosci. Lett. 2001;312:180-182.
[4] Hori J, Ng TF, Shatos M, et al. Neural progenitor cells lack immunogenicity and resist destruction as allografts. Stem Cells. 2003;21:405-416.
[5] Odeberg J,Piao JH,Samuelsson EB,et al. Low immunogenicity of in vitro-expanded human neural cells despite high MHC expression. J.Neuro Immunol. 2005;161: 1-11.
[6] Fändrich F, Dresske B, Bader M, et al.Embryonic stem cells share immune-privileged features relevant for tolerance induction. J Mol Med. 2002;80:343-350.
[7] Zappia E,Casazza S,Pedemonte E,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis inducing T-cell anergy. Blood.2005;106: 1755-1761.
[8] Einstein O, Fainstein N, Vaknin I, et al.Neural precursors attenuate autoimmune encephalomyelitis by peripheral immunosuppression. Ann.Neurol. 2007;61:209-218.
[9] Einstein O,Karussis D,Grigoriadis, N,et al. Intra ventricular transplantation of neural precursor cells pheres attenuates acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;24:1074-1082.
[10] Cusimano M,Biziato D,Brambilla E, et al.Transplanted neural stem/precursor cells instruct phagocytes and reduce secondary tissue damage in the injured spinal cord. Brain. 2012;35(Pt.2):447-460.
[11] Sergent-Tanguy S,Véziers J, Bonnamain V,et al. Cell surface antigens on rat neural progenitors and characterization of the CD3 (+)/CD3 (-) cell populations. Differentiation. 2006;74: 530-541.
[12] Johansson S, Price J, Modo M. Effect of inflammatory cytokines on major histocompatibility complex expression and differentiation of human neural stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26:2444-2454.
[13] Laguna Goya R,Busch R,Mathur R, et al.Human fetal neural precursor cells can up-regulate MHC class I and class II expression and elicit CD4 and CD8 T cell proliferation. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;41:407-414.
[14] Carpentier PA, Palmer TD. Immune Influence on Adult Neural Stem Cell Regulation and Function. Neuron. 2009;64(1): 79-92.
[15] 吴旋,黎海蒂,李树浓,等.小鼠胚胎干细胞体外分化为神经前体细胞的研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2001,23(11):1260-1263.
[16] Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al.Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[17] 龚非力.医学免疫学[M].北京:科学出版社,2000.
[18] Frank MG, Barrientos RM, Biedenkapp JC, et al. mRNA up-regulation of MHC II and pivotal pro-inflammatory genes in normal brain aging. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27(5):717-722.
[19] Lawrence JM, Morris RJ, Wilson DJ, et al. Mechanisms of allograft rejection in the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1990;37: 431-462.
[20] Nicholas MK, Stefansson K, Antel JP, et al. An in vivo and in vitro analysis of systemic immune function in mice with histologic evidence of neural transplant rejection. J Neurosci Res. 1987;18:245-257.
[21] Taylor CJ, Bolton EM,Bradley JA.Immunological considerations for embryonic and induced pluripotent stem cell banking. Phil Trans R Soc B. 2011;366:2312-2322.
[22] Drukker M, Katz G, Urbach A, et al. Characterization of the expression of MHC proteins in human embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:9864-9869.
[23] Strom TB, Field LJ, Ruediger M. Allogeneic stem cells, clinical transplantation and the origins of regenerative medicine. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:601-605.
[24] Zavazava N.Immunity of embryonic stem cell-derived hematopoietic progenitor cells. Semin Immunopathol. 2011; 33(6):613-617.
[25] Boyd AS, Wood KJ. Characteristics of the early immune response following transplantation of mouse ES cell derived insulin-producing cell clusters. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e10965.
[26] Jacobs SA, Roobrouck VD, Verfaillie CM,et al. Immunological characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells and multipotent adult progenitor cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013;91: 32-39.
[27] Nimer A, Wennersten F, Holmin A, et al. MHC expression after human neural stem cell transplantation to brain contused rats,Neuroimmunology. 2004;15(12):1871-1875.
[28] McLaren FH, Svendsen CN, Van der Meide P, et al. Analysis of neural stem cells by flow cytometry: cellular differentiation modifies patterns of MHC expression. J Neuroimmunol. 2001; 112:35-46.
[29] Modo M, Mellodew K, Rezaie P. In vitro expression of major histocompatibility class I and class II antigens by conditionally immortalized murine neural stem cells. Neurosci Lett. 2003; 337:85-88.
[30] Chiu AY, Rao MS. Cell-Based Therapy for Neural Disorders -Anticipating Challenges.Neurotherapeutics. 2011;8:744-752.
[31] Nicoleau C, Viegas P, Peschanski M,et al.Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Therapy for Huntington’s Disease: Technical, Immunological, and Safety Challenges.Neurotherapeutics. 2011;8:562-576.
[32] Bakay RAE, Boyer KL, Freed CR, et al. Immunological responses to injury and grafting in the central nervous system of nonhuman primates. Cell Transplant. 1998;7:109-120.
[33] Litchfield TM, Whiteley SJO, Yee KT, et al, Characterization of the immune response in a neural xenograft rejection paradigm. J Neuroimmunol. 1997;73:135-144.
[34] Pederson EB, Zimmer J, Finsen B. Triple immunosuppression protects murine intracerebral hippocampal xenografts in adult rat hosts: Effects on cellular infiltration, major histocompatibility complex antigen induction and blood–brain barrier leakage. Neuroscience. 1997;78: 685-701.
[35] Brevig T, Holgersson J, Widner H. Xenotransplantation for CNS repair: Immunological barriers and strategies to overcome them. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23: 337-344.
[36] Poltorak M, Freed WJ. Immunological reactions induced by intracerebral transplantation: evidence that host microglia but not astroglia are the antigen-presenting cells. Exp Neurol. 1989; 103: 222-233.
[37] 雷万龙,袁群芳,冯志博.大鼠脑缺血区局部炎症和细胞免疫反应的研究[J]. 中华神经科杂志,2001,34(5):276-279.
[38] 陈玉社,公丕欣,夏作理.脑淋巴引流与神经免疫[J].中国微循环, 2003,7(4):254-256.
[39] 梅爱农,张苏明,常丽英,等.鼠胚胎干细胞及其衍生神经前体细胞的免疫原性检测[J].神经损伤与功能重建,2008,3(5):307-309.
[40] Ma MC, Ding SL,Lundqvist A,et al.Major Histocompatibility Complex-I Expression on Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Vascular Progenitor Cells Is Critical for Syngeneic Transplant Survival. Stem Cells. 2010;28(9):1465-1475.
[41] Bifari F, Pacelli L, Krampera M. Immunological properties of embryonic and adult stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2010; 2(3):50-60.
[42] Drukker M, Katchman H, Katz G, et al. Human embryonic stem cells and their differentiated derivatives are less susceptible to immune rejection than adult cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24:221-229.
[43] Bonde S, Chan KM, Zavazava N. ES-Cell derived hematopoietic cells induce transplantation tolerance. PLoS ONE. 2008;3:e3212. |