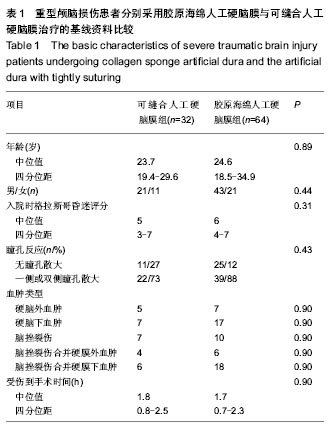
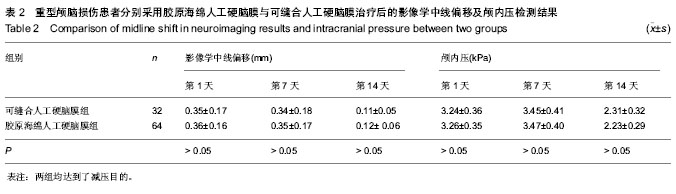
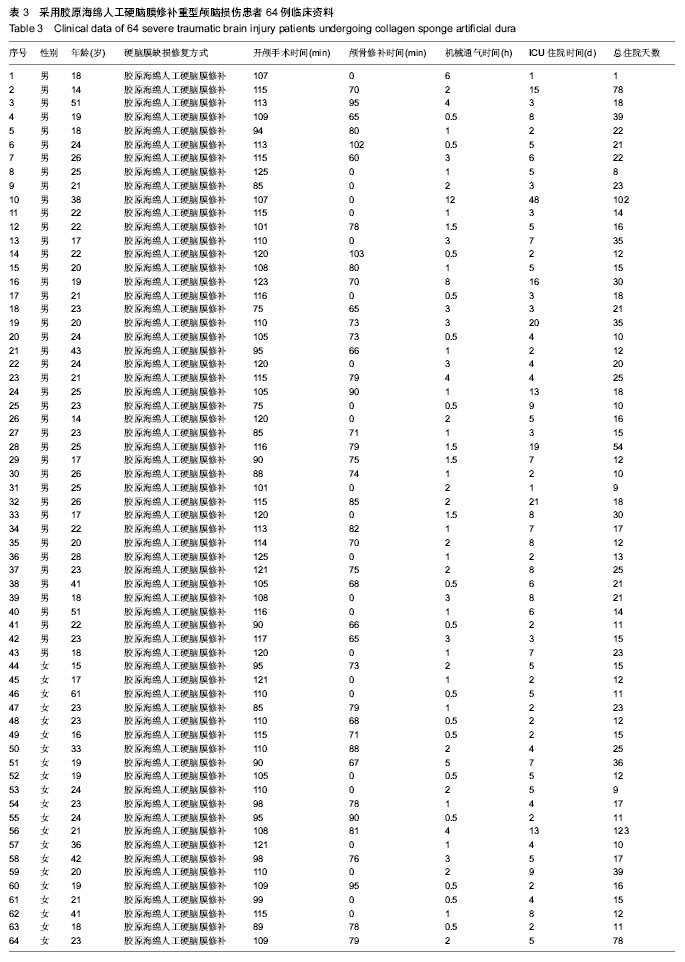
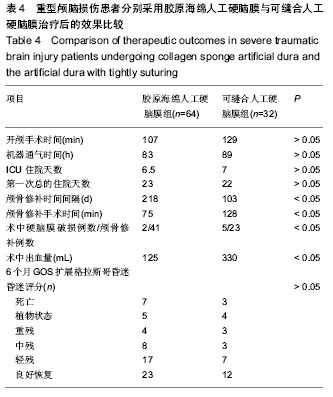
| [1] 陈鸿光,边玉松,关茂武,等.去骨瓣减压术后减压窗明显膨出患者的早期颅骨修补[J].中华神经外科杂志,2009,25(12):1135-1137.[2] 周玉峰,黄梅,邓聪颖,等.人工硬脑膜材料的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(16):2945-2948. [3] 张念平,付振,王元飞,等.硬脑膜修补材料在神经外科手术中的应用[J].中国医学创新,2010,7(2):129-131.[4] 杨健,杨金星,梅佩冬,等.生物型人工硬脑膜在外伤大骨瓣减压术中应用安全性观察[J].中外医学研究,2013,11(24):12-13.[5] 李文辉,吴日乐,岑莲.人工硬脑膜修补材料的研究及其临床应用[J].组织工程与重建外科,2013,9(2):113-115.[6] 李文生,黄瑞宏,周希汉,等.人工硬脑膜补片在标准大骨瓣减压术中的应用[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2013,18(4):234-235.[7] 孙梅.硬脑膜替代材料在神经外科手术中的应用[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2003,8(8):382-384.[8] 王茂德.癫痫的手术治疗现状[J].国外医学:神经病学神经外科学分册,1995,22(3):131-134.[9] 谭启富.癫痫的手术治疗[J].医师进修杂志,1995,18(5):4-6.[10] 于书卿,赵继宗,孟国路,等.胶原海绵人工脑膜临床应用研究[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2003,2(4):7-9.[11] 于书卿,付辉,郑细良,等.847例胶原海绵人工硬脑膜的临床应用[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2006,5(3):272-274.[12] Pafizek J,Husek Z,Mericka P,et al. Ovineperiardium: a new material for duraplasty. Neurosurg.1996;84:508-513. [13] 陈瑶刚,赵明媚,宁铁英,等.人工脑膜在急诊颅脑手术中的应用价值[J].河北医学,2010,16(6):688-689.[14] 李冰,赵诚.标准外伤大骨瓣手术治疗重型颅脑创伤的疗效分析[J].中华神经外科杂志,2011,27(10):1057-1058.[15] 江基尧.现代颅脑损伤学[M].3版.上海:第二军医大学出版社, 2010: 188.[16] 江基尧,朱诚,罗其中.颅脑创伤临床救治指南[M].2版.上海:第二军医大学出版社,2003:29-40.[17] 陈悦达,洪健,孙洪生,等.人工硬脑膜在颅脑创伤手术中的应用[J].透析与人工器官,2009,20(4):1-4.[18] 钱惠农,王有刚,姜峰.改良人工硬脑膜成形术的临床应用观察(附46例报告)[J].山东医药,2010,50(30):44-45. [19] von der Brelie C,Soehle M,Clusmann HR,et al.Intraoperative sealing of dura mater defects with a novel, synthetic, self adhesive patch:application ex- perience in 25 patients.Br J Neurosurg.2012;26(2):231-235.[20] 王铁霞,徐锡萍,杨景,等.人工生物膜修补硬脑膜缺损的实验研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2003,13(13):108-109.[21] 漆建,余定庸,唐文国,等.应用特制生物膜修补硬脑膜[J].中国临床神经外科杂志,2002,10(7):303-304.[22] 余定庸,漆建,唐文国,等.猪腹膜修补硬膜缺损108例初步报告[J].中华神经外科杂志,1998,14(4):23.[23] 张祖权,刘多.生物人工脑膜用于修补硬脑膜缺损95例临床观察[J].重庆医学,2009,38(16):2065-2067. [24] Leiggener CS,Curtis R, M uller AA,et a.l.Influence of copolymer composition of polylactide implants on crania l bone regeneration .Biomaterials.2006;27(2):202-207.[25] 曹国彬,陈秀梅,沈少仪,等.生物型硬脑膜补片在神经外科手术中的应用[J].中国老年学杂志,2012,32(16):5593-5594.[26] 穆霄静,侯芳,徐敏宁,等.脱细胞生物膜修复硬膜缺损的多中心临床试验研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2011,36(1):73-74.[27] Narotam PK,Jose S,Nathoo N,et al.Collagen matrix (DuraGen) in dural repair: analysis of a new modified technique.Spine. 2004;29(24):2861-2867;discussion 2868-2869.[28] Narotam PK,van Dellen JR,Bhoola KD. A clinicopathological study of collagen sponge as a dural graft in neurosurgery.J Neurosurg.1995;82(3):406-412.[29] Danish SF,Samdani A,Hanna A,et al. Experience with acellular human dura and bovine collagen matrix for duraplasty after posterior fossa decompression for Chiari malformations.J Neurosurg.2006;104(Suppl):16-20. [30] 曹胜武,傅震,耿晓增,等.硬膜替代材料胶原海绵应用于神经外科手术患者207例回顾性分析[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(45):160-164.[31] 董震,王和平,陈坚.胶原海绵人工硬膜在凸面脑膜瘤手术中的组织相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(27):5331-5333.[32] 李安源,岩亮,范寿成,等.胶原海绵人工硬脑膜在143例颅脑手术中的应用[J].云南医药, 2012,33(4):371-372. |