| [1] 谭包生.规范技术,科学发展[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012,47(10): 577-579.[2] Tang CB,Liul SY,Zhou GX,et al.Nonlinear finite element analysis of three implant- abutment interface designs.Int J Oral Sci.2012;4(2):101-108.[3] 陈淑杰,胡秀莲,邸萍,等.计算机辅助设计和导板引导种植技术在无牙颌种植固定修复中的应用[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012, 47(4):250-252.[4] 肖慧娟,杨云东,施斌,等.种植体即刻负重或早期负重与延期负重相比对种植体成功率影响的Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2008,8(2):120-126.[5] 郭晶.慢性牙周炎患者行种植早期负荷的短期前瞻性临床研究[D].中山大学,2010.[6] 莫嘉骥,姒蜜思,周仲豪,等.Straumann种植体早期稳定性相关因素的研究[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2012,10(5):381-385.[7] Bhola M,Neely AL,Kolhatka S.Immediate implant placement:clinical decisions,advantages and disadvantages.J Prosthodont.2008;17(7):576-581.[8] 瞿利军,赖红昌.Straumann种植体早期负荷与延迟负荷稳定性的比较研究[J].口腔医学,2011,31(8):476-479.[9] 孙园园,肖菲,赵保东,等.种植体稳定系数测定与种植体负重时机选择[J].现代生物医学进展,2012,12(10):1911-1915.[10] Turkyilmaz I. Influence of bone density on implant stability parameters and implant success : a retrospective clinical study.Clin Oral Implant s Res.BMC Oral Health.2008;8(1): 32-35.[11] 张辉,邓飞龙,陈卓凡,等.谐振频率法分析骨挤压术对种植体初期稳定性的影响[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2009,14(2):49-53.[12] Streckbein P,Streckbein RG,Wilbrand JF,et al.Non-linear 3D evaluation of different oral implant-abutment connections.J Dent Res.2012;91(12):1184-1189.[13] 刘杰彪.上颌前牙埋伏阻生开窗拔除后即刻种植疗效观察[J].中国实用医刊,2012,39(8):87-88.[14] 徐普,杨玄.种植体即刻负重的临床修复设计[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2010,45(4):252-255.[15] 张晓,孙凤,张峰,等.上颌窦底提升自体骨与异种骨移植延期种植的临床疗效评价[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012,47(10): 584-587.[16] 赵旭,邸萍,林野,等.“All-on-4”无牙颌种植即刻修复技术的临床应用与进展[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012,47(10):594-598.[17] 鲍琰,肖立群,施斌,等.Straumann种植体骨愈合期稳定性变化的临床动态监测[J].口腔医学研究,2009,25(6):739-741.[18] 包雪梅,陈岩.正畸微种植体初始稳定性的研究进展[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2012,19(2):118-120.[19] 徐普,谈顺,邢璐,等.平台转换技术对种植体-骨界面影响的组织学观察[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2011,46(12):759-761.[20] Freitas Júnior AC,Bonfante EA,Silva NR,et al.Effect of implant-abutment connection design on reliability of crowns: regular vs. horizontal mismatched platform.Clin Oral Implants Res.2012;23(9):1123-1126.[21] 陈岩,赵文婷,咏梅,等.正畸微种植体表面阳极氧化处理对周围骨组织的影响[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2012,19(3):149-151.[22] 郭冬梅,常少海,胡玲玲,等.Tomas微种植体矫治力系统竖直倾斜磨牙的三维有限元研究[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2012,19(2): 86-91.[23] 李滨飞.平台转换理念对种植体设计的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012,47(4):255-256.[24] 胡炜,艾婷婷,任翀,等.使用改型腭杆辅助压低过长上后牙的临床研究[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2012,19(1):2-5.[25] 马莉莎,唐亮,潘燕环,等.双端种植固定桥修复前后种植体-骨界面的动力学研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012,47(7): 435-438.[26] 高岩,周磊,蒋颖,等.两种波段紫外线对微弧氧化纯钛表面理化性质及体外生物活性影响的研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2012, 47(6):359-363.[27] Capek L,Simunek A,Slezak R et al.Influence of the orientation of the Osstell transducer during measurement of dental implant stability using resonance frequency analysis: a numerical approach.Med Eng Phys.2009; 31(7): 764-769.[28] 邸萍,林野,李健慧,等."All-on-4"种植即刻修复技术的临床应用研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2010,45(6):357-362.[29] 胡敏,姜欢,于东升,等.利用种植体矫治严重近中倾斜的第二磨牙[J].中华口腔正畸学杂志,2012,19(2):115-117.[30] 吴茴,李健慧,邸萍,等.口腔短种植体长期修复效果的评估[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2010,45(12):712-716. |
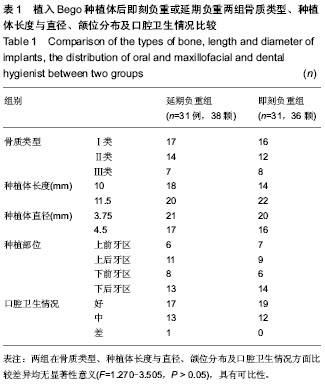
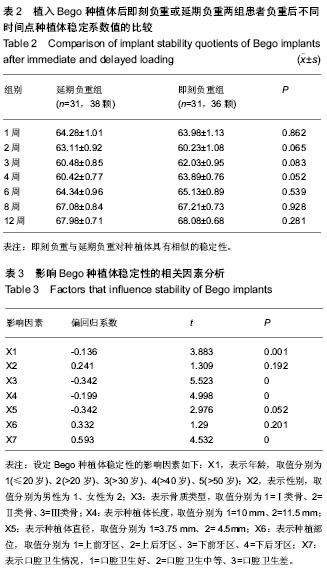
.jpg)
.jpg)